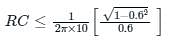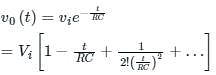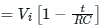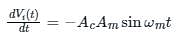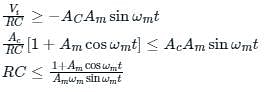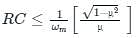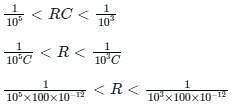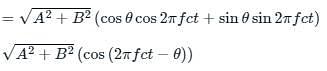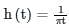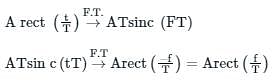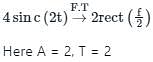Test: Amplitude Demodulation - Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) MCQ
8 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Amplitude Demodulation
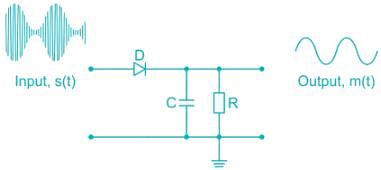
The process of recovering information signal from received carrier is known as ______.
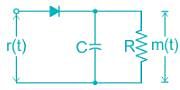
In an amplitude modulated signal, modulating frequency is 10 kHz and modulation index is 0.6. What should be the best suited RC time constant for the envelop detector?
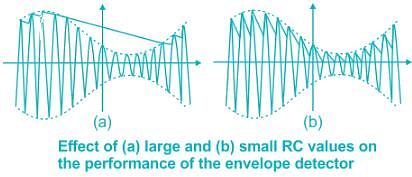
The diagonal clipping in Amplitude Demodulation (using envelope detector) can be avoided if the RC time constant of the envelope detector satisfies the following condition, (ωm is the message bandwidth and ωc is the carrier frequency, both in rad/sec)
A modulated signal is given
x(t) = 10 cos (2π × 105 t) + 6 cos (2π × 103t)cos (2π × 105t)
This signal is to be detected by a linear diode. The most suitable value of resistance if the capacitor is of 100 pF is
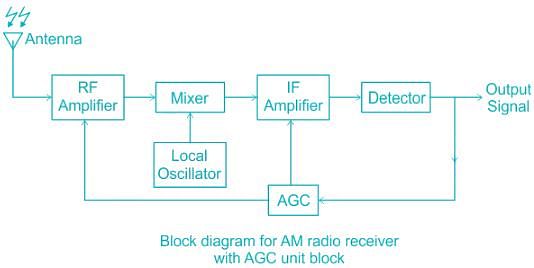
The most common detector used in an AM radio broadcast receiver is:
A signal A cos 2πfct + B.Sin 2πfct is fed into envelope detector. The output of the envelop detector follows ______ at output.
The input 4sinc(2t) is fed to a Hilbert transformer to obtain y(t), as shown in the figure below:

Here 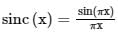 The value (accurate to two decimal places)
The value (accurate to two decimal places) 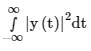 is ___.
is ___.