Test: Structural Organisation in Animals - NEET MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Structural Organisation in Animals
Which of the following tissues has the most regenerative power?
Assertion (A): The ovaries in female reproductive systems are responsible for producing ova and are located near the kidneys.
Reason (R): Ovaries have a functional connection with the kidneys to facilitate hormonal regulation.
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
In frog, during aestivation and hibernation gaseous exchange takes place through
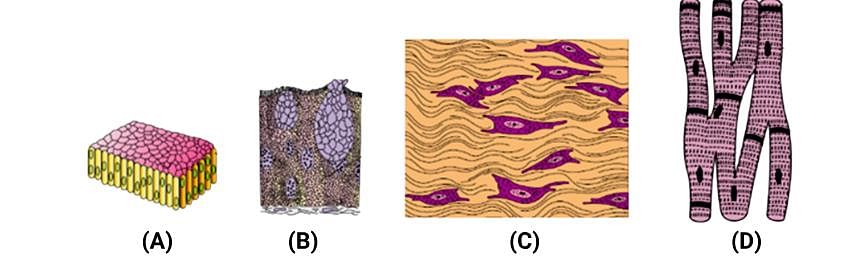
The four sketches (A, B, C, and D) given below, represent four different types of animal tissues. Which one of these is correctly identified in the options given, along with its correct location and function?

Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
i. The nervous system of the cockroach consists of segmentally arranged ganglia connected by longitudinal connectives on the dorsal side.
ii. The head of a cockroach contains the brain, which is located in the supra-oesophageal ganglion, supplying nerves to the antennae and compound eyes.
iii. A cockroach can survive for up to one week without its head due to the decentralized nature of its nervous system.
iv. Cockroaches have simple eyes that consist of hexagonal ommatidia, and they rely on these for high-resolution vision.
The most abundant type of animal tissue in the complex animals is
Consider the following parts of the brain of frog:
I. Olfactory lobes
II. Optic lobes
III. Cerebral hemispheres
IV. Diencephalon
Forebrain includes:
Which of the following is incorrect statement about frog?
Which of the following is not a secretion of exocrine glands?
The epithelium found in the lining layer of stomach and intestine is
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
i. Frogs have a closed type vascular system that includes a heart with three chambers.
ii. The lymphatic system in frogs consists of lymph, lymph channels, and lymph nodes, but does not include any blood components.
iii. The ventricle of a frog's heart opens into a conus arteriosus, which is located on the dorsal side of the heart.
iv. Frogs possess a hepatic portal system that connects the liver and intestine, allowing for specialized blood flow.
Which of the following represents the intercellular matrix of cartilage?
Assertion (A): Loose connective tissue, such as areolar tissue, serves as a support framework for epithelium due to its loosely arranged cells and fibers.
Reason (R): Adipose tissue, another type of loose connective tissue, primarily functions to store fats and is not involved in supporting epithelium.
Fibres and fibroblasts are compactly packed in
Which of the following represent the intercellular matrix of a bone?
Assertion (A): Squamous epithelium is primarily involved in diffusion processes due to its thin structure.
Reason (R): Cuboidal epithelium is specialized for secretion and absorption, not diffusion.
Which of the following tissue exerts the greatest control over the body?
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
i. The digestive system of frogs consists of a long alimentary canal to accommodate their carnivorous diet.
ii. The pancreas produces pancreatic juice that aids in the digestion of carbohydrates and proteins.
iii. Bile, secreted by the liver, is stored in the gall bladder and helps emulsify fats.
iv. The undigested solid waste in frogs exits the body through the stomach.