Test: Digestive Glands (Old NCERT) - Grade 11 MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Digestive Glands (Old NCERT)
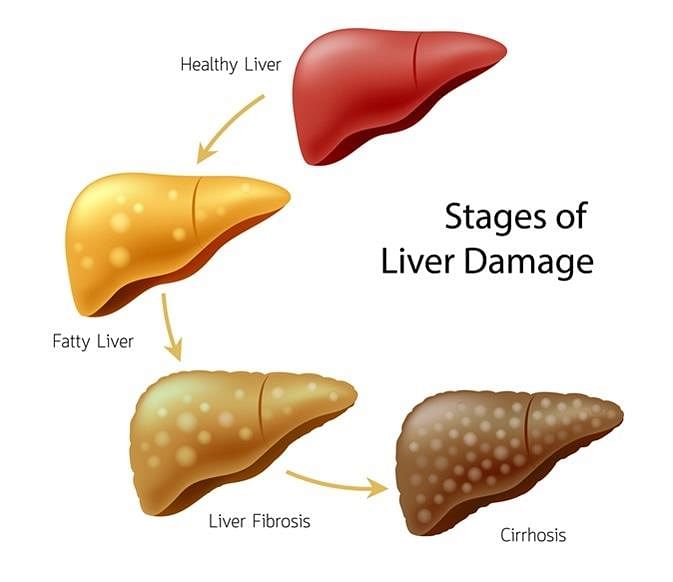
A person who is addicted to alcohol gets his liver destroyed because:
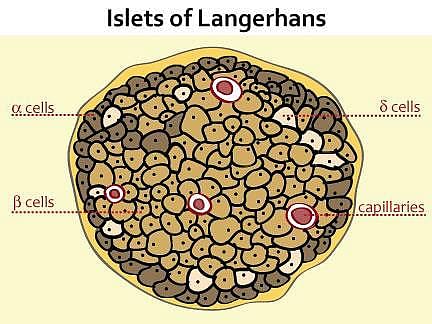
In pancreas, pancreatic juice and hormones are secreted by:
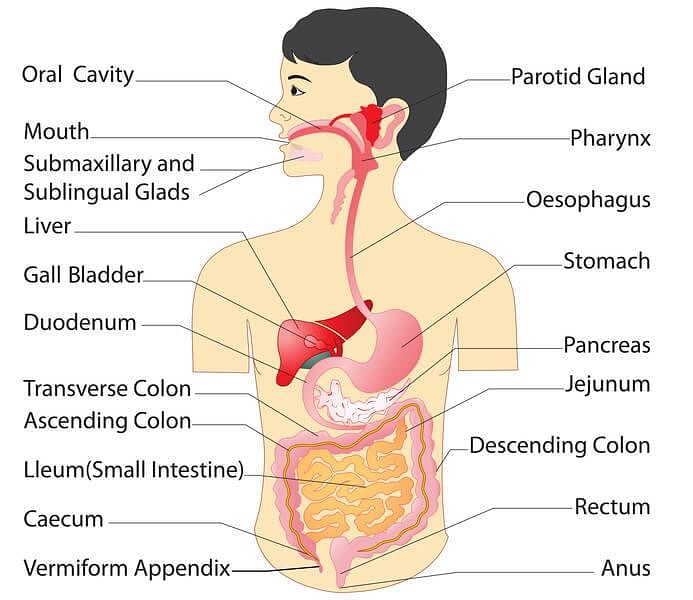
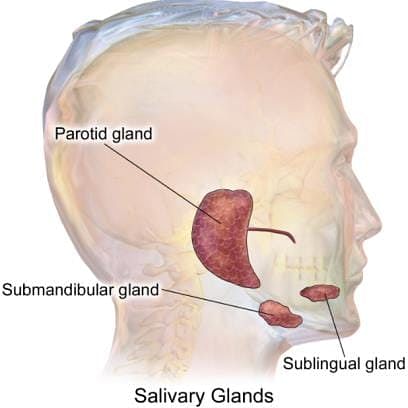
Name the Glands associated with the Human Digestive System.
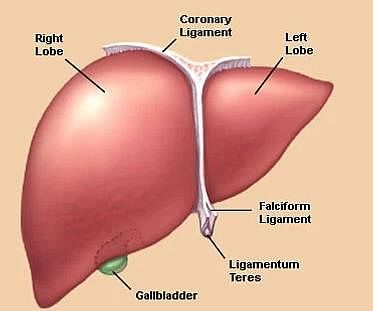
Which of the following is not a function of the liver?
Insulin is secreted by which pancreatic cells? [RPMT-89]
Which substance of saliva destroys the harmful bacteria? [RPMT-91]
Which one of the following is not a constituent of saliva?
Which one of the following is not a function of the liver?
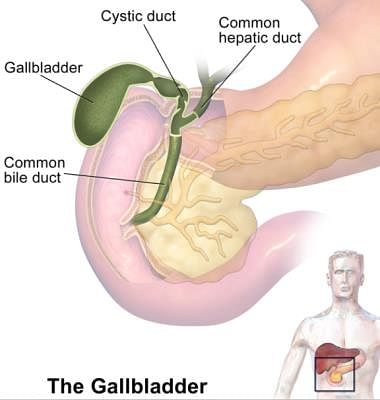
______ stores the liver’s digestive juice until it is needed by the intestines.
The glucose is converted into glycogen in liver and stored in:
The largest salivary gland present in human is:
A gland not associated with the alimentary canal is ______.