Test: Respiration in Plants - Fermentation (July 5) - NEET MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Respiration in Plants - Fermentation (July 5)
________ is an obligate anaerobe.
Which of the following options does not hold good regarding anaerobic respiration of fermentation?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Identify the enzymes 1 and 2 in the given reaction and select the correct option.


What does A, B and C depict in the given pathways of anaerobic respiration?
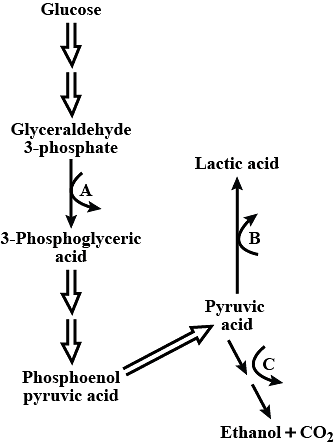
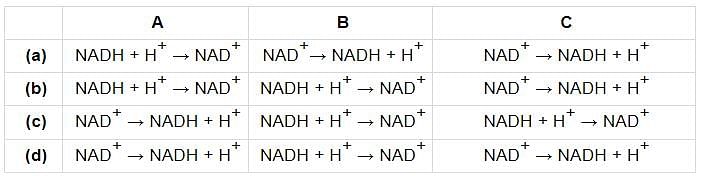
Select the incorrectly matched pair.
The given experimental set-up demonstrates
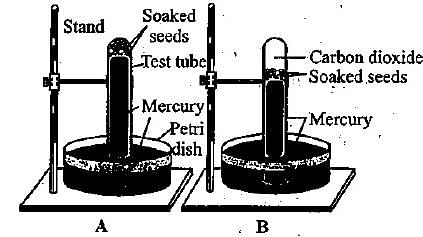
Mercury (Hg) is generally used in anaerobic respiration experiments because it does not react with ___________.
Which of the following describes the significance of fermentation?
(i) Production of alcohol in the brewing industry
(ii) Making of dough in the baking industry
(iii) Curing of tea and tobacco
(iv) Production of vinegar by acetic acid bacteria
A test tube containing molasses solution and yeast is kept in a warm place overnight. The gas collected from this mixture
Dough kept overnight in warm weather becomes soft and spongy due to



















