Thermodynamics MCQ - 4 (Advanced) - JEE MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Thermodynamics MCQ - 4 (Advanced)
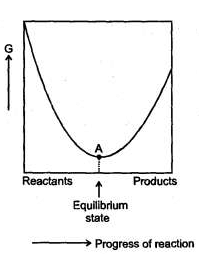
For a reversible reaction at constant temperature and at constant pressure the equilibrium composition of reaction mixture corresponds to the lowest point on Gibbis energy Vs progress of reaction diagrams as shown. At equilibrium Gibbs energy of reaction is equal to Zero.
Q.
The value of log10 keg is equal to Kg is the equilibrium constant]
For a reversible reaction at constant temperature and at constant pressure the equilibrium composition of reaction mixture corresponds to the lowest point on Gibbis energy Vs progress of reaction diagrams as shown. At equilibrium Gibbs energy of reaction is equal to Zero.

Q.
Which diagram represents the large value of equilibrium constant for the reversible reaction
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
For a reversible reaction at constant temperature and at constant pressure the equilibrium composition of reaction mixture corresponds to the lowest point on Gibbis energy Vs progress of reaction diagrams as shown. At equilibrium Gibbs energy of reaction is equal to Zero.

For a reaction M2 O(s)→ 2M(S) →2M(s) + 1/2O2(g) ΔH = 30 KJ/mol and ΔS = 0.07 KJ/mol /K at latm. The reaction would not be spontaneous at temperatures
The contributions of both heat (enthalpy) and randomness (entropy) shall be considered to the overall spontaneity of a process. When deciding about the spontaneity of a chemical reaction or other process, we define a quantity called the Gibb's energy change (ΔG).
ΔG = ΔH – TΔS
where, ΔH = Enthalpy change ; ΔS = Entropy change;
T = Temperature in kelvin.
If ΔG < 0, Process is spontaneous ; ΔG = 0, Process is at equilibrium, AG > 0, Process is non-spontaneous.
Q.
For the change
H20 (s, 273 K, 2 atm) → H20 (l, 273K, 2 atom),
choose the correct option.
The contributions of both heat (enthalpy) and randomness (entropy) shall be considered to the overall spontaneity of a process. When deciding about the spontaneity of a chemical reaction or other process, we define a quantity called the Gibb's energy change (ΔG).
ΔG = ΔH – TΔS
where, ΔH = Enthalpy change ; ΔS = Entropy change;
T = Temperature in kelvin.
If ΔG < 0, Process is spontaneous ; ΔG = 0, Process is at equilibrium, AG > 0, Process is non-spontaneous.
5 mol of liquid water is compressed from 1 bar to 10 bar at constant temperature. Change in Gibb's energy (ΔG) in Joule is t [Density of water = 1000 kg/m3].
The contributions of both heat (enthalpy) and randomness (entropy) shall be considered to the overall spontaneity of a process. When deciding about the spontaneity of a chemical reaction or other process, we define a quantity called the Gibb's energy change (ΔG).
ΔG = ΔH – TΔS
where, ΔH = Enthalpy change ; ΔS = Entropy change;
T = Temperature in kelvin.
If ΔG < 0, Process is spontaneous ; ΔG = 0, Process is at equilibrium, AG > 0, Process is non-spontaneous.
Q.
Quick lime, Ca0 is produced by heating limestone, CaC03 to drive off C02 gas.
CaC03 (s) → CaO (s) + C02 (g), (ΔH°) = 180 KJ, ΔS° = 150 J/K.
Assuming that variation of enthalpy change and entropy change with temperature to be negligible, choose the correct option :
The feasibility of a chemical reaction can be explained based on H, S and G, so answer the following :

















