Test: Hydrogen Bonding (June 2) - NEET MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Hydrogen Bonding (June 2)
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-12) This section contains 12 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q. Which of the following compounds are soluble in H2O ?
In which of the following boiling point of Column I is not higher than that of Column II?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
In dimer formation of 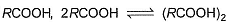 which O-atom(s) is/are involved through H-bonding?
which O-atom(s) is/are involved through H-bonding?
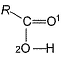
In the following alcohol, which — OH group is involved to the maximum extent in H-bonding?
What is the dominant intermolecular force or bond that must be overcome in converting liquid CH3CH2OH to vapours?
Number of water molecules directly attached to one water molecule is
Direction (Q. Nos. 13-16) This section contains 4 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d)
(Multiple Answer Correct)
Q. In which of the following I is more volatile than II?
Hydrogen bonding plays a central role in the following phenomenon
(Multiple Answer Correct)
[JEE Advanced 2014]
Direction (Q. Nos. 17) Choice the correct combination of elements and column I and coloumn II are given as option (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE option is correct.
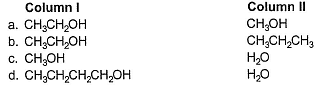
Q. Match the species in Column I with rank order of their boiling point in Column II. (Species with lowest boiling points is at SN1).

















