Test: Accounting & Financial Management of Banking - 3 - Bank Exams MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Accounting & Financial Management of Banking - 3
What is the purpose of using equivalent units in process costing?
Directions: On 1st April 2000, X Ltd purchased a Plant for 45,000. It was estimated that the effective life of the plant will be 10 years and after 10 years its scrap value will be 5000. On 1st April, 2001, the company purchased additional machine for 250000 of which the effective life will be 15 years and scrap value 2,500. On 1st October, 2002, a new machine was purchase for 12,000 of which the scrap value will be 2000 and the effective life 20 years. If the depreciation is provided on straight line method. Then,
Q. What will be the depreciation on first machine purchased.
For which of the following entries, compound entries can be passed?
I. By debiting one account and crediting two or more accounts.
II. By crediting one account and debiting two or more accounts.
III. By debiting two or more accounts and crediting two or more accounts such as Opening Entry.
I. By debiting one account and crediting two or more accounts.
II. By crediting one account and debiting two or more accounts.
III. By debiting two or more accounts and crediting two or more accounts such as Opening Entry.
What are the different kinds of adjustments which are made to the bank statement balance while reconciliation?
I. Bank errors
II. Interest fees
III. Unpresented checks
A company bought machinery at a cost of ₹ 6500 and spent ₹ 300 on erection charges. It is estimated that its working life is 2 years and the value of scrap is ₹ 1020. Calculate the amount of annual depreciation.
From the following statements choose the one statement that justifies the Deferred payment guarantees?
Which of the following statement/s is/are incorrect regarding the bill of exchange?
I. Drawer is a person on whom the bill is drawn
II. It is signed by the maker of the bill
III. It contains a conditional order
IV. It is an instrument in writing
As per the companies act 2013, there should be the gap of how many months between the two call of share?
Before the method LERMS the Reserve Bank fixed the buying and selling rates and the forex market would remain within the ceiling and the floor, thus fixed by the Reserve Bank. What does 'L' stand for in LERMS
Which one of the following is not a feature of a written down value method of depreciation?
I. The book value of the asset becomes zero at any one point of time.
II. The depreciation is calculated on the book value of assets and not on the cost.
III. The amount of depreciation charged on a specific asset reduces every year.
IV. There is no need to estimate the residual value and estimated life at the time of deciding the amount of depreciation.
Which of the following statements are correct regarding the Profit and Loss Appropriation account
I. Profit and Loss Appropriation account is different from profit and loss account and is normally put below the net profit figure in the same statement.
II. The net profit is transferred to the debit side of the profit and loss appropriation account.
III. Profit and Loss account shows only the net profit or net loss from operation of business while the Profit and Loss appropriation accounts shows all non-operational adjustments.
Which among the following is not a feature of the Basel Committee on Bank Supervision (BCBS)?
Mr A wants to implement the application and use of the same costing principles and procedures by different divisions of his company. Which of the following techniques of costing is more appropriate in the given situation?
From the following equations find the correct accounting equation
I. Asset = liability + equity
II. Asset = liability + [Capital + (revenue - expenses) - drawings]
III. Asset + expenses + drawings = liability + Capital + revenue
Under Costing Profit and loss account which of the following are debited?
I. Cost of sales
II. Over-absorbed overheads
III. Abnormal losses
Which of the following statements are correct regarding the Features of a Joint Stock Company
I. A company has a perpetual succession. Death or insolvency of any shareholder does not affect the existence of the company.
II. The common seal is treated as the company's signature and is affixed on all important documents and contracts as per the resolutions passed by the Board.
III. The liability of the members of the joint stock company is unlimited.
Which of the following statement/s is/are correct regarding calls in advance?
I. Interest on Calls-in-Advance must be paid even when no profit is earned by the company
II. The interest payable on Calls-in- Advance is an appropriation of the profits of the company
III. A Company is liable to pay interest @ 12% p.a on Calls-in- Advance, if the articles do not specify the rate of interest.
Accounting Standard Board was set up by
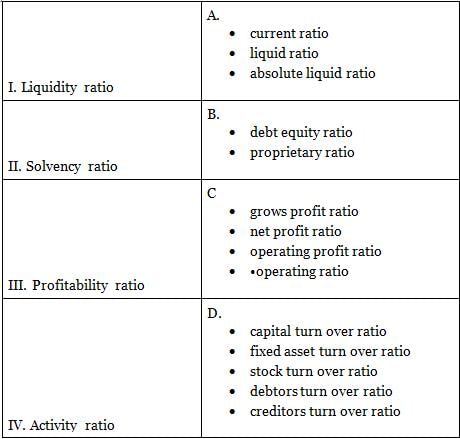
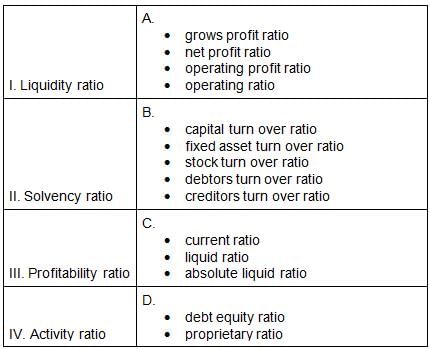
Match the following classification of ratios?
Which of the following statement/s is/are correct about forward rate agreement
I. A forward rate agreement (FRA) is an over-the-counter (OTC) contract between parties that determines the rate of debt to be paid on an agreed-upon date in the future.
II. A forward rate agreement (FRA) is an over-the-counter (OTC) contract between parties that determines the rate of interest to be paid on an agreed-upon date in the future.
III. A forward rate agreement (FRA) is an over-the-counter (OTC) contract between parties that determines the rate of commodity to be paid on an agreed-upon date in the future.
Which of the following are features of the capital expenditure budget?
(l) Long-term perspective
(ll) Strategic focus
(lll) Comprehensive in nature
(lV) Cost Estimation
A company needs a methodology for quantifying risk and translating that risk into estimates of expected return on equity. Which approach of cost of equity will be used?
Which of the following is the second step in accounting cycle?
__________ ratio are also known as financial ratios and used to evaluate the financial performance and position of the company.
____________ of a bond is the total return an investor can expect to receive if the bond is held until its maturity date.
Directions: Current ratio of X Ltd. is 4.5:1. It is found that the working capital of the company is Rs 81,000.
Q. The current assets of X Ltd. is Rs._______.
According to which accounting concept fixed assets are kept at the cost of purchases and not their market value?
Under the First In First out method of process costing, the Closing stock of work in process is valued at ____
Which of the following terms represents the temporary assets acquired by the bank for granting loans and advances?
Which of the following statement/s is/are incorrect regarding the Balance sheet?
I. Balance sheet is always prepared for a particular period.
II. It is an account containing information regarding assets, liabilities and capital.
III. It shows the nature and value of assets, the nature and value of liabilities and the position of capital.