Test: Animal Kingdom- Basis of Classification (April 13) - NEET MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Animal Kingdom- Basis of Classification (April 13)
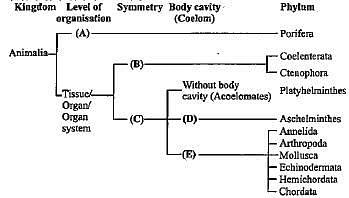
Study carefully the given flow chart and fill in the blanks (A), (B), (C), (D) and (E).


The given figure shows a cross section of the body of an invertebrate. Identify the animal which has such body plan.


| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Diploblastic and triplo blastic are terms that describe
Read the given statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1: All triploblastic animals are eucoelomates.
Statement 2: They have a false coelom.
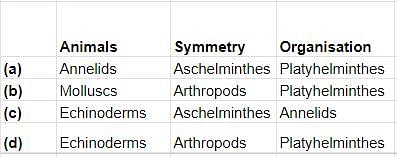
Which of the following is correctly matched?
Which of the following statements is incorrect with regard to bilateral symmetry?
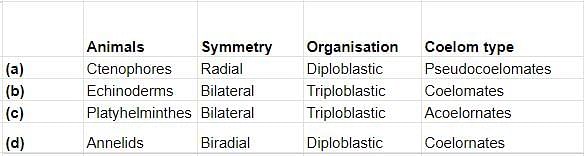
Select the correct matching of animals, their symmetry, organisation and coelom type.
The figures given below show the types of coelom. Identify them and select the correct group of organisms which possess them.

Which of the following are correct?
(i)Diploblastic:Poriferans, Coelenterates
(ii)Triploblastic:Platyheliminthes to Chorodates
(iii)Acoelomate:Poriferans,Coelenterates,Platyhelminthes
(iv)Pseudocoelomate:Aschelminthes /Roundworms
(v)Eucoelomate:Annelids to Chordates
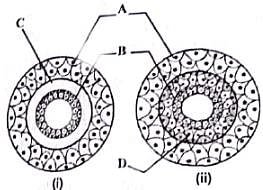
Examine the figures of diploblastic (i) and triploblastic (ii) organization in animals given below and identify the labelled parts A to D.