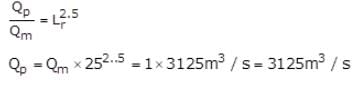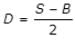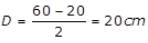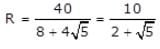JKSSB JE Civil Mock Test - 8 - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - JKSSB JE Civil Mock Test - 8
Which one of the following is known as elastic rail clip?
As per Indian Standard, average design period of water distribution systems is,
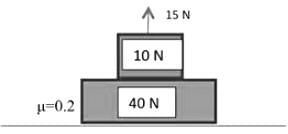
Two separate blocks are placed one over another as shown in figure. What is the maximum magnitude of the frictional force acting on the lower block on ground? The coefficient of friction between the ground and block is μ = 0.2.

In a reinforced and plain concrete footing on soil, the thickness of the edge shall not be less than,
A BG track have a sleeper density of (M + 5). Determine the number of sleepers required for constructing a railway track of 2600 m.
A prototype is 25 times the model size for a spillway. If the discharge over the model is 1 m3/s, discharge over the prototype will be,
Which of the following is used to fix tie bar to CI sleepers?
Which of the following is not true for unconfined compression test?
A B.G. track is laid with a wooden sleeper. The sleeper spacing and width of the sleeper are 60 cm and 20 cm respectively. What will be the minimum depth of ballast?
Find the hydraulic mean depth of a trapezoidal channel having bed width of 8 m, depth of flow as 4 m and side slope as 1 horizontal to 2 vertical.
The function of the cross groyne in a Denehey's T-shaped groyne is to,
What is the function of parapet wall provided in hilly roads?
Which of the following is correct for water supply pipes made of cast iron?
Which of the following measure is taken to prevent electrolysis in water supply pipe lines?
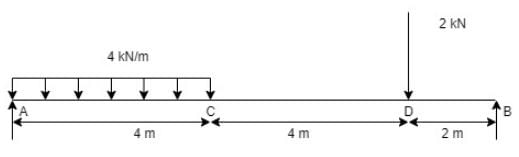
At some distance 'x' from 'A', shear force is zero in the given figure. The value of 'x' is,
The minimum specific energy for a rectangular channel is 4.5 m. What will be the critical depth of flow for the channel?
A beam, 600 mm deep and 250 mm wide, is subjected to shear force and torsional moment of 160 kN and 40 kNm. The equivalent shear is,
Which among the following is not a requirement for ideal track fastening?
Which among the following is not an advantage of steel sleepers?
Check measurements of works are done for the purpose of,
The specified ruling gradient on a M.G section of railway track, is 1 in 200. What will be the steepest gradient that can be provided if a 4o curve is situated on this track?
Which of the following organizations was set up on the recommendations of the Jayakar Committee and is the apex body of highway engineers in India?
Which of the following statement is incorrect about security money deposit?
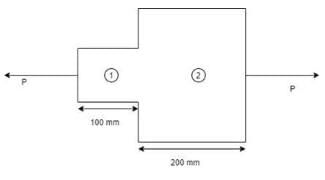
In the given figure, a bar is subjected to axial tensile load of P kN resulting in total extension of 0.3 mm. If A1 = 0.0025 m2 and A2 = 0.005 m2, the value of P will be,
(E = 2 x 105 N/mm2)
Which of the following is not a component of diversion head works?
While performing a compass survey, the fore bearing of a line AB was found to be 280°. The magnetic declination was 15° West. The true bearing of line AB will be,