Test: Earth and Universe - Class 6 MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Earth and Universe
It takes about _______________days for the Moon to complete its cycle of phases.
Which is a group of constellation through which the Sun appears to move?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
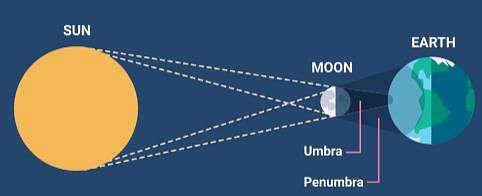
Which eclipse do you experience if you are standing in the Moon’s umbra?
Which of these planets has the highest gravitational pull?
It takes about ___________ days for the Moon to revolve around the Earth.
Where are asteroids primarily located in our solar system?
There are eight planets in our universe. Say O, P, Q, R, S, T, U, and V. We can call it planet ‘S’. Among all, this is called the red planet because its soil and rocks are red in colours. This planet resembles Earth the most. Scientists believe that it is the
only planet, besides Earth, where life may exist.
‘S’ in the above paragraph is _____________.