BPSC Prelims Past Year Paper- 2020 - BPSC (Bihar) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - BPSC Prelims Past Year Paper- 2020
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
The first man who placed his foot on the moon is
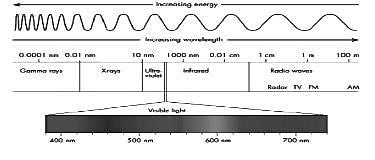
The radiation used in the treatment of muscle ache are
The total resistance of a circuit having two parallel resistors is 1.403 kilo-ohm. If one of the resistors is 2.0 kilo-ohm then the other resistor will be
Which of the following does not change when light travels from one medium to another?
The number of neutrons in the nucleus of plutonium nuclide (94Pu242) is
The highest viscosity among the following is of
The breath test conducted by police to check drunken driver has which one of the following on the filter paper?
Glucose is converted to ethyl alcohol by the enzyme
The incomplete burning of petrol and diesel produces
The pH of a solution changes from 3 to 6. The H+ ion concentration will
A mixture of sand and naphthalene can be separated by
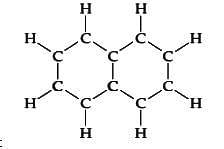
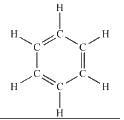
The numbers of sigma and pi bonds in benzene are
The poorest conductor of heat among the following is
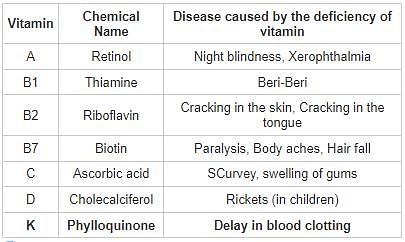
The vitamin which is effective in blood clotting is
The Nobel Prize for developing treatment of Parkinson's disease was given to
The malfunctioning of thyroid gland is due to the deficiency of
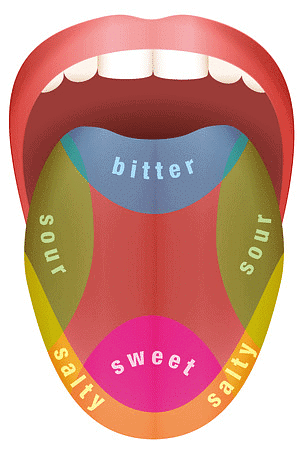
The sensitive area of the human tongue to bitterness is
Among the following, which is not a true fruit?
Legumes are highly nutritious because they are rich in
Clove, a spice, is obtained from which part of the plant?