Test: Genetic Code & Translation (December 17) - NEET MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Genetic Code & Translation (December 17)
Some amino acids are coded by more than one codon, hence the genetic code is
During translation, activated amino acids get linked to (RNA). This process is commonly called as
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
The mutations that involve addition, deletion or substitution of a single base pair in a gene are referred to as
Choose the correct answer from the alternatives given :
Direction : Read the sequence of nucleotides in the given segment of mRNA and the respective amino acid sequence in the polypeptide chain.

Polypeptide Met-Phe-Met-Pro-Val-Ser
Which codons respectively code for proline and valine amino acids in the given polypeptide chain, respectively?
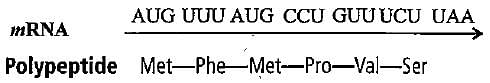
Choose the correct answer from the alternatives given:
Identify the labels A, B, C and Din the given structure of tRNA and select the correct option.

Given below are the steps of protein synthesis. Arrange them in. correct sequence and select the correct option.
(i) Codon-anticodon reaction between mRNA and aminoacyl tRNA complex.
(ii) Attachment of mRNA and smaller sub-unit of ribosome.
(iii) Charging or aminoacylation of tRNA.
(iv) Attachment of larger sub unit of ribosome to the mRNA-tRNAMet complex.
(v) Linking of adjacent amino acids.
(vi) Formation of polypeptide chain.
UTRs are the untranslated regions present on
The difference(s) between mRNA and tRNA is/are that:
(i) mRNA has more elaborate 3 - dimensional structure due to extensive base - pairing
(ii) tRNA has more elaborate 3 - dimensional structure due to extensive pairing
(iii) tRNA is usually smaller than mRNA
(iv) mRNA bears anticodon but tRNA has codons
Which out of the following statements is incorrect?
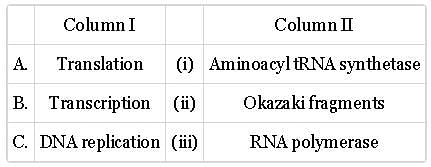
Match column with column II and select the correct option from the given codes.