Test: State, Economy and Development - UGC NET MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: State, Economy and Development
Which of the following pairs of list and contents is/are correctly matched?
(a) Rajni Kothari: Caste in Indian Politics
(b) Jai Prakash Narayan: Caste in India: Their mechanism Genesis and development
(c) M. N. Shriniwas: Caste in modern India and other Essays
Select the correct answer using the code given below :
The period 1990 and beyond was federally important to Indian politics for which of the following reasons?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Who among the following has called the emergency provisions of the constitution of India as the 'Union's Long Arm'?
The Panchayati Raj system in India has been discussed in which among the following committees?
1. Ashok Mehta Committee
2. JVP Committee
3. Balwant Rai Mehta Committee
4. Gadgil Committee
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
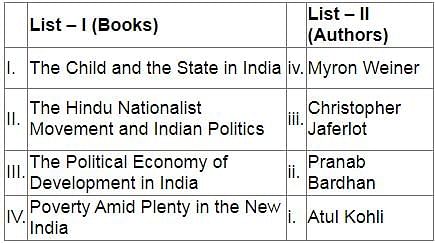
Match List-I and List-II and select the correct answer from the codes given below

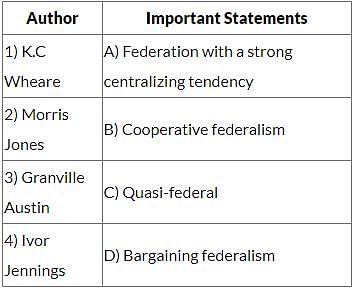
Match List 1 with List 2 and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:
Which of the following statements with regard to the impact of planning in India is correct:
Which of the following scholar/ scholars used terminology 'Federal Market Economy' in context to Indian Democracy?
Who is the author of the book Democracy and Development in India from Socialism to Pro-Business?
Lohia opined:
A. Freedom and bread are inseparable
B. The removal of inequality from human society was one of the seven revolutions
C. If socialism is to be defined in two words then they are equality and prosperity
D. The desire for equality in the modern world has become the desire for being similar and not equal
Choose the correct answer from the options given below: