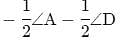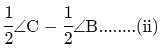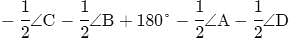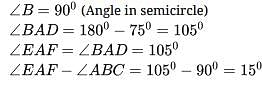Maths Mock Test- 5 - Class 9 MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Maths Mock Test- 5
The line drawn from the center of the circle to any point on its circumference is called:
In the figure, O is the center of the circle. If ∠OAB = 40o, then ∠ACB is equal to :
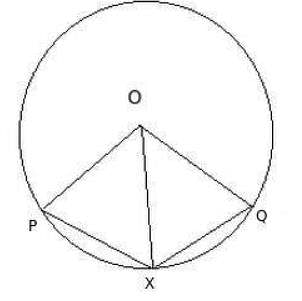
X is a point on a circle with centre O. If X is equidistant from the two radii OP, OQ, then arc PX : arc PQ is equal to
In the adjoining figure, m ║ n, if ∠1 = 500, then ∠2 is equal to –
If APB and CQD are 2 parallel lines, then the bisectors of the angles APQ, BPQ, CQP and PQD form, square only if
If bisectors of ∠A and ∠B of a quadrilateral ABCD intersect each other at P, of ∠B and ∠C at Q, of ∠C and ∠D at R and of ∠D and ∠A at S, then PQRS is a
The Diagonals AC and BD of a Parallelogram ABCD intersect each other at the point O such that ∠DAC = 30∘ and ∠AOB = 70∘. Then, ∠DBC?
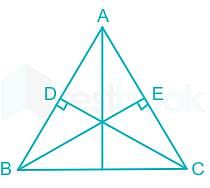
D and E are the mid-points of the sides AB and AC. Of △ABC. If BC = 5.6cm, find DE.
BC is a diameter of the circle and ∠BAO = 60o . Then ∠ADC is equal to
What fraction of the whole circle is minor arc RP in the given figure ?
AB is a chord of a circle with radius ‘r’. If P is any point on the circle such that ∠APB is a right angle , then AB is equal to
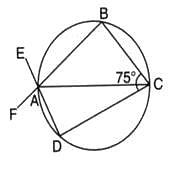
In the given figure, AC is a diameter of the given circle and ∠BCD = 75o. Then, ∠EAF−∠ABC is equal to
If one of the factor of x2 + x – 20 is (x + 5). Find the other
In quadrilateral ABCD, BM and DN are drawn perpendiculars to AC such that BM = DN. If BR = 8 cm. then BD is
If the altitudes from two vertices of a triangle to the opposite sides are equal, then the triangles is
In △AOC and △XYZ, ∠A =∠X, AO = YZ, AC = XY, then by which congruence rule △AOC ≅ △XYZ