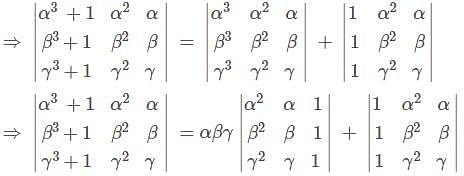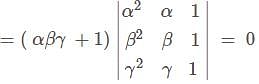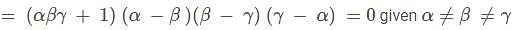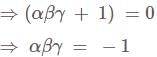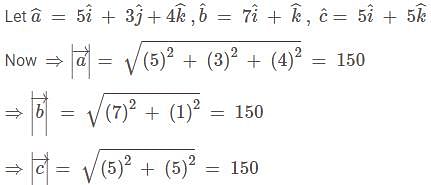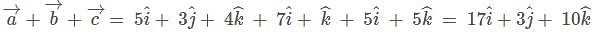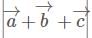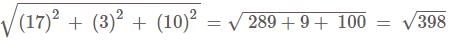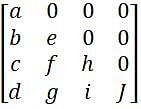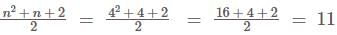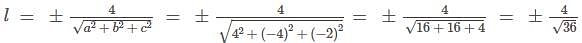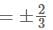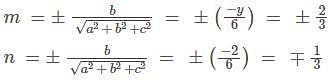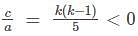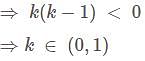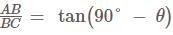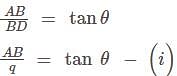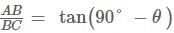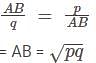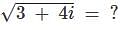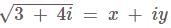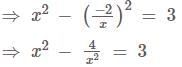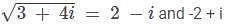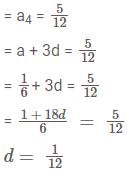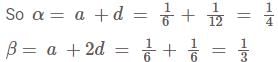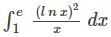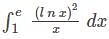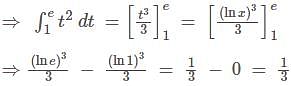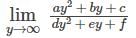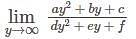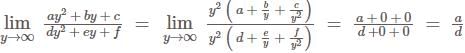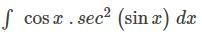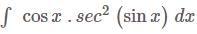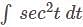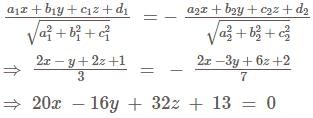DSSSB TGT Mathematics Mock Test - 2 - DSSSB TGT/PGT/PRT MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - DSSSB TGT Mathematics Mock Test - 2
Which point is not included in the professional skills of a teacher?
Which is not the characteristics of a successful teacher?
Which of the following is more helpful in the development of alertness ?
'Unknown to known' is advanced in whicb method
If 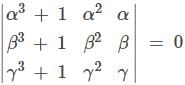 and α, β and γ are all different, then αβγ = ?
and α, β and γ are all different, then αβγ = ?
How many words ending and beginning with consonant can be formed by using letters of “ERUASION”.
If log x , log y and log z are in A.P. then x,y and z are in :
If in a triangle, XYZ (sinx + sinY + sinZ)(sinx + sinY - sinZ) = 3sinx sinY, then anglez is equal to
The position vectors of the vertices of a triangle are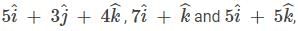 then the distance between the circumcentre and the orthocentre of the triangle is
then the distance between the circumcentre and the orthocentre of the triangle is
Direction: Read the following information and answer the two questions that follow:
If x cos 2 α + y sin 2α = z has “tanA” and “tanB” as its solution then find
tan A + tan B=?
What are the maximum number of distinct entries in lower triangular matrix of order 4.
Find the direction cosines of the line joining the points A(7, -8, -2) and B(3, -4, 0)
The least value of m for which function f(t) = t2 + mt + 1 is a increasing function in the interval 1 ≤ t ≤ 2
The set of values of k for which the roots of the equation 5x2 + 7x + k(k - 1) are of opposite sign is:
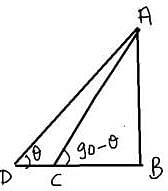
The angles of elevation of the peak of a hill from two points D and C at a distance p and q from the foot of the hill are complementary. The height of the hill is.
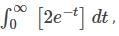 where [.] denotes the greatest integer function, is equal to
where [.] denotes the greatest integer function, is equal to
If equation lx2 + mx +n = 0 (0 < I < m < n) has non-real complex roots is z1and z2, then
The equation of plane bisecting the acute angle between the planes 2x - y + 2z + 1 = 0 and 2x - 3y + 6z + 2 = 0