Test: Beams & Slabs - 2 - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Beams & Slabs - 2
A simply supported RC beam having clear span 5 m and support width 300 mm has the cross section as shown in figure below.
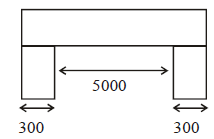
What is the effective span of the beam as perIS:456?
What is the modular ratio to be used in an analysis of RC beams using working stress method if the grade of concrete is M20?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
In RCC beams, as the percentage area of tensile steel increase
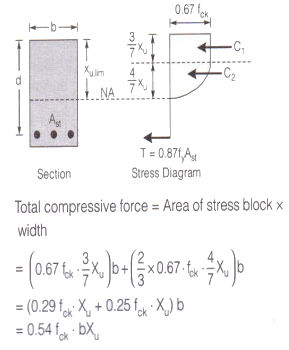
The total compressive force at the time of failure of a concrete beam section of width 'b' without considering the partial safety factor of the material is
A floor slab of thickness t, is cast monolithically transverse to a rectangular continuous beam of span, L and width, B. If the distance between two consecutive points of contraflexure is, L0, the effective width of compression flange at a continuous support is (GATE 2012)
A reinforced concrete member is subjected to combined action of combined action of compressive axial force and bending moment. If ec is the best least compressive strain in the member, fy, the yield stress of steel and, Es, the modulus of elasticity of steel, the maximum permissible compressive strain in concrete member will be
The span to depth ratio limit is specified in IS : 456-1978 for the reinforced concrete beams, in order to ensure that the
As per the provisions of IS : 456–2000, in the limit state method for design of beams, the limiting value of the depth of neutral axis in a reinforced concrete beam of effective depth 'd' is given as
If the permissible stress in steel in tension is 140 N/mm2, then the depth of neutral balanced section using working stress method is
Which one of the following statements about the percentage of tensile steel required to produce a balanced reinforced concrete section is correct
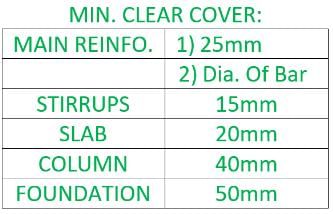
Minimum clear cover (in mm) to the main steel bars in slab, beam, column and footing respectively are?
Beam sections designed in accordance with LSM as compared to sections designed in accordance with WSM will have
If the depth of actual neutral axis in a beam is more than the depth of critical neutral axis, the beam is called:
For a continuous slab of 3m*3.5m size the minimum overall depth of slab to satisfy verticle deflection limits is
The minimum reinforced using mild steel in slab should not be less than.
In the reinforced concrete slab, the spacing between main reinforcement should nto exceed
The slab is designed as one way if the ratio of long span to short span is
The precast prestressed hollow core slabs, with or without topping is an important structural element in __________
For a simply supported beam of span 15m, the minimum effective depth to satisfy the vertical deflection limits should be
Half of the main steel in a simply supported slab is bent up near the support at a distance of x from the centre of slab bearing where x is equal to
If the size of panel in a flat slab is 6m x 6m, then as per Indian Standard Code, the widths of column strip and middle strip are