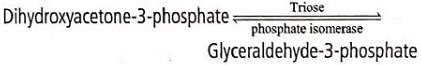Test: Enzymes (May 28) - NEET MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Enzymes (May 28)
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Feedback inhibition of enzymes is affected by which of the following:
Enzymes with slightly different molecular structure but performing identical activity are
Which of the following statements is incorrect regarding enzymatic activity?
Read the given statements and select the correct options.
Statement 1: Low temperature destroys enzymes by causing their denaturation.
Statement 2: High temperature preserves the enzymes in their inactive stages.
The inhibitor which does not resemble the substrate in structure and binds to the enzyme at site other than the active site is called
Dihydroxyacetone-3-phosphate and glyceraldehyde-3- phosphate are interconvertible. The enzyme responsible for this interconversion belongs to the cateogry of
Enzymes are most functional within the temperature range of