Test: Cell - Structure & Functions (June 17) - NEET MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Cell - Structure & Functions (June 17)
Match the following and select the correct answer: [2014]




When the centromere is situated in the middle of two equal arms of chromosomes, the chromosome is referred as: (2021)
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
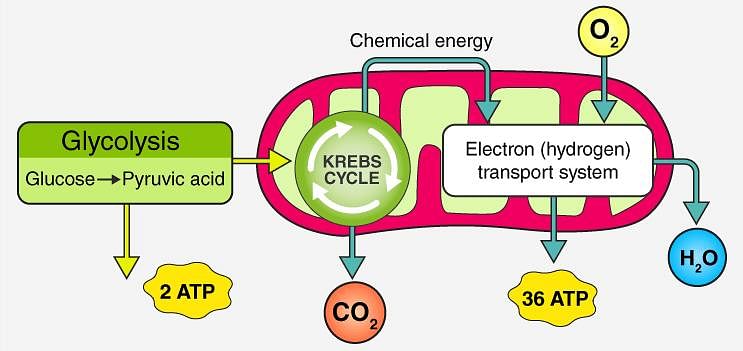
Which of the following cell organelles is responsible for extracting energy from carbohydrates to form ATP? (2017)
Which of the following is not a characteristic feature during mitosis in somatic cells ? [2016]
In meiosis crossing over is initiated at [2016]
Choose the correct option for the following events of meiosis in correct sequence: [2015 RS]
(A) Crossing over
(B) Synapsis
(C) Terminalisation of chiasmata
(D) Disappearance of nucleolus
Which of the following statements is not correct? (2019)
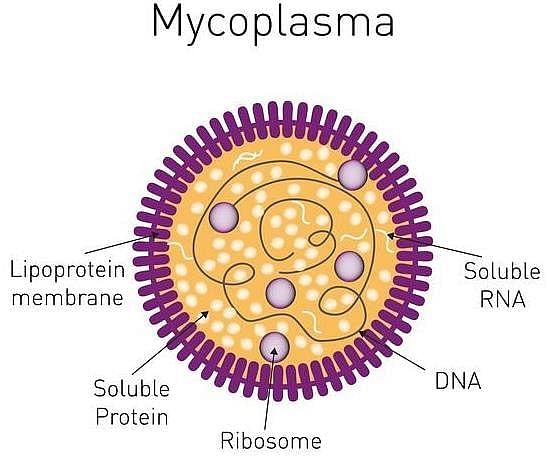
Which of the following are not membrane bound? [2015 RS]
Nuclear envelope is a derivative of : [2015 RS]
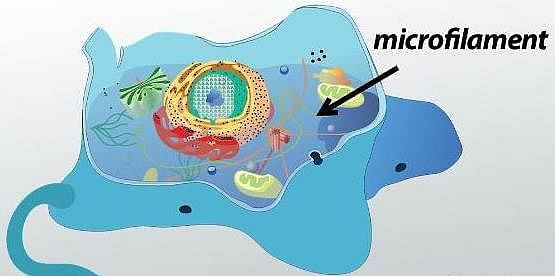
Microtubules are the constituents of: [2016]
The solid linear cytoskeletal elements having a diameter of 6 nm and made up of a single type of monomer are known as: [2014]
The enzyme recombinase is required at which stage of meiosis: [2014]
During which phase(s) of cell cycle, amount of DNA in a cell remains at 4C level if the initial amount is denoted as 2C? [2014]