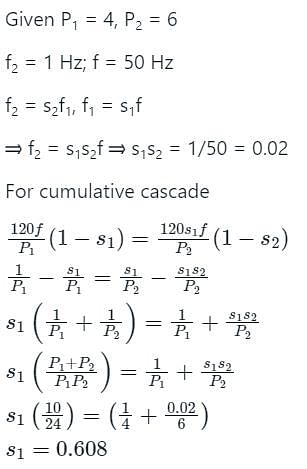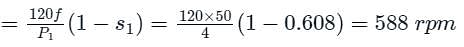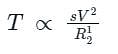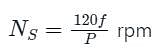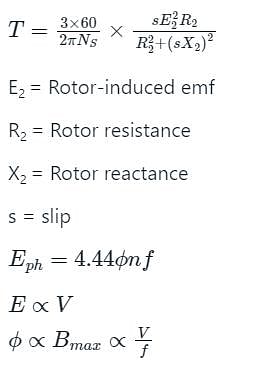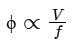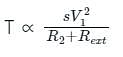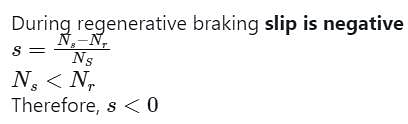Test: Three phase Induction Motor Speed Control - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Three phase Induction Motor Speed Control
In a three-phase induction motor regenerative braking occurs when:
A 4-pole induction motor (main) and a 6-pole motor (auxiliary) are connected in cumulative cascade. Frequency in the secondary winding of the auxiliary motor is observed to be 1 Hz. For a supply frequency of 50 Hz the speed of the cascade set is:
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
The rotor of an induction motor cannot run with synchronous speed because
Under no load condition if the applied voltage to an induction motor is reduced from the rated voltage to half the rated value,
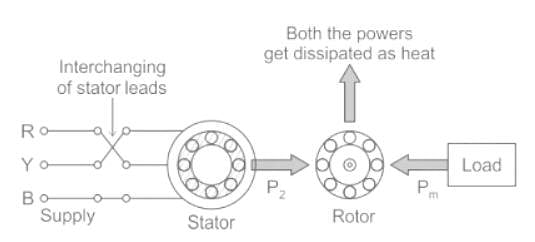
During plugging of a three-phase induction motor:
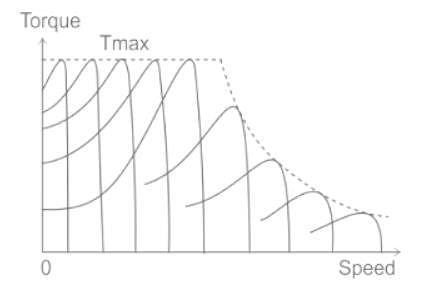
A constant V/f controlled induction motor is fed from a variable voltage variable frequency three phase voltage source inverter. The motor is operated within the base speed. Which of the following is true in torque-speed characteristics of this motor?
The speed of an induction motor is increased by increasing the frequency by 20%. If the magnetising current of the machine is to remain constant, then
When single phasing occurs in a three phase induction motor under running conditions, it
Which of the following methods of speed control of induction motor can be only used for wound rotor type induction motor?
What is the condition to achieve regenerative braking of induction motor?