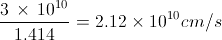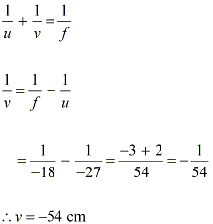Test: Ray Optics and Optical Instruments - 2 - CUET Humanities MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Ray Optics and Optical Instruments - 2
A lens of focal length 50 cm forms an image of a distant object, which subtends an angle of 1 milliradian at the lens. What is the size of the image?
F1 and F2 are focal lengths of the objective and the eyepiece of a telescope, respectively. The angular magnification for this telescope is equal to
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
A pIano-convex lens acts like a concave mirror of 28 cm focal length when its plane surface is silvered and like a concave mirror of 10 cm focal length when its curved surface is silvered. What is the refractive index of the material of the lens?
The refractive index of glass with respect to a medium is 4/3. If the difference between the velocities of light in medium and in glass is 6.25 x 107 m/s, then what is the velocity of light in the medium?
A small telescope has an objective lens of focal length 144 cm and an eyepiece of focal length 6.0 cm. What is the magnifying power of the telescope and the separation between the objective lens and the eyepiece?
A light ray is travelling between two media as given below. The angle of incidence on the boundary in all the cases is 30º. Identify the correct sequence of increasing order of angles of refraction.
- Air to water
- Water to glass
- Glass to water
(Refractive indices of glass and water are 3/2 and 4/3, respectively.)
White light is incident on one of the refracting surfaces of a prism of angle 5°. If refracting indices for red and blue colours are 1.659 and 1.641, respectively, then the angular dispersion between these two colours, when they emerge out of the prism, is
Oceans appear bluish in colour due to
The minimum deviation produced by a glass prism having an angle of 60° is 30°. If the velocity of light in vacuum is 3 × 1010 cm/s, then what is its velocity in glass?
A small candle, 2.5 cm in size, is placed 27 cm in front of a concave mirror of radius of curvature 36 cm. At what distance from the mirror, should a screen be placed in order to obtain a sharp image?


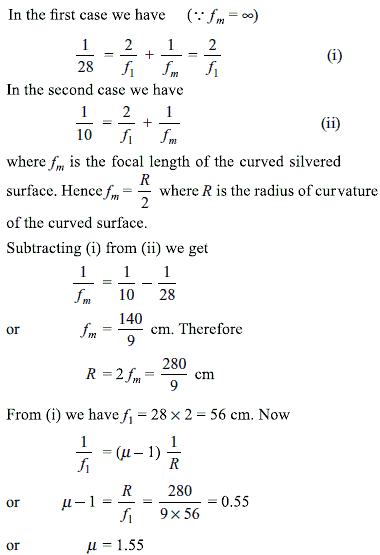
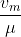
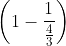
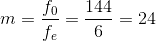
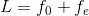
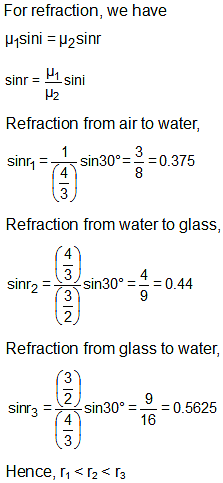
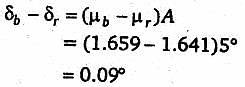
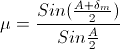 =
= 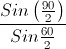 =
= 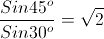
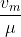
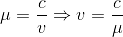 , where v is the speed of the light in glass.
, where v is the speed of the light in glass.