Test: Physical Spectroscopy - 2 - Chemistry MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Physical Spectroscopy - 2
Which is the correct order of increasing wave number of the stretching vibrations of (1) C-H (alkane), (2) O-H (alcohol), (3) C=O (ketone), and (4) C≡C (alkyne)?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
How many signals does the aldehyde (CH3)3CCH2CHO have in 1H NMR and 13C NMR spectra?
Which of hydrogens a-d in the following molecule gives a triplet signal in a normal 1H NMR spectrum?
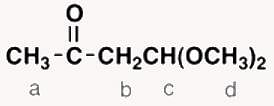
Which hydrogen of 1-chloropent-2-ene shows the largest chemical (downfield) shift in its NMR spectrum?
Which carbon of (a)-(d) of hex-3-en-2-one shows the largest (most downfield) chemical shift in the NMR spectrum?
Which of the following statements regarding IR spectroscopy is wrong?
Which of the following statements regarding NMR spectroscopy is wrong?
Which of the following statements regarding mass spectrometry is wrong?
Absorption of radiation in the UV range attributable to n→π* electronic transitions is characteristic of which of the following types of compounds?
Which is the correct order of increasing wave number of the stretching vibrations of (1) C-H (alkane), (2) C-H (alkene), (3) C-H (alkyne), and (4) C-H (arene)?
How many signals does the unsaturated ketone
(CH3)2CHCH2C(O)CH=CH2 have in 1H NMR and 13C NMR spectra?
Which of the following statements in the context of 1H NMR spectroscopy is true?
Which carbon of (a)-(d) of hex-3-en-2-one has the smallest (most upfield) chemical shift in the NMR spectrum?
Which of (a)-(d) indicates the multiplicities for hydrogens on C1, C3, and C4 of butanone attributable to spin-spin coupling in its 1H NMR spectrum.
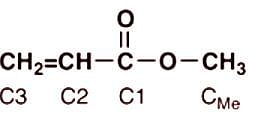
Which of (a)-(d) indicates the correct order of carbon chemical shifts of the four carbons of the following compound.
Which of the following statements regarding electron-impact mass spectrometry is true?
Which of the following statements regarding mass spectrometry is false?

















