Test: Indian Economy and Indian Financial System - 5 - Bank Exams MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Indian Economy and Indian Financial System - 5
Directions: Consider the following passage and answer the questions that follow:
The Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management Act (FRBM Act), 2003, establishes financial discipline to reduce fiscal deficit. The FRBM Bill was introduced by the then finance minister, Yashwant Sinha, in 2000. The Bill, approved by the Union Cabinet in 2003, became effective from July 5, 2004. The FRBM Act aims to introduce transparency in India's fiscal management systems.
Q. Which of the following is not the objective of the Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management Act,2003?
The Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management Act (FRBM Act), 2003, establishes financial discipline to reduce fiscal deficit. The FRBM Bill was introduced by the then finance minister, Yashwant Sinha, in 2000. The Bill, approved by the Union Cabinet in 2003, became effective from July 5, 2004. The FRBM Act aims to introduce transparency in India's fiscal management systems.
Directions: Consider the following passage and answer the questions that follow:
The Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management Act (FRBM Act), 2003, establishes financial discipline to reduce fiscal deficit. The FRBM Bill was introduced by the then finance minister, Yashwant Sinha, in 2000. The Bill, approved by the Union Cabinet in 2003, became effective from July 5, 2004. The FRBM Act aims to introduce transparency in India's fiscal management systems.
Q. As per FRBM Act, in which of the following ways, Government can borrow from RBI to meet temporary excess of cash disbursement over cash receipts?
The Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management Act (FRBM Act), 2003, establishes financial discipline to reduce fiscal deficit. The FRBM Bill was introduced by the then finance minister, Yashwant Sinha, in 2000. The Bill, approved by the Union Cabinet in 2003, became effective from July 5, 2004. The FRBM Act aims to introduce transparency in India's fiscal management systems.
Which among the following statements is/are TRUE?
I. An asset is said to be liquid if it is easy to sell or convert into cash without any loss in its value.
II. A liquid asset allows any individual or a company to access cash at any time they want.
III. At the time of investing, the investor must keep some of the liquid assets in his portfolio.
I. An asset is said to be liquid if it is easy to sell or convert into cash without any loss in its value.
II. A liquid asset allows any individual or a company to access cash at any time they want.
III. At the time of investing, the investor must keep some of the liquid assets in his portfolio.
Which of the following statement are correct regarding equipment leasing as a departmental service
I. These activities should be treated on par with loans and advances and should accordingly be given a risk weight of 100%, for calculation of capital to risk asset ratio.
II. The facilities extended by way of equipment leasing services would be covered within the exposure ceilings with regard to single borrowers (25% of the bank's capital funds; 35% provided the additional credit exposure is on account of extension of credit to infrastructure projects)
III. The exposure ceiling for the borrower group (40% of the bank's capital funds; 50% provided the additional credit exposure is on account of extension of credit to infrastructure projects).
The World Bank consists of two main institutions: the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD) and the ____________.
In the factoring service who is concerned as a Factor?
What does the term vesting stage mean in relation to pension
Which of the following statement/(s) is/are correct regarding the Priority Sector Lending Certificates?
I. PSLC are non-tradable certificates issued with Priority Sector loans as underlying.
II. All PSLCs expire by March 31st irrespective of the date it was first sold.
III. Eligible Participants are Scheduled Cooperative Banks, Urban Cooperative Banks, and Local Area Banks.
Social capital is an important constituent of the prosperity of a company. Social networks in an organization includes which of the following?
The period of lending or call money is ___ and for term money is ____.
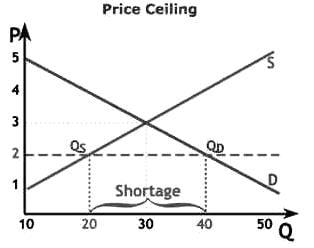
Which among the following statements is/are TRUE w.r.t. Price Ceiling?
I. Government imposes a price ceiling to control the maximum prices that can be charged by suppliers for the commodity.
II. prolonged application of a price ceiling can lead to black marketing and unrest in the supply side
III. It has been found that higher price ceilings are highly effective.
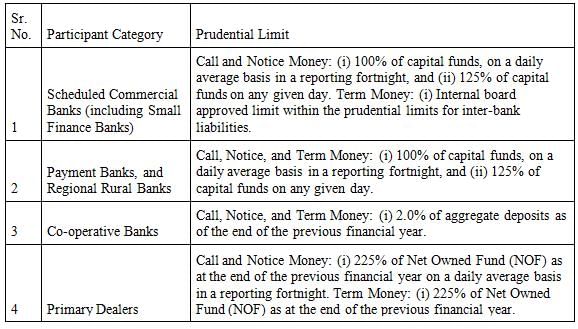
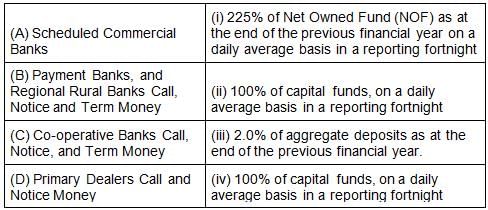
Match the following as per Prudential limits for outstanding borrowing transactions in Call, Notice, and Term Money Markets?
A consumer's income is ₹100, and he wants to spend the money on two commodities, say X and Y and both of these goods are priced at ₹50 each.
Which of the following options are practical for the consumer?
I. option is to buy two units of commodity X
II. option is to buy two units of commodity Y
III. option is to buy one unit of commodity X and one unit of commodity Y
Assertion: The primary sector plays a vital role in providing raw materials for various industries.
Reason: The primary sector involves activities related to extraction and production of natural resources.
According to the Negotiable Instruments Act 1881, in respect of the accommodation bill, the party lending his name to oblige the other party is known as _____.
What is the corpus of the Contingency Fund, as authorised by Parliament?
Which among the following is NOT TRUE w.r.t. Asset turnover ratio?
I. 'Sponsors' are people who promote and refer to any organisation or a corporate entity with a capital of Rs 100 crore, which establishes the InvIT and is designated as such at the time of the application made to Sebi
II. Project manager is an entity or limited liability partnership (LLP) or organisation that supervises assets and investments of the InvIT and guarantees activities of the InvIT
III. Investment manager refers to the person who acts as the project manager and whose duty is to attain the execution of the project and in case of PPP projects.
Arrange the following milestones related to Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) in chronological order:
I. Millennium Development Goals (MDGs)
II. Adoption of the SDGs
III. United Nations Earth Summit
IV. Establishment of the UN Sustainable Development Commission
What is a unique feature of an e-Insurance Account (e-IA)?
Which of the following is/are matched incorrectly?
I. Quasi-Judicial: SEBI is empowered to implement the regulations and judgment made and to take legal action against the violators
II. Quasi-Executive: SEBI reserves the right to frame rules and regulations to protect the interest of the investors
III. Quasi-legislative: SEBI has the authority to deliver judgment related to fraud and other unethical practices in terms of the securities market
_________ is a qualitative or selective method of credit control which aims to control and regulate the purposes for which credit is granted by commercial banks.
Which among the following is a feature of Arbitrageurs?
What is the limit of borrowing under ICD ___% of the Net Owned Funds and the minimum tenor of borrowing is for ___
Which of the following statements accurately describes the role of Qualified Institutional Placement (QIP) in the primary market?
Statement I: QIP involves issuing securities to retail investors to raise capital.
Statement II: QIP is a method used by retail investors to buy shares in the secondary market.
Statement III: QIP targets institutional investors like mutual funds and foreign institutional investors (FIIs).
Statement IV: QIP is a regulatory authority that oversees primary market activities.
When an asset is acquired on a lease basis, it is shown in __ of the Financial statement.
Which one of the following statements is true?
Growth oriented definition was introduced by ________.
What is financial contagion in economics aspects?
_______ is the number of times a company sells and replaces its stock of goods during a period.
Arrange the following CSR-related initiatives in India in chronological order:
I. Enactment of Companies Act 2013 with CSR provisions
II. Launch of the National Skill Development Mission
III. Introduction of mandatory CSR spending in India
IV. Launch of the Swachh Bharat Abhiyan (Clean India Campaign)