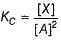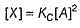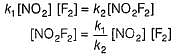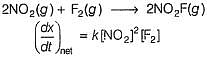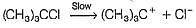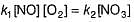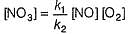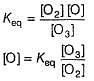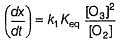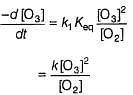Test: Collision Theory of Chemical Reactions & Reaction Mechanism (November 25) - NEET MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Collision Theory of Chemical Reactions & Reaction Mechanism (November 25)
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-14) This section contains 14 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
A chemical reaction proceeds through the following steps :
Step I, 2A ⇌ X fast
Step II, X+B ⇌ Y slow
Step III, Y+B ⇌ Product fast
Q. The rate law for the overall reaction is
Step II, X+B ⇌ Y slow
Step III, Y+B ⇌ Product fast
A chemical reaction is said to take place through the various stages with ΔG° values indicated by the graph:

Stages I and II represent respectively

| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
For the reaction, 
Steps are


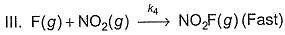
For the following SN reaction,
Rate-determining step is
Consider the following reaction,
The rate equation for this reaction is, rate = k[CI2] [H2S]
Which of these mechanisms is/are consistent with this rate equation?
[AIEEE2010]
Consider the three following proposed mechanism for the overall equation.
Q.
Which mechanism predicts a third order reaction?
Based on the following steps:
Rate law is
Passage I
The ozone in the earth’s ozone layer decomposes according to the equation,
It involves
(Time is in seconds and concentration in mol L-1)
Q.
What is the rate at a time of 50% decomposition of O3, when [O3]0 = 1.0 M?
Passage III
is believed to proceed through the following three step mechanism:
Q.
Identify the false statement.
For the overall reaction between A and 6 to yield C and D, two mechanisms are proposed.
Q.
At what concentration of A and/or B will the inherent rates be equal?