Test: Assertion and Reason - CUET Humanities MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Assertion and Reason
Directions: In the following question, two statements are given. One is assertion and the other is reason. Examine the statements carefully and mark the correct option.
Assertion (A): Kinetic energy is zero to move a positive test charge from infinity to the particular point against the electrostatic force due to the electric field.
Reason (R): Kinetic energy is directly proportional to the mass, that's why kinetic energy is zero for test charge.
Assertion (A): Kinetic energy is zero to move a positive test charge from infinity to the particular point against the electrostatic force due to the electric field.
Reason (R): Kinetic energy is directly proportional to the mass, that's why kinetic energy is zero for test charge.
Directions: In the following question, two statements are given. One is assertion and the other is reason. Examine the statements carefully and mark the correct option.
Assertion (A): In an LCR circuit, the algebraic sum of the potential drop across the circuit elements is always equal to the applied mains voltage.
Reason (R): The potential drop across the resistance is equal to the sum of the potential drop across the inductor and capacitor.
Assertion (A): In an LCR circuit, the algebraic sum of the potential drop across the circuit elements is always equal to the applied mains voltage.
Reason (R): The potential drop across the resistance is equal to the sum of the potential drop across the inductor and capacitor.
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Directions: In the following question, two statements are given. One is assertion and the other is reason. Examine the statements carefully and mark the correct option.
Assertion (A): The ratio of the amplitude of magnetic field to the amplitude of electric field is constant and it is equal to the speed of light.
Reason (R): It is equal to B/E = 3 × 102 m/s.
Assertion (A): The ratio of the amplitude of magnetic field to the amplitude of electric field is constant and it is equal to the speed of light.
Reason (R): It is equal to B/E = 3 × 102 m/s.
Directions: In the following question, two statements are given. One is assertion and the other is reason. Examine the statements carefully and mark the correct option.
Assertion (A): Same charge enclosed in spheres of different sizes has different total electric flux.
Reason (R): Spheres of different sizes have different area, and electric flux is directly proportional to area vector.
Directions: In the following question, two statements are given. One is assertion and the other is reason. Examine the statements carefully and mark the correct option.
Assertion (A): In electric flux, area vector is always normal to area element.
Reason (R): Electric flux is the dot product of electric field and area vector.
Directions: In the following question, two statements are given. One is assertion and the other is reason. Examine the statements carefully and mark the correct option.
Assertion (A): Electric potential on the plane is zero if plane bisects the dipole perpendicularly.
Reason (R): Electric potential is always zero at the centre of two charges.
Directions: In the following question, two statements are given. One is assertion and the other is reason. Examine the statements carefully and mark the correct option.
Assertion (A): When a magnet is heated to a high (1000°C) temperature, it loses its magnetism.
Reason (R): At high temperature, particle of magnet vibrates at high speed.
Directions: In the following question, two statements are given. One is assertion and the other is reason. Examine the statements carefully and mark the correct option.
Assertion (A): We use the satellites for long distance TV transmission.
Reason (R): TV signals are not reflected by the ionosphere.
Directions: In the following question, two statements are given. One is assertion and the other is reason. Examine the statements carefully and mark the correct option.
Assertion (A): If we place a dielectric in a capacitor, the capacitance of the capacitor will increase.
Reason (R): Dielectric reduces the value of the electric field, that's why potential difference also decreases.
Directions: In the following question, two statements are given. One is assertion and the other is reason. Examine the statements carefully and mark the correct option.
Assertion (A): The electromagnetic waves exert pressure on the surface of the matter when they fall on it.
Reason (R): Electromagnetic waves are composed of oscillating magnetic and electric fields.
Directions: In the following question, two statements are given. One is assertion and the other is reason. Examine the statements carefully and mark the correct option.
Assertion (A): A wire is not caring current when charge is flowing through it.
Reason (R): When charge changes its position, it produces current.
Directions: In the following question, two statements are given. One is assertion and the other is reason. Examine the statements carefully and mark the correct option.
Assertion (A): The ratio of total electric flux of charge +q enclosed in a sphere of radius 10 cm to the same charge enclosed in a cube of side 7 cm is unity.
Reason (R): According to Gauss law, net electric flux through enclosed surface is 1/ε times the total charge enclosed by the surface. Net electric flux through both the surfaces is same.
Directions: In the following question, two statements are given. One is assertion and the other is reason. Examine the statements carefully and mark the correct option.
Assertion (A): If a plane bisects the dipole perpendicularly, we can call it equipotential surface.
Reason (R): Potential on the whole plane due to dipole is same.
Directions: In the following question, two statements are given. One is assertion and the other is reason. Examine the statements carefully and mark the correct option.
Assertion (A): The energy of charged particle changes when it moves inside the magnetic field.
Reason (R): It is so because there is force on the charged particle due to the magnetic field.
Directions: In the following question, two statements are given. One is assertion and the other is reason. Examine the statements carefully and mark the correct option.
Assertion (A): The oscillations of moving coil of galvanometer generally takes a long time to die out.
Reason (R): It is because of induced current.


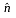 =
= 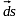 (vector) n cap is normal to ds.
(vector) n cap is normal to ds.














