CTET & State TET Exam > CTET & State TET Tests > Science (Animal Kingdom) - CTET & State TET MCQ
Science (Animal Kingdom) - CTET & State TET MCQ
Test Description
10 Questions MCQ Test - Science (Animal Kingdom)
Science (Animal Kingdom) for CTET & State TET 2024 is part of CTET & State TET preparation. The Science (Animal Kingdom) questions and answers have been prepared
according to the CTET & State TET exam syllabus.The Science (Animal Kingdom) MCQs are made for CTET & State TET 2024 Exam.
Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for Science (Animal Kingdom) below.
Solutions of Science (Animal Kingdom) questions in English are available as part of our course for CTET & State TET & Science (Animal Kingdom) solutions in
Hindi for CTET & State TET course.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for CTET & State TET Exam by signing up for free. Attempt Science (Animal Kingdom) | 10 questions in 10 minutes | Mock test for CTET & State TET preparation | Free important questions MCQ to study for CTET & State TET Exam | Download free PDF with solutions
Science (Animal Kingdom) - Question 1
Which of the following diseases is known as cattle plague?
Detailed Solution for Science (Animal Kingdom) - Question 1
Science (Animal Kingdom) - Question 2
Read the statements and choose the correct option:
Assertion (A): FMD outbreaks are usually controlled by locking and restricting the movement of affected animals, and cleansing and disinfecting equipment and vehicles used.
Reasoning (R): FMD(Food and mouth) is caused by an Aphthovirus of the family Picornaviridae
Detailed Solution for Science (Animal Kingdom) - Question 2
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Science (Animal Kingdom) - Question 3
Which of the following is used for control and prevention of the spread of animal diseases?
Detailed Solution for Science (Animal Kingdom) - Question 3
Detailed Solution for Science (Animal Kingdom) - Question 4
Detailed Solution for Science (Animal Kingdom) - Question 5
Detailed Solution for Science (Animal Kingdom) - Question 6
Science (Animal Kingdom) - Question 7
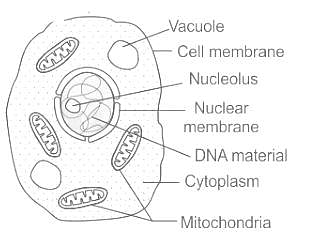
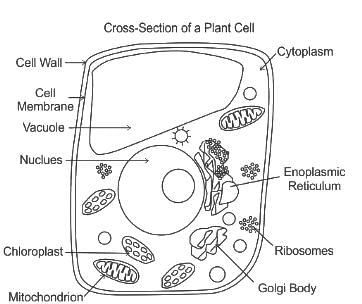
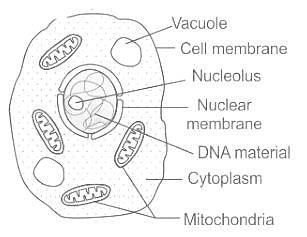
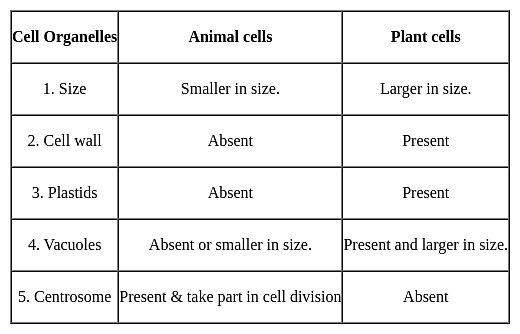
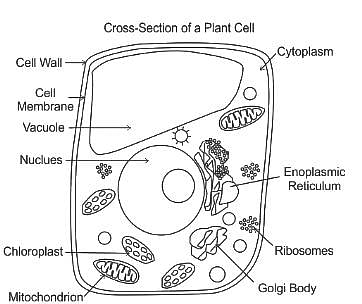
Cell wall is absent in which one of the following organisms?
Detailed Solution for Science (Animal Kingdom) - Question 7
Detailed Solution for Science (Animal Kingdom) - Question 8
Science (Animal Kingdom) - Question 9
How does a eukaryotic cell wall differ from that of a prokaryote? It is due to the presence of
Detailed Solution for Science (Animal Kingdom) - Question 9
Science (Animal Kingdom) - Question 10
Which of the following represents a set of cell organelles found in animal cell?
Detailed Solution for Science (Animal Kingdom) - Question 10
Information about Science (Animal Kingdom) Page
In this test you can find the Exam questions for Science (Animal Kingdom) solved & explained in the simplest way possible.
Besides giving Questions and answers for Science (Animal Kingdom), EduRev gives you an ample number of Online tests for practice
Download as PDF