Revisal Problems (Past 13 Years) JEE Main (Chemical Bonding) - JEE MCQ
24 Questions MCQ Test - Revisal Problems (Past 13 Years) JEE Main (Chemical Bonding)
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-20) This section contains 20 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c), and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct
Q. Some of the following compounds have more than one type of bonding.
KCN, NH4CI, NaCI, H2O, H2SO4,CaO, MgCI2, CH4, H2
These are
Out of the following paramagnetic species are 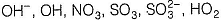
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
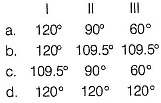
The Cl— C— Cl angles in
I. 1,1,2, 2-dichloroethene
II. tetrachloromethane and
III. 1, 1-dichloroelhane
respectively will be
II. tetrachloromethane and
III. 1, 1-dichloroelhane
Metallic bonding is explained by
The shape of IF7 molecule is
AsF5 molecule is trigonal bipyramidal. The hybrid orbitals used by As atoms for bonding are
P4 is stable form of phosphorus.The percentage of p - character in the orbital forming (P—P) bonds in P4 is
Central O-atom in O3 is ...... hybridised.
Among the following species, isostructural pairs are
If there are five electron pairs in outer shell of an atom, then structure and bond angle as predicted by Sidgwick-Powell theory is
Consider the following molecules
I. Acetic acid
II. o-nitrophenol
III. m-nitrophenol
IV. o-boric acid
Select the species showing intramolecular (X)and intermolecular the H-bonding (Y).
In which of the following molecules would you expect the nitrogen-to-nitrogen bond to be the shortest?
Chelation can occur in
The correct order of dipole moment of HF, H2S and H2O molecules is in order.
Solubility of the salts of group IIA (alkaline earth metals) is in orde
unpaired ele ctrons are present in
EN values of elements are given
Q. Out of KCI, PH3, GeCI, H2S and CsF ionic compounds are
Ionisation potential of sodium is (5.1 eV) and the electron affinity of chlorine is (3.6 eV). Working Space Energy required to transfer one electron from and an isolated sodium atom to an isolated gaseous atom is
Consider the following complexes.
Q. Fe is sp3d2 hybridisation in w hich of the above complexes
Direction (Q. Nos. 21-24) This section is based on statement I and statement II. Select the correct answer from the codes given below.
Q.
Statement I : The chlorine to oxygen bond distance in
Statement II : There must be considerable double bond character.
Statement I : (N—N) bond length in N2O4 is larger than normal (N—N) bond length in N2H4.
Statement I : I Nitrogen completes its octet in N2O4.
Statement I : is linear in structure.
Statement II : l2 is a Lewis acid and l- is a Lewis base.
Statement I : is form ed but
is not formed.
Statement II : F- is not a Lewis base.

















