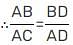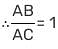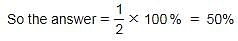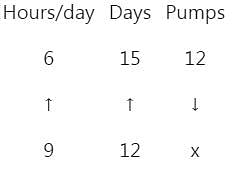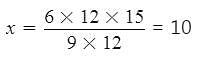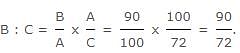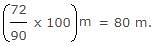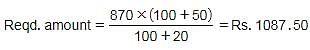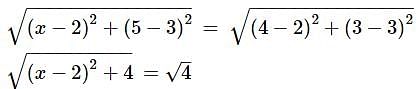Indian Coast Guard Navik GD Mock Test - 6 - Indian Coast Guard Navik GD/DB MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Indian Coast Guard Navik GD Mock Test - 6
Directions: In each of these questions, two equations (I) and (II) are given. You have to solve both the equations and give answer.
I. x – √196 = 0
II. y2 – 196 = 0
I. x – √196 = 0
II. y2 – 196 = 0
If 2 log4x = 1 + log4 (x-1), find the value of x. ?
Find the number of multiples of 4 falling between 10 and 250 is:
If the cost of x meters of wire is ‘d’ rupees, that find the cost (in Rupees) of ‘y’ meters of wire at the same rate.
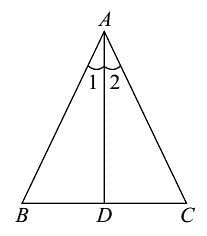
If the bisector of an angle of Δ bisects the opposite side, then the Δ is :
A sailor goes 24 km downstream in 48 minutes and returns in 1 hour 20 minutes. What is the ratio of the upstream speed to the downstream speed?
A train crosses a pole and a bridge in 20 seconds and 30 seconds respectively, the length of the bridge is what percentage of the length of the train?
12 pumps working 6 hours a day can empty a completely filled reservoir in 15 days. How many such pumps working 9 hours a day will empty the same reservoir in 12 days ?
In a 100 m race, A can give B 10 m and C 28 m. In the same race B can give C:
A, B, C subscribe Rs 50,000 for a business. A subscribes Rs 4000 more than B and B Rs 5000 more than C. Out of a total profit of Rs 35,000, A receives?
A shopkeeper sells an item for Rs. 870 and earns 20% profit. At what price should he sell that item to make a profit of 50%?
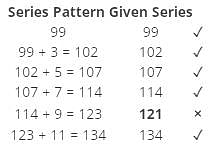
Directions: Find the wrong term in the given series.
99 102 107 114 121 134
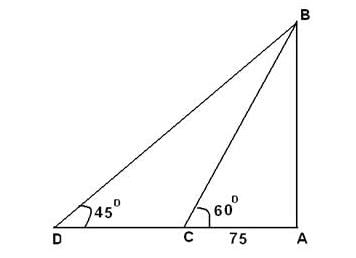
A man is watching form the top of the tower a boat speeding away from the tower. The boat makes the angle of depression of 60° with the man's eye when at a distance of 75 meters from the tower. After 10 seconds the angle of depression becomes 45°. What is the approximate speed of the boat, assuming that it is running in still water?
The weight of a basketball is about 700000 mg. It is
If repetition is allowed, how many 3-digit numbers can be formed using digits 1, 3, 5, 6 and 8?
If the Price of 6 toys is Rs. 264.37, What will be the approximate price (Rs) of 5 toys?
If the points A(4, 3)and B(x, 5) are on the circle with Centre O (2, 3). Find the value of x.
What is the volume of a cube with 16 meters side?
Who discovered the principle of superposition in quantum mechanics?
Which of the following is the correct conversion factor to convert cubic centimeters to milliliters?
What is the chemical formula for water?
According to Goldstein’s experiment, on passing high voltage electricity through gases at very low pressure resulted in the discovery of:
How many groups are there in the periodic table?
Which of the solid does not contain a covalent bond
Which of the following is an example of oxidation?
Which of the following substances can be used for identifying an acid solution?
What is the unit of electric charge used in electrolysis?