Revisal Problems (Past 13 Years) JEE Advanced (Hydrocarbons) - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Revisal Problems (Past 13 Years) JEE Advanced (Hydrocarbons)
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-10) This section contains 10 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q. In the following reaction X is
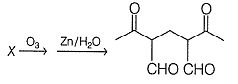
How many dichlorinated isomers (including stereoisomers) can be formed by the halogenation of CH3CH2CH2CH3 with Cl2 in the presence of light?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
What is the major product expected from the following reaction?
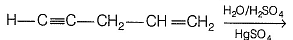
Addition of Br2 to cis-2-hexene gives racemic mixture, even though attack of the bromide ion on unsymmetrical bromonium ion intermediate is not equally likely at both carbons. The reason for the racemic products are
Which of the following hydrocarbon is most difficult to prepare by Wurtz’s reaction?
If potassium salt o f the following acids is electrolysed in aqueous solution, what would be the increasing order of their reactivity?
In the following synthesis the major product formed is a
Which could be the major product of the following reaction?
The major substitution product of the following reaction is
The major substitution product of the following reaction is
Direction (Q. Nos. 11-16) This section contains 6 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.
Q. Which of the following alkene cannot be prepared by controlled hydrogenation of an alkyne?
Consider the following reaction.
Q. Which of the following is/are true statement?
Which of the following reactants, reagents and products are correctly matched?
In which of the following reactions, reactants and products are correctly matched?
Which of the following will evolve hydrogen gas on heating with potassium metal?
What product(s) are expected when excess of beonzene is treated with 3-propenol in presence of HF?
Direction (Q. Nos. 17-20) This section is based on Statement I and Statement II. Select the correct answer from the codes given below.
Q.
Statement I : Free radical bromination of an alkane brings about bromination predominantly at the highest degree carbon.
Statement II : Bromine is more reactive than chlorine in free radical halogenations of an alkane.
Statement I : Sulphonation of benzene is reversible in nature.
Statement II : Deuterated benzene reacts slower than benzene in sulphonation with hot cone. H2SO4.
Statement I : Addition of halogens in dry condition to an alkene is regioselective, i.e.devoid of any rearrangement.
Statement II : Addition of halogen at carbon-carbon double bond proceed via a cyclic halonium ion intermediate.
Statement I : Ozonolysis of 3-hexyne followed by hydrolysis gives propanoic acid.
Statement II : The byprod uct H2O2 oxidises ozonide to acid.
Direction (Q. Nos. 21-26) This section contains 2 paragraphs, each describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Six questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer among the four given options (a), (b), (c) and (d).
Passage I
An alkane (A) molecular formula C6H14 reacts with chlorine in the presence of ultraviolet light to yield three positional isomers as monochloro derivatives (B), (C)and (D). Of these, only (C) and (D) undergo dehydrohalogenation with sodium ethoxide in ethanol to produce an alkene. Moreover, (C) and (D) yields the same alkene (E) (C6H12). Hydrogenation of (E) produces (A). Treating (E)with HCI produces a compound (F) that is an isomer of (B), (C) and (D). Treating (F) with Zn and acetic acid gives a compound (G), which is isomeric with (A).
Q. The most likely structure of A is
Passage I
An alkane (A) molecular formula C6H14 reacts with chlorine in the presence of ultraviolet light to yield three positional isomers as monochloro derivatives (B), (C)and (D). Of these, only (C) and (D) undergo dehydrohalogenation with sodium ethoxide in ethanol to produce an alkene. Moreover, (C) and (D) yields the same alkene (E) (C6H12). Hydrogenation of (E) produces (A). Treating (E)with HCI produces a compound (F) that is an isomer of (B), (C) and (D). Treating (F) with Zn and acetic acid gives a compound (G), which is isomeric with (A).
Q. Which of the following is true regarding C and D?
Passage I
An alkane (A) molecular formula C6H14 reacts with chlorine in the presence of ultraviolet light to yield three positional isomers as monochloro derivatives (B), (C)and (D). Of these, only (C) and (D) undergo dehydrohalogenation with sodium ethoxide in ethanol to produce an alkene. Moreover, (C) and (D) yields the same alkene (E) (C6H12). Hydrogenation of (E) produces (A). Treating (E)with HCI produces a compound (F) that is an isomer of (B), (C) and (D). Treating (F) with Zn and acetic acid gives a compound (G), which is isomeric with (A).
Q. The compound G reacts with chlorine in the presence of ultraviolet light to yield how many isomers as monochloro derivatives?
Passage II
An organic compound A has molecular formula C10H14 and it does not decolourise bromine water solution. A on treatment with Br2 / Fe yields three products in principle but in actual practice, only two of these are produced as mono-bromo derivative. A on heating with Br2 yields B (C10H13Br)as the major monobromo derivative which is optically inactive. A on heating with alkaline KMnO4 yields C(C8H6O4) which does not form anhydride on heating.
Q. What is most likely structure of A?
Passage II
An organic compound A has molecular formula C10H14 and it does not decolourise bromine water solution. A on treatment with Br2 / Fe yields three products in principle but in actual practice, only two of these are produced as mono-bromo derivative. A on heating with Br2 yields B (C10H13Br)as the major monobromo derivative which is optically inactive. A on heating with alkaline KMnO4 yields C(C8H6O4) which does not form anhydride on heating.
Q. The structure of B is
Passage II
An organic compound A has molecular formula C10H14 and it does not decolourise bromine water solution. A on treatment with Br2 / Fe yields three products in principle but in actual practice, only two of these are produced as mono-bromo derivative. A on heating with Br2 yields B (C10H13Br)as the major monobromo derivative which is optically inactive. A on heating with alkaline KMnO4 yields C(C8H6O4) which does not form anhydride on heating.
Q. What is C?
Direction (Q. Nos. 27 and 28) Choices for the correct combination of elements from Column I and Column II are given as options (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which one is correct.
Q. Consider the compounds on left column and match with reactions from right column by which they can be prepared
Consider the compounds of Column I for electrophilic substitution reaction with Cl2 in Working Space presence of AICI3. Match them with the nature of reaction and product formed from the Column II.
Direction (Q. No. 29-32) This section contains 4 questions. When worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).
Q. An aromatic compound has molecular formula C7H8O . How many isomers are possible for this compound with a phenyl ring in each of them?
Consider the following reaction,
Q. How many different products (including stereoisomers) would be formed?












