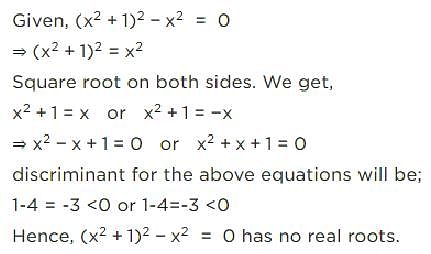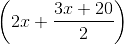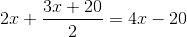Kerala PSC KAS Prelims Paper 1 Mock Test - 3 - Kerala PSC KAS MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Kerala PSC KAS Prelims Paper 1 Mock Test - 3
One-third of Rahul's savings in National Savings Certificate is equal to one-half of his savings in Public Provident Fund. If he has Rs. 1,50,000 as total savings, how much has he saved in Public Provident Fund ?
A fires 5 shots to B's 3 but A kills only once in 3 shots while B kills once in 2 shots. When B has missed 27 times, A has killed:
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
In a cricket match Kumble took three wickets less than twice the number of wickets taken by Srinath. The product of the number of wickets taken by these two is 20, then the number of wickets taken by Kumble is
Solve the quadratic equation x2 – ix + 6 = 0
II. Read the following information carefully to answer the following questions:
There are six persons in a family A, B, C, D, E, and F. C is the sister of F. B is the brother of E’s husband. D is the father of A and grandfather of F. there are two fathers, three brothers and a mother in the group.
Q.
Who is E’s husband?
When a positive number n is divided by 7 leaves the remainder 2, when 3n is divided by the same number, then the remainder is
The number of prime factors of 510510
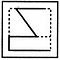
In each of the following questions, you are given a figure (X) followed by four alternative figures (1), (2), (3) and (4) such that figure (X) is embedded in one of them. Trace out the alternative figure which contains fig. (X) as its part.
Find out the alternative figure which contains figure (X) as its part.
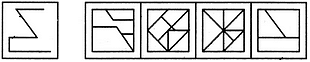
Which one will replace the question mark ?

Two matrices are shown in the figure below. Their rows and columns are labelled as (0,1,2,3,4) and (5,6,7,8,9) in the manner shown. Find the correct row-column pairs out of the following matrices that decode to the word - CAGE
The average weight of a class of 10 students is increased by 2 kg when one student of 30kg left and another student joined. After a few months, this new student left and another student joined whose weight was 10 less than the student who left now. What is the difference between the final and initial averages?
Last year, the ratio between the salaries of A and B was 3 : 4. But, the ratios of their individual salaries between the last year and this year were 4 : 5 and 2 : 3, respectively. If the sum of their present salaries is Rs. 4160, then how much is the salary of A now?
A sum of money is divided among A, B and C in the ratio 2 : 3 : 4. C gives Rs. 20 to B and B gives half of what he has now to A. Now, A and C have equal amount. What is the sum of money divided among the three?
In a swimming pool measuring 90 m by 40 m, 150 men take a dip. If the average displacement of water by a man is 8 cubic metres, what will be the approximate rise in water level?
Consider the following statements
1. Under the El Nino event, the surface temperature of the Pacific ocean increased more than usual causing heavy rainfalls in Australia.
2. While El-Nino leads to drought events in the subcontinent, La-Nina is primarily associated with flood events.
Which of the given above statements is/are correct?
Consider the following statements with respect to new National Pension Scheme:
-
The scheme is open to all Indian citizens on a voluntary basis.
-
Non-resident Indians are also eligible for this scheme.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
With reference to Pradhan Mantri Swasthya Suraksha Yojana (PMSSY), consider the
following statements:
PMSSY has the objective of correcting regional imbalances in the availability of affordable primary healthcare services.
The nodal Ministry is the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
India is a signatory to which of the following Intellectual Property Rights (IPR) related conventions?
-
Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS) Agreement.
-
The Berne Convention
-
The Paris Convention for the Protection of Industrial Property
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
Consider the following statements:
The International Covenant on Economic, Social, and Cultural Rights (ICESCR) is a legally binding document.
The Committee on Economic, Social, and Cultural Rights is the supervisory body of the ICESCR.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Framers of our Constitution made the Directive Principles non-justiciable because:
Inadequate financial resources at the disposal of the state.
Diversity and backwardness of the country acting as a stumbling block in their implementation.
Fundamental rights already have been made justiciable and making Directive principles justiciable would be meaningless.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
Which of the following provisions can be amended by a simple majority of Parliament?
Admissionor establishment of new states
Use of official language
Elections to Parliament and state legislatures
Conferment of more jurisdiction on the Supreme Court
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
All citizens enjoy the same political and civil rights of citizenship all over the country. But citizens can be discriminated in which of the following cases?
-
When Parliament prescribes residence within a state as a condition for employment.
-
When a state provides for special benefits to its residents in relation to rights not given by the Constitution to the Indian citizen.
-
To protect the interests of any scheduled tribe.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
Consider the following statements regarding National Emergency:
Approval of parliament is necessary for the revocation of the National Emergency.
Maximum time period for the operation of the National Emergency is three years.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Muhammad Shah’s reign witnessed the establishment of the independent states of
Hyderabad
Bengal
Awadh
Punjab
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
Which of the following statements are incorrect regarding Bahadur Shah I?
He adopted a pacific policy with the Marathas, the Rajputs and the Jats.
He introduced izara system to improve the financial condition of the empire.
He followed a policy of religious tolerance by abolishing Jaziya and pilgrimage tax.
Select the answer using the code given below:
With reference to the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO), consider the following statements.
It was established by the Chicago Convention under the aegis of the United Nations.
It regulates the international aviation sector.
Which of the statements given above is/are not correct?
Consider the following statements regarding the Dutch:
They founded their first factory in Masulipatnam.
They captured Nagapatam from the Portuguese.
They carried opium and rice from the Ganga valley.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
In October 1940, Gandhiji gave a call for Limited Satyagraha, why was the Satyagraha Limited?
leaders.