Test: Extrinsic Semiconductors - Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Extrinsic Semiconductors
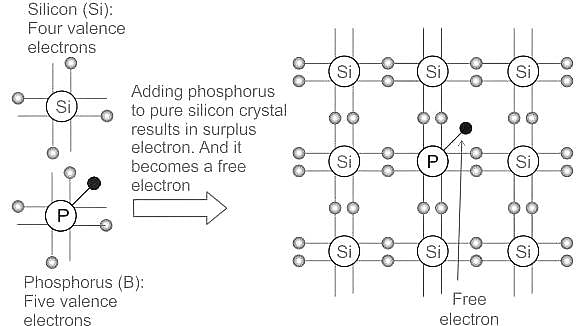
When Si is doped with ________ an n-type semiconductor is formed.
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Two statements are given-one labelled Assertion (A) and the other labelled Reason (R). Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) as given below.
ASSERTION(A): The electrical conductivity of a semiconductor increases on doping.
REASON: Doping always increases the number of electrons in the semiconductor.
ASSERTION(A): The electrical conductivity of a semiconductor increases on doping.
REASON: Doping always increases the number of electrons in the semiconductor.
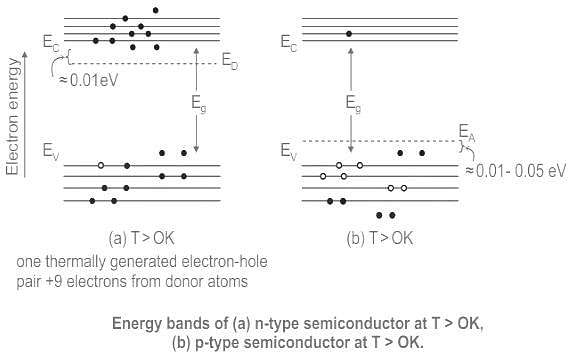
A semiconductor is doped with phosphorous atoms as impurity. The impurity levels created in the semiconductor are close to the
To obtain electrons as majority charge carriers in a semiconductor the impurity mixed is:
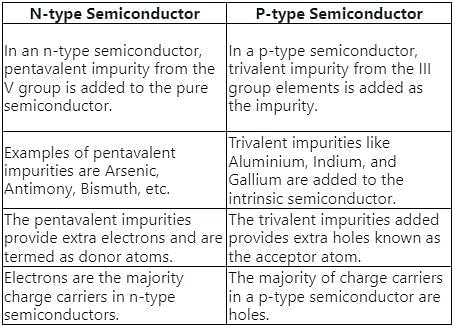
What is the difference between intrinsic semiconductor and extrinsic semiconductor?
Pick statement that is correct for a p-type semi-conductor:
The Fermi level for an extrinsic ‘n’ type semiconductor: