Revisal Problems (Past 13 Years) JEE Advanced (Chemical Kinetics) - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Revisal Problems (Past 13 Years) JEE Advanced (Chemical Kinetics)
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-12) This section contains 12 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
For the first order gaseous phase reaction, A → B + C
initial pressure is 200 mm and after 20 min, total pressure is 250 mm. Thus, half-life period is
For the elementary reaction (M → N), the rate of disappearance of M increases by a factor of 8 upon doubling the concentration of M. The order of the reaction with respect to M is
[JEE Advanced 2014]
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
For the reaction,
experimental data for the measured initial rates is given below.
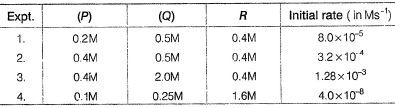
Q.
The order of the reaction with respect of P,Q and R respectively is
Reaction coordinate diagram for the reaction
For a reaction, k = 1.2 x 103 mol-1 L s-1 and Ea = 2.0 x 102 kJ mol-1
When T→ ∞, Arrhenius pre-exponential factor is
Half-life period of the first order reaction is 100 days. After 144.3 days, concentration of the reactant is reduced to ......of the original value.
For the following chemical equation, a first order reaction, A(g) → nB(g) total pressure of the system as a function of time is
What function of [X], plotted against time will give a straight line for a second order reaction?
The rate constant at 298 K for the reaction of and OH+ to form NH4OH is 4 .0 x 1010 M-1 s-1. Thus, rate constant for proton transfer to NH3 is
For a reaction A → Product
[A]0 = Initial concentration, [A] = Concentration of the reactant A after time t.
Then
For a second order reaction,
where and a and b are the initial concentrations of A and B. Reaction w ould be pseudo-unimolecular when
A certain reaction, A + B → Product
is first order w.r.t. each reactant with k = 5.0 x 10-3 M-1 s-1
then concentration of A remaining after 100 s is
Direction (Q. Nos. 13-16) This section contains 4 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.
Q.
Rate constant k varies with tem perature as given by the equation
Select the correct statement(s) about this equation.
Which is/are the graphical representation for the zeroth order reaction?
Select the correct staiement(s) about half-life period,
For the reaction,
In alkaline aqueous solution, the value of the second order (in BrC-), rate constant at 80°C in the rate law for was found to be 0.056 L mol-1 s-1
Select the correct alternate reaction.
Direction (Q. No. 17) Choices for the correct combination of elements from Column I and Column II are given as options (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which one is correct.
Q. Rate law of the nth order reaction is given by
Match the different properties in Column I with their related values of half-life in Column II and select the correct answer from the codes given.
Direction (Q. Nos. 18-27) This section contains 5 paragraphs, each describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Ten questions related to the paragraphs have been given. Each question has only one correct answer among the four given options (a), (b), (c) and (d).
Passage I
A 22.4 L flask contains 0.76 mm of O3 at 298 K. It reacts with oxygen atoms as
O + O3 → 2O2, k = 1.5 x 107 L mol-1 s-1 at the rate of 0.15 mol L-1 s-1.
Q.
What is the concentration of oxygen atoms needed to maintain this rate?
Passage I
A 22.4 L flask contains 0.76 mm of O3 at 298 K. It reacts with oxygen atoms as
O + O3 → 2O2, k = 1.5 x 107 L mol-1 s-1 at the rate of 0.15 mol L-1 s-1.
Q.
What is the rate of formation oxygen (O2) under these conditions?
Passage II
The complex ion of Fe2+ with the chelating agent diphyridyl (abbreviated as dipy) has been studied kinetically in both the forward and the reverse directions.
Q.
Half-life of the reverse reaction is
Passage II
The complex ion of Fe2+ with the chelating agent diphyridyl (abbreviated as dipy) has been studied kinetically in both the forward and the reverse directions.
Q.
Stability constant in terms of pk is
Passage III
Also, t1 = t2 and [A]0 = [B]0 = a
Q.
The ratio of the rates of these two reactions at the start of the reaction is
Passage III
Also, t1 = t2 and [A]0 = [B]0 = a
Q.
The ratio of the rates of these two reaction after a lapse of one half-life is
Passage IV
The rate constant for the decomposition of ethylene oxide into CH4 and CO may be described by
Q.
Energy of activation for this reaction is
Passage IV
The rate constant for the decomposition of ethylene oxide into CH4 and CO may be described by
Q.
What is the rate constant at 670 K?
Passage V
The following first order reaction is conducted in CCI4(l)at 45°.
An 80.0 g sample of N2O5(g)is dissolved inCCI4(l) and allowed to decompose at 450°C.
Q.
Time taken for the quantity of N2O5 to be reduced to 2.5 g is
Passage V
The following first order reaction is conducted in CCI4(l)at 45°.
An 80.0 g sample of N2O5(g)is dissolved inCCI4(l) and allowed to decompose at 450°C.
Q.
Volume of O2 produced at STP at this point is
Direction (Q. Nos. 28-37) This section contains 10 questions. When worked out will result in one integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).
The concentration of R in the reaction,
R→ P
was measured as a function of time and the following data is obtained :
Q.
What is the order of reaction?
[IIT JEE 2010]
For the reaction system,
volume is suddenly reduced to half its value by increasing the pressure on it. If the reaction is of first order w.r.t. O2 and the second order w.r.t. NO, the rate of reaction will increase ......times of its initial value.
For the reaction,
Initial pressure of A and B are respectively 0.60 atm and 0.80 atm. At a time when pressure of C is 0.20 atm, ratio of initial rate and final rate is y. What is the value of y?

















