Revisal Problems (Past 13 Years) JEE Main (Thermodynamics) - JEE MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Revisal Problems (Past 13 Years) JEE Main (Thermodynamics)
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-20) This section contains 20 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q. The amount of heat evolved when 500 cm3 of 0.1 M HCI is mixed with 200 cm3 of 0.2 M NaOH is
Given, ΔfH°(NH3) = -46.1 kJ mol-1 and ΔfH° of the following reaction is -187.6kJ
N2H4(g) + H2(g) → 2NH3(g)
Q. Thus, ΔfH° (N2H4) is
N2H4(g) + H2(g) → 2NH3(g)
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
In the following reaction,
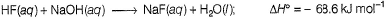
This value is much higher than the heat of neutralisation of strong acid with strong base (-57.3 kJ mol-1) . This is because
For the above reaction, 2NO(g) + O2(g) → 2NO2(g)
Select incorrect relation
At what temperature will the equilibrium constant for the formation of NOCI(g) be
Keq = Kp = 1.0 x 103
For the reaction at 298 K
Thus ΔG° for the given reaction is
Methane is a commercial source of H2 through the reaction
Based on the following thermochemical equations (II to IV)
Q. ΔH of equation (I) is
Given,
Thus, for the reaction
Thus, for the reaction
Vapour pressure of a liquid is 10 mm at 300 K, 20 mm at 400 K. What is the vapour pressure at 500 K?
The combustion of hydrogen-oxygen mixture is used to produce very high temperatures (= 2500 °C) needed for certain types of welding operations.
Q. Quantity of heat, (in kJ) evolved when a 180 g mixture containing equal parts of H2 and O2 mass is burned, is
Due to dissolution of ammonium chloride in H2O, temperature falls rapidly. Thus,
The standard heat of combustion of benzoic acid, C6H5COOH(s), at 1 bar and 298 K is -329.3 kJ mol-1. The standard heat of combustion at constant volume is
Bond dissociation energies of H—H, O=O, O—H and O—O are x1, x2, x3, and x4 respectively.
Thus, heat of formation of H2O2(g) is
Thus, melting point of NaCI (s) is
Quantity of work (in joules) done by the gas if it expands against a constant pressure of 0.980 atm and the change in volume (Δ/) is 25.0 L, is
The combustion of 1.0 g of sucrose (C12H22O11) in a bomb calorimeter causes the temperature to rise from 25.0°C to 28.5°C. The heat of combustion of sucrose is (heat capacity of the calorimeter system is 4.90 kJ K-1
A gas, while expanding absorbs 25 J of heat and does 243 J of work. Thus, ΔE (change in internal energy) for the gas is
1.0 L of liquid water freezes under a constant pressure of 1.0 atm and forms 1.1 L of ice.
Thus, work done is
In the following adiabatic expansion of 1 mole of CO2 gas, temperature T is
For the dissociation of PCI5(g)
Slope of the linear curve is such that θ = tan-1 (-1.5)
Q. Thus, ΔH° is

















