Test: Cell: The Unit of Life - 1 - NEET MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Cell: The Unit of Life - 1
Which of the following statements with reference to cytoskeleton is not correct?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Read the following statements carefully and determine how many are incorrect:
Statement A: Lipid component of the plasma membrane mainly consists of phosphoglycerides.
Statement B: Polar molecules can pass through the lipid bilayer of plasma membrane, therefore they do not require carrier proteins to facilitate their transport.
Statement C: Secondary wall is capable of growth and it is formed on the outer side of the cell.
Statement D: Quasi fluid nature of lipid enables lateral movement of proteins within the overall lipid bilayer of plasma membrane.
Statement E: Middle lamella glues the different neighbouring cells together.
Statement A: Lipid component of the plasma membrane mainly consists of phosphoglycerides.
Statement B: Polar molecules can pass through the lipid bilayer of plasma membrane, therefore they do not require carrier proteins to facilitate their transport.
Statement C: Secondary wall is capable of growth and it is formed on the outer side of the cell.
Statement D: Quasi fluid nature of lipid enables lateral movement of proteins within the overall lipid bilayer of plasma membrane.
Statement E: Middle lamella glues the different neighbouring cells together.
What is the primary function of leucoplasts in plant cells?
Which of the following statement is correct for the given diagram?

Which of the following is the correct sequence/route of the secretory product?
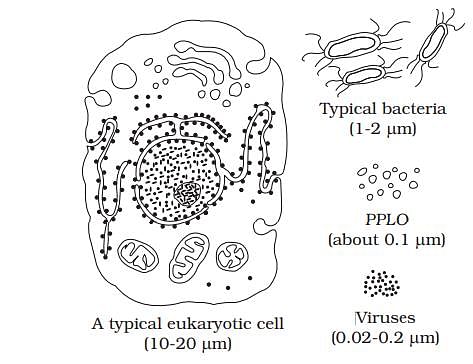
Arrange the following in the increasing order of their size:
The inner membrane of mitochondria thrown into folds to form finger like structure is called
In prokaryotes, the reserved food material is stored in
What is the primary function of the centromere in a chromosome?
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
1. The nuclear envelope is composed of two parallel membranes that are separated by a perinuclear space, which ranges from 10 to 50 nm.
2. Nuclear pores are exclusively found on the inner membrane of the nuclear envelope and allow only the movement of RNA molecules from the nucleus to the cytoplasm.