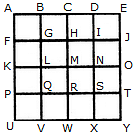MCQ: Analysis (Analytical Reasoning) - 3 - SSC CGL MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - MCQ: Analysis (Analytical Reasoning) - 3
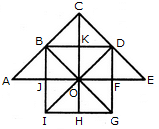
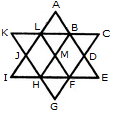
Find the number of triangles in the given figure.
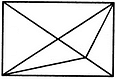

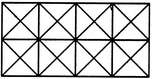
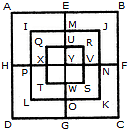
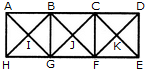
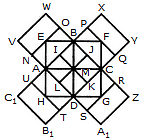
Count the number of triangles and squares in the given figure.

| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
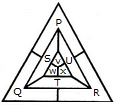
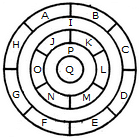
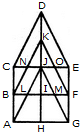
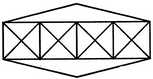
What is the minimum number of colours required to fill the spaces in the given diagram without any two adjacent spaces having the same colour?
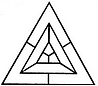

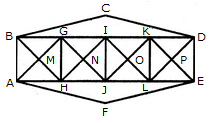
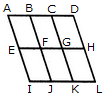
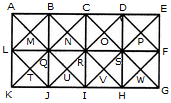
Count the number of squares in the given figure.
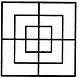
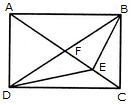
Find the number of quadrilaterals in the given figure.
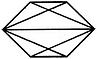
Count the number of squares in the given figure.
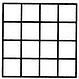
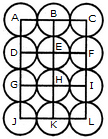
In the adjoining figure, if the centres of all the circles are joined by horizontal and vertical lines, then find the number of squares that can be formed.
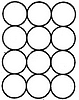
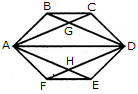
Count the number of parallelogram in the given figure.
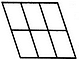
Count the number of triangles and squares in the given figure.
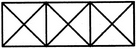
What is the minimum number of different colours required to paint he given figure such that no two adjacent regions have the same colour?
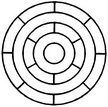
Count the number of triangles and squares in the given figure.
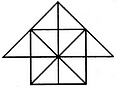
Count the number of parallelogram in the given figure.
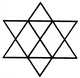
Count the number of squares in the given figure.
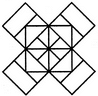
How many triangles and parallelograms are there in the following figure?
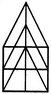
Count the number of squares in the given figure.