Test: Roots, Stems and Leaves - 3 - ACT MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Roots, Stems and Leaves - 3
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Roots originate from the base of the stem and constitute the fibrous root system in which of the following plants?
Actinomorphic nature of flower is represented by which of the following symbols?
Which of the following conditions is correct with respect to family Solanaceae?
Arrangement of leaves on a stem branch is: [MPPMT–1996]
Which of the following statements is/are false about the leaf?
a. The leaf develops at the node and bears a bud in its axil.
b. The leaf is the most important vegetative organ for photosynthesis.
c. Pulvinus provides rigidity to the leaf blade and acts as a channel for transporting water, minerals and food materials.
Which among the following is incorrect about importance of root system?
Which among the following is not correct about different modifications of stem?
Which among the following is incorrect about bulb?
Which among the following is incorrect about different parts of the leaf?
Arrangement of sepals & petals with respect of other is:
Consider the following statement and answer the question that follows.
Various groups of floral parts develop one after another from the receptacle.
Which of the following parts of a plant are the first to form?
The technical term used for the androecium in the flower of pea is
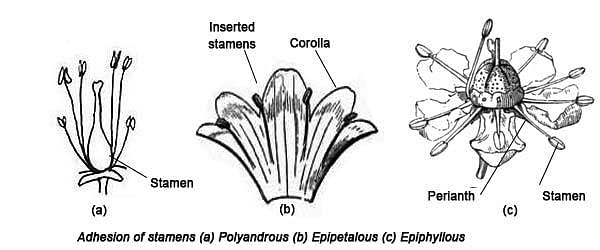
If the filaments are fused in a single group the condition is:
A typical flower with superior ovary and other floral parts inferior is:
The tissue which attaches the ovules inside the ovary is:
Arrangement of ovules in the cavity of ovary is: