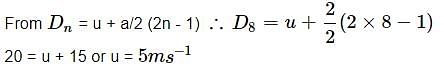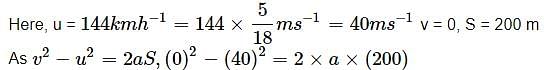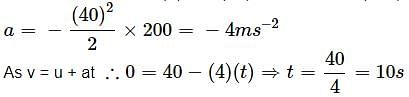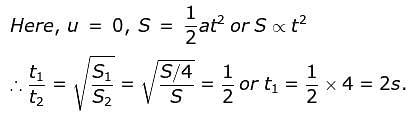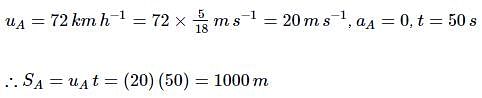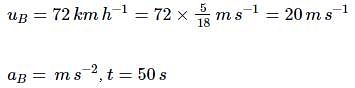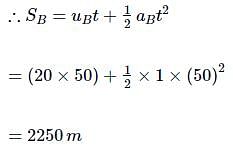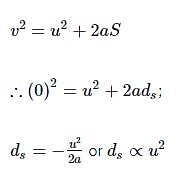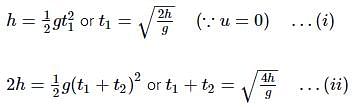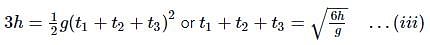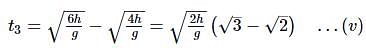Test: Kinematic Equations for Uniformly Accelerated Motion (April 23) - NEET MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Kinematic Equations for Uniformly Accelerated Motion (April 23)
Which of the following equations does not represent the kinematic equations of motion?
Which of the following statements is not correct?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
A body covers 20 m, 22 m, 24 m, in 8th, 9th and 10th seconds respectively. The body starts
A car moving along a straight road with speed of 144 km/h is brought to a stop within a distance of 200 m. How long does it take for the car to stop?
A player throws a ball upwards with an initial speed of 30 m s−1. How long does the ball take to return to the player's hands? (Take g = 10 m s−2).
A girl standing on a stationary lift (open from above) throws a ball upwards with initial speed 50 m s−1. The time taken by the ball to return to her hands is (Take g = 10 m s−2).
A body sliding on a smooth inclined plane requires 4 seconds to reach the bottom starting from rest at the top. How much time does it take to cover one-fourth distance starting from rest at the top
Two trains A and B of length 400 m each are moving on two parallel tracks with a uniform speed of 72 km h-1 in the same direction, with A ahead of B. The driver of B decides to overtake A and accelerates by 1 ms-2. If after 50s, the guard of B just brushed past A, what was the original distance between them?
Stopping distance of a moving vehicle is directly proportional to
A particle is released from rest from a tower of height 3h. The ratio of the intervals of time to cover three equal heights h is