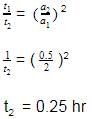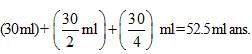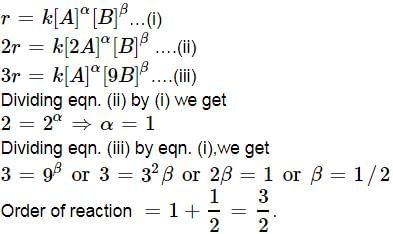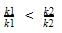P. Bahadur Test: Chemical Kinetics - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - P. Bahadur Test: Chemical Kinetics
The time for half life period of a certain reaction A → Products is 1 h. When the initial concentration of the reactant 'A' is 2.0 mol L–1, how much time does it take for its concentration to come from 0.50 to 0.25 mol L–1, if it is a zero order reaction?
N205 → 2NO2 + O2
When N205 decompose, its t12 does not change with its changing pressure during the reaction, so which one is the correct representation for "pressure of 2NO2" vs lime° during the reaction when initial N205 is equals to Po
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
In a hypothetical reaction
A(aq)  2B(aq) + C(aq) (Ist order decomposition)
2B(aq) + C(aq) (Ist order decomposition)
'A' is optically active (dextro-rototory) while 'B' and 'C' are optically inactive but 'B' takes part in a titration reaction (fast reaction) with H202. Hence the progress of reaction can be monitored by measuring rotation of plane of plane polarised light or by measuring volume of H202 consumed in titration.
In an experiment the optical rotation was found to be 0 = 30° at t = 20 min and 8 =15° at t= 50 min. from start of the reaction. If the progress would have been monitored by titration method, volume of H202 consumed at t = 30 min. (from start) is 30 ml then volume of H202 consumed at t = 90 min will be:
 2B(aq) + C(aq) (Ist order decomposition)
2B(aq) + C(aq) (Ist order decomposition)The elementary reaction A + B → products has k = 2 x 10-5 M-1 S-1 at a temperature of 27°C. Several experimental runs are carried out using stoichiometric proportion. The reaction has a temperature coefficient value of 2.0. At what temperature should the reaction be carried out if inspite of halving the concentrations,the rate of reaction is desired to be 50% higher than a previous run.
At a certain temperature, the first order rate constant k1 is found to be smaller than the second order rate constant k2. If the energy of activation E1 of the first order reaction is greater than energy of activation E2 of the second order reaction, then with increase in temperature.
For the system
A2(g) + B2(g) 2AB(g), AH = – 80 KJ/ mole
If the activation energy for the forward step is 100 kcal /mole. What is the ratio of temperature at which the forward and backward reaction shows the same % change of rate constant per degree rise of temperature ? (1 cal = 4.2 J)
All reactions are of Ist order
At time t = ti (ti > 0)
Therefore at
time t = t2 (where t2 > ti)
which of the following is correct.
In the formation of HBr from H2 & Br2 , following mechanism is observed.
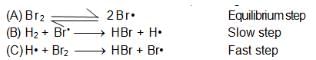
Calculate the rate of reaction, it concentration of hydrogen is twice that of bromine and the rate constant is equal to one rutherford. If conc. of bromine is 1 M.
A graph between log t112 and log a (abscissa) a being the initial concentration of A in the reaction For reaction A →4 Product, is the rate law is
The reaction A (g) + B (g)  C (g) + D (g) is elementry 2nd order reaction. When started with equimolar amounts of A and B, at equilibrium, it is found that the concentration of A is twice that of C. Specific rate for forward reaction is 2 x 10-3 mol-1 Lsec-1. The specific rate constant for backward reaction is :
C (g) + D (g) is elementry 2nd order reaction. When started with equimolar amounts of A and B, at equilibrium, it is found that the concentration of A is twice that of C. Specific rate for forward reaction is 2 x 10-3 mol-1 Lsec-1. The specific rate constant for backward reaction is :
For the reaction R – X + OH- ROH + X- The Rate is given of Rate = 5.0x 10-5[R – X [OH-] + 0.20x 10-5[R – X] what percentage R – X Reaction by SN2 mechanism when [OH-–] = 1.0x 10-2 M
For a 1st order reaction (gaseous) (cont. V, T)
a A → 4 (b 1) B + 1 C
(with b > a) the pressure of the system rose by in a time of 10 min. The half life of the reaction is therefore.
For a certain reaction the variation of the rate constant with temperature is given by the equation
The value of tile temperature coefficient of the reaction is
For a reaction A + B → C + D if the concentration of A is doubled without altering the concentration of B, the rate gets doubled. If the concentration of B is increased by nine times without altering the concentration of A, the rate gets tripled. The order of the reaction is
A reaction takes place in three steps ; the rate constants are Br k2 and k3.The overall rate constant If energies of activation are 40 , 30 and 20 kJ, the overall energy of activation is (assumming 'A' to be constant for all )
The inversion of cane sugar proceeds with half life of 600 minute at pH = 5 for any concentration of sugar, However at pH = 6, the half life changes to 60 minute, The rate law expression for sugar inversion can be written as
Some graph are sketch for the reaction A→B (assuming different orders).Where 'α' represent the degree of dissociation.
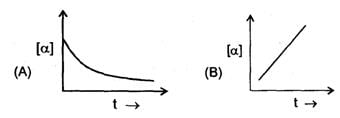
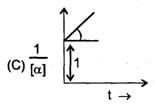
The order of reaction is respectively.
Compounds A and B react with a common reagent with first order kinetics in both cases. If 99% of A must react before 1% of B has reacted. What is the minimum ratio for their respective rate constants?
The activity per ml of a solution of radioactive substance is x. How much water be added to 200 ml of this solution so that the acitivity falls to x/20 per ml after 4 half-lives ?
A hypothetical reaction :
A2 + B2 → 2AB Follows mechanism as given below :

The order of overall reaction is
For the decomposition of H202(aq) it was found that Vo2 (t =15 min.) was 100 mL (at 0°C and 1 atm) while Vo2(maximum) was 200 mL (at 0°C and 2 atm). If the same reaction had been followed by the titration method and if (t = 0) had been 40 mL, what would
(t = 15 min) have been ?
The high temperature (z, 1200K) decomposition of CH3COOH(g) occurs as follows as per simultaneous 1St order reactions.
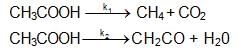
What would be the % of CH4 by mole in the product mixture (excluding CH3COOH)?
For the system
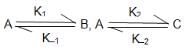
which was started with only A the equilibrium concentration [A]eq is correctly related to [B]eq and [C]eq. as:
A certain reaction A -3 B follows the given concentration (Molarity)-time graph. Which of the following statement is true?
The activation energies of two reactions are Ea and Ea’ with Ea > Ea’ If temperature of the reacting systems is increased from T1 to T2, predict which of the following alternatives
A simple mechanism for enzyme-catalyzed reaction is given by the following of equations
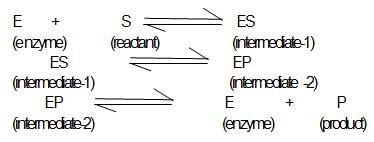
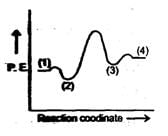
This is known as the Michaleis-mechanism. The potential energy diagram is shown in the figure. Which of the following sets of identifications is correct ? (Assume that the temperature and pressure are constant).

Statement-1 : If the activation energy of reaction is zero temperature will have no effect on the rate constant.
Statement-2 : Lower the activation energy fasten is the reaction.
Statement-1 : If the order of reaction is zero than degree of dissociation will be independent upon initial concentration.
Statement-2 : The degree of dissociation of Zero order reaction is given by 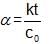
Statement-1 : For a reaction A(g) → B(g)
— re = 2.5 PA at 400K
— re = 2.5 PA at 600K
activation energy is 4135 J/mol.
Statement-2 : Since for any reaction, values of rate constant at two different temp is same therefore activation energy of the reaction is zero.
Statement-1 : For A+ 2B → C (rate = K [A]1[B]°), the half life time of reaction is only defined when conch of A and B are in stoichometric ratio
Statement-2 : For above given order half life of reaction is directly proportional to conch of A and not to conch of B due to its zero order.