Test: Genetics and Evolution (December 23) - NEET MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Genetics and Evolution (December 23)
The two polynucleotide chains in DNA are
[2007]
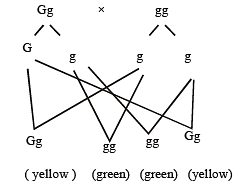
In pea plants, yellow seeds are dominant to green. If a heterozygous yellow seeded plant is crossed with a green seeded plant, what ratio of yellow and green seeded plants would you expect in F1 generation ?
[2007]
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Industrial melanism is an example of
[2003]
In a random mating population in equilibrium, which of the following brings about a change in gene frequency in a non-directional manner? [2003]
Sickle cell anaemia has not been eliminated from the African population because
[2006]
Both sickle cell anemia and Huntington's chorea are
[2006]
During transcription, the DNA site at which RNA polymerase binds is called
[2003]
Two different species can not live for long duration in the same niche or habitat. This law is
[2002]
Which one of the following describes correctly the homologous structures ?
[2003]
Darwin in his 'Natural Selection Theory' did not believe in any role of which one of the following in organic evolution ?
[2003]
Two genes R and Y are located very close on the chromosomal linkage map of maize plant. When RRYY and rryy genotypes are hybridized, the F2 segregation will show
[2007]
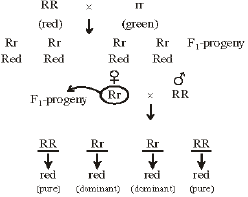
A common test to find the genotype of a hybrid is by
[2007]
In recent years, DNA sequences (nucleotide sequence) of mt-DNA and Y chromosomes were considered for the study of human evolution, because
[2003]