Test: Reproductive Health - NEET MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Reproductive Health
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
In ET technique the embryo is transferred into _________.
Introduction of sex education in schools should be encouraged to _________.
Disease or infections which are transmitted through sexual intercourse are collectively called?
Lactational amenorrhea is a kind of periodic abstinence in which chances of fertilization is prevented upto a maximum period after parturition is:
Which of the following contraceptive methods is useful to control STDs as well as unwanted pregnancy?
Which period of menstrual cycle is called the risky period of conception?
What is not the correct step in preventing transmission of STD?
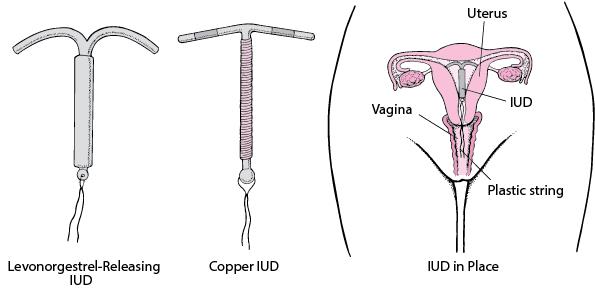
Identify the intra-uterine contraceptive device from the figure given below
Absence of menstruation during a period of intense lactation following parturition is called as?
Medical Termination of Pregnancy (MTP) is considered safe up to how many weeks of pregnancy?
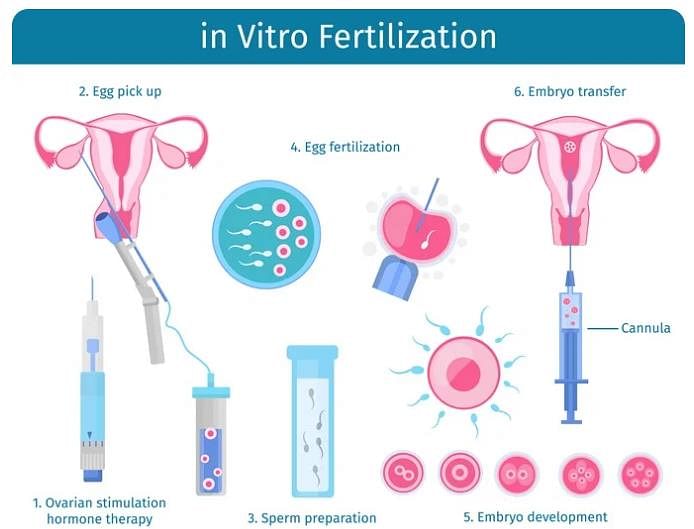
In IVF technique, fusion of ovum and sperm takes place in _________.
The average number of children which an average couple has or would have during their lifetime is called as?
Nowadays, there are fewer childless couples. This is due to _________.
Inability to conceive or produce children even after two years of unprotected sexual co-habitation is called?
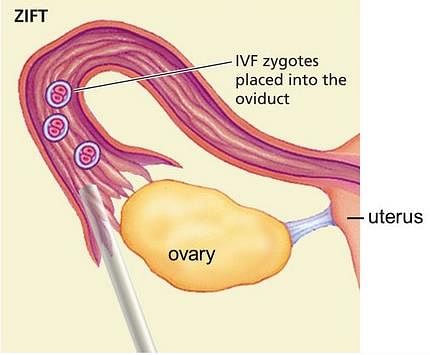
_________ involve the transfer of embryo at the 8-celled stage in the fallopian tube of female.
Choose the correct statements:
I. According to the WHO, reproductive health is total well-being in the physical, social, emotional, behavioural aspects of reproduction.
II. According to the WHO, reproductive health is total well being only in the social and emotional aspects of reproduction.
III. A reproductively healthy society has people with physically and functionally normal reproductive organs.
IV. Reproductively healthy societies have abnormal sex-related emotional and behavioural interactions.
Select the option which correctly fills up the blanks in the following statements.
A. Destruction of embryo or foetus in the uterus is called _____________.
B. Government of India legalized MTP in the year ____________.
C. Natural family planning method is also called _____________.
D. ____________ is a method in which the male partner withdraws his penis from vagina just before ejaculation.
E. ____________ is the copper releasing and is a hormone releasing intra uterine devices.
Options: