Legal Studies: CUET Mock Test - 5 - CUET Humanities MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Legal Studies: CUET Mock Test - 5
Directions: The question is based on the reasoning and arguments, or facts and principles set out in the passage. Some of these principles may not be true in the real or legal sense, yet you must conclusively assume that they are true for the purpose. Please answer the question on the basis of what is stated or implied in the passage. Do not rely on any principle of law other than the ones supplied to you, and do not assume any facts other than those supplied to you when answering the question. Please choose the option that most accurately and comprehensively answers the question.
Copyrights are generally owned by the people who create the work of expression.
Some exceptions:
If a work is created by an employee in the course of his or her employment, the employer owns the copyright. If the work is created by an independent contractor and the independent contractor signs a written agreement stating that the work shall be made for hire, the commissioning person or organisation owns the copyright only if the work is a part of a larger literary work, such as an article in a magazine or a poem or story in an anthology; part of a motion picture or other audiovisual work, such as a screenplay; a translation; a supplementary work such as an afterword, an introduction, chart, editorial note, bibliography; a compilation; an instructional text; a test or answer material for a test; or an atlas. Works that don't fall within one of these eight categories constitute works made for hire only if created by an employee within the scope of his or her employment.
If the creator has sold the entire copyright, the purchasing business or person becomes the copyright owner.
When two or more authors prepare a work with the intent to combine their contributions into inseparable or interdependent parts, the work is considered joint work and the authors are considered joint copyright owners. Authorship is retained but in some cases this copyright owner can be the publisher. Say a joint work is when a book or article has two or more authors. However, if a book is written primarily by one author, but another author contributes a specific chapter to the book and is given credit for that chapter, then this probably wouldn't be a joint work because the contributions aren't inseparable or interdependent. The U.S. Copyright Office considers joint copyright owners to have an equal right to register and enforce the copyright. Unless the joint owners make a written agreement to the contrary, each copyright owner has the right to commercially exploit the copyright, provided that the other copyright owners get an equal share of the proceeds between them.
If at the time of creation, the authors did not intend their works to be part of an inseparable whole, the fact that their works are later put together does not create a joint work. Rather, the result is considered a collective work. In this case, each author owns a copyright in only the material he or she added to the finished product. For example in the 1980s, Vladimir wrote a famous novel full of complex literary allusions. In 2018, his publisher issues a student edition of the work with detailed annotations. The student edition is a collective work. Vladimir owns the copyright in the novel, but the professor owns the annotations.
[Extracted with edits and revision from Copyright Ownership: Who Owns What?, article by stanford]
Q. X is a part-time employee of a company called ZMY Infrastructures. X prepares a blueprint design of a building which is very much liked by the managers of the company. However, X has other plans and wants to move to another company with this same design. Can the other company claim copyright over it?
Copyrights are generally owned by the people who create the work of expression.
Some exceptions:
If a work is created by an employee in the course of his or her employment, the employer owns the copyright. If the work is created by an independent contractor and the independent contractor signs a written agreement stating that the work shall be made for hire, the commissioning person or organisation owns the copyright only if the work is a part of a larger literary work, such as an article in a magazine or a poem or story in an anthology; part of a motion picture or other audiovisual work, such as a screenplay; a translation; a supplementary work such as an afterword, an introduction, chart, editorial note, bibliography; a compilation; an instructional text; a test or answer material for a test; or an atlas. Works that don't fall within one of these eight categories constitute works made for hire only if created by an employee within the scope of his or her employment.
If the creator has sold the entire copyright, the purchasing business or person becomes the copyright owner.
When two or more authors prepare a work with the intent to combine their contributions into inseparable or interdependent parts, the work is considered joint work and the authors are considered joint copyright owners. Authorship is retained but in some cases this copyright owner can be the publisher. Say a joint work is when a book or article has two or more authors. However, if a book is written primarily by one author, but another author contributes a specific chapter to the book and is given credit for that chapter, then this probably wouldn't be a joint work because the contributions aren't inseparable or interdependent. The U.S. Copyright Office considers joint copyright owners to have an equal right to register and enforce the copyright. Unless the joint owners make a written agreement to the contrary, each copyright owner has the right to commercially exploit the copyright, provided that the other copyright owners get an equal share of the proceeds between them.
If at the time of creation, the authors did not intend their works to be part of an inseparable whole, the fact that their works are later put together does not create a joint work. Rather, the result is considered a collective work. In this case, each author owns a copyright in only the material he or she added to the finished product. For example in the 1980s, Vladimir wrote a famous novel full of complex literary allusions. In 2018, his publisher issues a student edition of the work with detailed annotations. The student edition is a collective work. Vladimir owns the copyright in the novel, but the professor owns the annotations.
[Extracted with edits and revision from Copyright Ownership: Who Owns What?, article by stanford]
Directions: The question is based on the reasoning and arguments, or facts and principles set out in the passage. Some of these principles may not be true in the real or legal sense, yet you must conclusively assume that they are true for the purpose. Please answer the question on the basis of what is stated or implied in the passage. Do not rely on any principle of law other than the ones supplied to you, and do not assume any facts other than those supplied to you when answering the question. Please choose the option that most accurately and comprehensively answers the question.
Copyrights are generally owned by the people who create the work of expression.
Some exceptions:
If a work is created by an employee in the course of his or her employment, the employer owns the copyright. If the work is created by an independent contractor and the independent contractor signs a written agreement stating that the work shall be made for hire, the commissioning person or organisation owns the copyright only if the work is a part of a larger literary work, such as an article in a magazine or a poem or story in an anthology; part of a motion picture or other audiovisual work, such as a screenplay; a translation; a supplementary work such as an afterword, an introduction, chart, editorial note, bibliography; a compilation; an instructional text; a test or answer material for a test; or an atlas. Works that don't fall within one of these eight categories constitute works made for hire only if created by an employee within the scope of his or her employment.
If the creator has sold the entire copyright, the purchasing business or person becomes the copyright owner.
When two or more authors prepare a work with the intent to combine their contributions into inseparable or interdependent parts, the work is considered joint work and the authors are considered joint copyright owners. Authorship is retained but in some cases this copyright owner can be the publisher. Say a joint work is when a book or article has two or more authors. However, if a book is written primarily by one author, but another author contributes a specific chapter to the book and is given credit for that chapter, then this probably wouldn't be a joint work because the contributions aren't inseparable or interdependent. The U.S. Copyright Office considers joint copyright owners to have an equal right to register and enforce the copyright. Unless the joint owners make a written agreement to the contrary, each copyright owner has the right to commercially exploit the copyright, provided that the other copyright owners get an equal share of the proceeds between them.
If at the time of creation, the authors did not intend their works to be part of an inseparable whole, the fact that their works are later put together does not create a joint work. Rather, the result is considered a collective work. In this case, each author owns a copyright in only the material he or she added to the finished product. For example in the 1980s, Vladimir wrote a famous novel full of complex literary allusions. In 2018, his publisher issues a student edition of the work with detailed annotations. The student edition is a collective work. Vladimir owns the copyright in the novel, but the professor owns the annotations.
[Extracted with edits and revision from Copyright Ownership: Who Owns What?, article by stanford]
Q. X is an independent contractor. He orally asks Y to create a work for hire. The work will be part of the book which will be published by X. Who is the copyright owner of the work?
Copyrights are generally owned by the people who create the work of expression.
Some exceptions:
If a work is created by an employee in the course of his or her employment, the employer owns the copyright. If the work is created by an independent contractor and the independent contractor signs a written agreement stating that the work shall be made for hire, the commissioning person or organisation owns the copyright only if the work is a part of a larger literary work, such as an article in a magazine or a poem or story in an anthology; part of a motion picture or other audiovisual work, such as a screenplay; a translation; a supplementary work such as an afterword, an introduction, chart, editorial note, bibliography; a compilation; an instructional text; a test or answer material for a test; or an atlas. Works that don't fall within one of these eight categories constitute works made for hire only if created by an employee within the scope of his or her employment.
If the creator has sold the entire copyright, the purchasing business or person becomes the copyright owner.
When two or more authors prepare a work with the intent to combine their contributions into inseparable or interdependent parts, the work is considered joint work and the authors are considered joint copyright owners. Authorship is retained but in some cases this copyright owner can be the publisher. Say a joint work is when a book or article has two or more authors. However, if a book is written primarily by one author, but another author contributes a specific chapter to the book and is given credit for that chapter, then this probably wouldn't be a joint work because the contributions aren't inseparable or interdependent. The U.S. Copyright Office considers joint copyright owners to have an equal right to register and enforce the copyright. Unless the joint owners make a written agreement to the contrary, each copyright owner has the right to commercially exploit the copyright, provided that the other copyright owners get an equal share of the proceeds between them.
If at the time of creation, the authors did not intend their works to be part of an inseparable whole, the fact that their works are later put together does not create a joint work. Rather, the result is considered a collective work. In this case, each author owns a copyright in only the material he or she added to the finished product. For example in the 1980s, Vladimir wrote a famous novel full of complex literary allusions. In 2018, his publisher issues a student edition of the work with detailed annotations. The student edition is a collective work. Vladimir owns the copyright in the novel, but the professor owns the annotations.
[Extracted with edits and revision from Copyright Ownership: Who Owns What?, article by stanford]
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Directions: The question is based on the reasoning and arguments, or facts and principles set out in the passage. Some of these principles may not be true in the real or legal sense, yet you must conclusively assume that they are true for the purpose. Please answer the question on the basis of what is stated or implied in the passage. Do not rely on any principle of law other than the ones supplied to you, and do not assume any facts other than those supplied to you when answering the question. Please choose the option that most accurately and comprehensively answers the question.
Copyrights are generally owned by the people who create the work of expression.
Some exceptions:
If a work is created by an employee in the course of his or her employment, the employer owns the copyright. If the work is created by an independent contractor and the independent contractor signs a written agreement stating that the work shall be made for hire, the commissioning person or organisation owns the copyright only if the work is a part of a larger literary work, such as an article in a magazine or a poem or story in an anthology; part of a motion picture or other audiovisual work, such as a screenplay; a translation; a supplementary work such as an afterword, an introduction, chart, editorial note, bibliography; a compilation; an instructional text; a test or answer material for a test; or an atlas. Works that don't fall within one of these eight categories constitute works made for hire only if created by an employee within the scope of his or her employment.
If the creator has sold the entire copyright, the purchasing business or person becomes the copyright owner.
When two or more authors prepare a work with the intent to combine their contributions into inseparable or interdependent parts, the work is considered joint work and the authors are considered joint copyright owners. Authorship is retained but in some cases this copyright owner can be the publisher. Say a joint work is when a book or article has two or more authors. However, if a book is written primarily by one author, but another author contributes a specific chapter to the book and is given credit for that chapter, then this probably wouldn't be a joint work because the contributions aren't inseparable or interdependent. The U.S. Copyright Office considers joint copyright owners to have an equal right to register and enforce the copyright. Unless the joint owners make a written agreement to the contrary, each copyright owner has the right to commercially exploit the copyright, provided that the other copyright owners get an equal share of the proceeds between them.
If at the time of creation, the authors did not intend their works to be part of an inseparable whole, the fact that their works are later put together does not create a joint work. Rather, the result is considered a collective work. In this case, each author owns a copyright in only the material he or she added to the finished product. For example in the 1980s, Vladimir wrote a famous novel full of complex literary allusions. In 2018, his publisher issues a student edition of the work with detailed annotations. The student edition is a collective work. Vladimir owns the copyright in the novel, but the professor owns the annotations.
[Extracted with edits and revision from Copyright Ownership: Who Owns What?, article by stanford]
Q. According to the article, what is the main difference between an author and a copyright holder?
Copyrights are generally owned by the people who create the work of expression.
Some exceptions:
If a work is created by an employee in the course of his or her employment, the employer owns the copyright. If the work is created by an independent contractor and the independent contractor signs a written agreement stating that the work shall be made for hire, the commissioning person or organisation owns the copyright only if the work is a part of a larger literary work, such as an article in a magazine or a poem or story in an anthology; part of a motion picture or other audiovisual work, such as a screenplay; a translation; a supplementary work such as an afterword, an introduction, chart, editorial note, bibliography; a compilation; an instructional text; a test or answer material for a test; or an atlas. Works that don't fall within one of these eight categories constitute works made for hire only if created by an employee within the scope of his or her employment.
If the creator has sold the entire copyright, the purchasing business or person becomes the copyright owner.
When two or more authors prepare a work with the intent to combine their contributions into inseparable or interdependent parts, the work is considered joint work and the authors are considered joint copyright owners. Authorship is retained but in some cases this copyright owner can be the publisher. Say a joint work is when a book or article has two or more authors. However, if a book is written primarily by one author, but another author contributes a specific chapter to the book and is given credit for that chapter, then this probably wouldn't be a joint work because the contributions aren't inseparable or interdependent. The U.S. Copyright Office considers joint copyright owners to have an equal right to register and enforce the copyright. Unless the joint owners make a written agreement to the contrary, each copyright owner has the right to commercially exploit the copyright, provided that the other copyright owners get an equal share of the proceeds between them.
If at the time of creation, the authors did not intend their works to be part of an inseparable whole, the fact that their works are later put together does not create a joint work. Rather, the result is considered a collective work. In this case, each author owns a copyright in only the material he or she added to the finished product. For example in the 1980s, Vladimir wrote a famous novel full of complex literary allusions. In 2018, his publisher issues a student edition of the work with detailed annotations. The student edition is a collective work. Vladimir owns the copyright in the novel, but the professor owns the annotations.
[Extracted with edits and revision from Copyright Ownership: Who Owns What?, article by stanford]
Through which of the following amendments did the Parliament allow itself with unlimited powers of amendments?
Which of the following statements is/are incorrect?
Statement I: A domestic law can be used to justify the breach of an international one.
Statement II: In case of dispute between International law and domestic law, international law will prevail always.
Which of the following statements is/are incorrect?
Statement I: American Bar Association is the largest voluntary professional body in the world.
Statement II: American Bar Association was founded in the year 1878.
Ajay, after completing his 10+2 exams, wants to get admission in a National Law School. Which of the following entrance tests can he appear for?
'No one can pass a better title than what he himself has'. This is explained by which of the following maxims?
Which of the following judicial decisions provides for cases that cannot be referred to Alternative Dispute Resolution process?
Assertion (A): The complaint mechanism procedure with the National Human Rights Commission is easy and straight forward.
Reason (R): Any one aggrieved of human rights violation or their representatives can lodge a complaint with the National Human Rights Commission.
Who among the following is the ex-officio member of the State Bar Council?
Which of the following statements is/are incorrect?
Statement I - International laws regulate the private, social, commercial and other activities of the individuals.
Statement II - International law governs the conduct of the citizens of a state.
The qualifying exam for being an Advocate on Record (AOR) can be taken by an advocate who has been enrolled with a Bar Council for at least:
Which of the following commissions are statutory bodies?
- National Commission for Schedule class
- National Commission for Women
- National Commission for Minorities
- National Commission for Backward Classes
- National Human Rights Commission
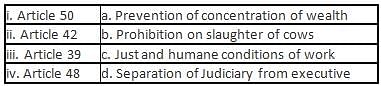
Match the following articles with their provisions.
Which of the following judges was impeached for misappropriation of funds?
Which Committee suggested to increase the retirement age of Supreme Court judges from 65 to 68 years?
Which of the following statements is/are correct?
Statement I: Under common law, legislature or executive has the power to create laws and rules.
Statement II: Common law system is followed in countries such as Germany, Russia, and Continental Europe.
Directions: The question is based on the reasoning and arguments, or facts and principles set out in the passage. Some of these principles may not be true in the real or legal sense, yet you must conclusively assume that they are true for the purpose. Please answer the question on the basis of what is stated or implied in the passage. Do not rely on any principle of law other than the ones supplied to you, and do not assume any facts other than those supplied to you when answering the question. Please choose the option that most accurately and comprehensively answers the question.
Copyrights are generally owned by the people who create the work of expression.
Some exceptions:
If a work is created by an employee in the course of his or her employment, the employer owns the copyright. If the work is created by an independent contractor and the independent contractor signs a written agreement stating that the work shall be made for hire, the commissioning person or organisation owns the copyright only if the work is a part of a larger literary work, such as an article in a magazine or a poem or story in an anthology; part of a motion picture or other audiovisual work, such as a screenplay; a translation; a supplementary work such as an afterword, an introduction, chart, editorial note, bibliography; a compilation; an instructional text; a test or answer material for a test; or an atlas. Works that don't fall within one of these eight categories constitute works made for hire only if created by an employee within the scope of his or her employment.
If the creator has sold the entire copyright, the purchasing business or person becomes the copyright owner.
When two or more authors prepare a work with the intent to combine their contributions into inseparable or interdependent parts, the work is considered joint work and the authors are considered joint copyright owners. Authorship is retained but in some cases this copyright owner can be the publisher. Say a joint work is when a book or article has two or more authors. However, if a book is written primarily by one author, but another author contributes a specific chapter to the book and is given credit for that chapter, then this probably wouldn't be a joint work because the contributions aren't inseparable or interdependent. The U.S. Copyright Office considers joint copyright owners to have an equal right to register and enforce the copyright. Unless the joint owners make a written agreement to the contrary, each copyright owner has the right to commercially exploit the copyright, provided that the other copyright owners get an equal share of the proceeds between them.
If at the time of creation, the authors did not intend their works to be part of an inseparable whole, the fact that their works are later put together does not create a joint work. Rather, the result is considered a collective work. In this case, each author owns a copyright in only the material he or she added to the finished product. For example in the 1980s, Vladimir wrote a famous novel full of complex literary allusions. In 2018, his publisher issues a student edition of the work with detailed annotations. The student edition is a collective work. Vladimir owns the copyright in the novel, but the professor owns the annotations.
[Extracted with edits and revision from Copyright Ownership: Who Owns What?, article by stanford]
Q. Mint writes a short story which is based on his real-life experience. Yusz also writes a short story based on his real-life experience. One day, Mint shares his story to Yusz. Yusz is pleased to read the short story of Mint and now wants to publish both the stories in one book. Can both of them be called joint copyright holders?
Directions: The question is based on the reasoning and arguments, or facts and principles set out in the passage. Some of these principles may not be true in the real or legal sense, yet you must conclusively assume that they are true for the purpose. Please answer the question on the basis of what is stated or implied in the passage. Do not rely on any principle of law other than the ones supplied to you, and do not assume any facts other than those supplied to you when answering the question. Please choose the option that most accurately and comprehensively answers the question.
Copyrights are generally owned by the people who create the work of expression.
Some exceptions:
If a work is created by an employee in the course of his or her employment, the employer owns the copyright. If the work is created by an independent contractor and the independent contractor signs a written agreement stating that the work shall be made for hire, the commissioning person or organisation owns the copyright only if the work is a part of a larger literary work, such as an article in a magazine or a poem or story in an anthology; part of a motion picture or other audiovisual work, such as a screenplay; a translation; a supplementary work such as an afterword, an introduction, chart, editorial note, bibliography; a compilation; an instructional text; a test or answer material for a test; or an atlas. Works that don't fall within one of these eight categories constitute works made for hire only if created by an employee within the scope of his or her employment.
If the creator has sold the entire copyright, the purchasing business or person becomes the copyright owner.
When two or more authors prepare a work with the intent to combine their contributions into inseparable or interdependent parts, the work is considered joint work and the authors are considered joint copyright owners. Authorship is retained but in some cases this copyright owner can be the publisher. Say a joint work is when a book or article has two or more authors. However, if a book is written primarily by one author, but another author contributes a specific chapter to the book and is given credit for that chapter, then this probably wouldn't be a joint work because the contributions aren't inseparable or interdependent. The U.S. Copyright Office considers joint copyright owners to have an equal right to register and enforce the copyright. Unless the joint owners make a written agreement to the contrary, each copyright owner has the right to commercially exploit the copyright, provided that the other copyright owners get an equal share of the proceeds between them.
If at the time of creation, the authors did not intend their works to be part of an inseparable whole, the fact that their works are later put together does not create a joint work. Rather, the result is considered a collective work. In this case, each author owns a copyright in only the material he or she added to the finished product. For example in the 1980s, Vladimir wrote a famous novel full of complex literary allusions. In 2018, his publisher issues a student edition of the work with detailed annotations. The student edition is a collective work. Vladimir owns the copyright in the novel, but the professor owns the annotations.
[Extracted with edits and revision from Copyright Ownership: Who Owns What?, article by stanford]
Q. X and Y are joint copyright holders of a work. X wants to commercially exploit the work and hence hands over the work to a publisher. The publisher agrees to publish only if the profit is shared in the ratio 2 : 1 : 1 between the publisher, X and Y. Is this agreement valid?
Consider the following statements regarding the Preamble of the Indian Constitution:
a. The Preamble of the Indian Constitution is a part of the Constitution but it is not enforceable by courts.
b. The Preamble cannot be amended like other provisions of the Constitution.
Which of the given statements is/are correct?
Who among the following was instrumental in setting up of the first National Law School in Bangalore?
Assertion (A): The major advantage of an ombudsman is that he/she avoids the conflicts of interest inherent in self-policing.
Reason (R): Duties of an ombudsman are to investigate complaints and attempt to resolve them, usually through recommendations (binding or not) or mediation. (ADR A/R)
Directions: Choose the correct meaning of the given term.
Donatio mortis causa
Under criminal law, illegal gambling would fall under which category of crime?
Directions: Choose the correct meaning of the given term.
Ex turpi causa non oritur actio
Which of the following is/are not the function(s) of the State authority?
Which form of Alternative Dispute Resolution is most suitable for resolving family disputes?

















