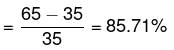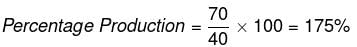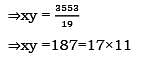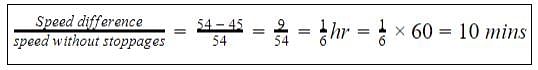APPSC (Arunachal Pradesh) Prelims Paper 2 Mock Test- 1 - APPSC (Arunachal Pradesh) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - APPSC (Arunachal Pradesh) Prelims Paper 2 Mock Test- 1
Study the following graph carefully to answer the questions given below it.
Production of Wheat (in Lakh tonnes) by three different countries America, Britain & Canada over the years
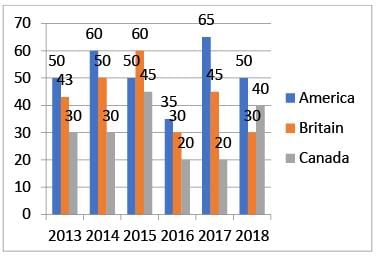
What is the difference (in tonnes) between the production of Canada in 2013 and that of America in 2016?
Production of Wheat (in Lakh tonnes) by three different countries America, Britain & Canada over the years

Study the following graph carefully to answer the questions given below it.
Production of Wheat (in Lakh tonnes) by three different countries America, Britain & Canada over the years

What is the percentage increase in production of America from 2016 to 2017?
Production of Wheat (in Lakh tonnes) by three different countries America, Britain & Canada over the years

Study the following graph carefully to answer the questions given below it.
Production of Wheat (in Lakh tonnes) by three different countries America, Britain & Canada over the years

For which of the following years the percentage of rise/fall in production from the previous year is the maximum for Britain?
Production of Wheat (in Lakh tonnes) by three different countries America, Britain & Canada over the years

Study the following graph carefully to answer the questions given below it.
Production of Wheat (in Lakh tonnes) by three different countries America, Britain & Canada over the years

The total production of company C in 2014 and 2018 is what percentage of the total production of company C in 2016 and 2017?
Study the following graph carefully to answer the questions given below it.
Production of Wheat (in Lakh tonnes) by three different countries America, Britain & Canada over the years

What is the difference (in Lakh tonnes) between the average production per year of the company with highest average production and that of the company with the lowest average production?
Highways are a critically important infrastructure for an emerging nation. And the design of appropriate contracts is the critical instrument for meeting the challenge of highways. What are these challenges? To put it in one sentence, the objective or the challenge is to maximise the difference between:
- The additional welfare that our citizens get from having more and better roads and,
- The present value of the cost of building those roads.
The broad principles above translate into these following general rules.
- We have to have a cut-off rule to decide which project is worthwhile and which are not.
- Between two identical roads if one can be done at lower cost, we should choose the one with the lower cost, subject to that being viable in the sense of (1), above.
- All costs do not take the form of brick and mortar. A build-up of fiscal deficit is also a form of cost. This may be difficult to reduce to the equivalent of brick and mortar cost but must not be omitted for that reason.
Some of the problems can be overcome if projects are awarded on the basis of a transparent and hands-off auction system. The heart of an efficient, cost effective and transparent system of PPP partnership whereby the government gives out the task of developing new highways to the private sector is the system of auction. Auction work best when the product is being sold lock, stock and barrel to a bidder. Hence, system such as BOT (toll) and annuitized BOT (toll) are better suited to being given out through competitive auction than the BOT (annuity). In the case of BOT (toll) and annuitized BOT the developer basically gets to own the road for the next 20 years. Hence, this comes close to a lock, stock and barrel sale.
Which of the following is suggested by the passage to overcome some of the problems associated with highway projects?
The broad principles which determine the validity/ suitability of a Highway/ road is to determine the difference between;
A possible theory of ocean formation is that the sinking plate cools the neighbouring mantle and produces convection currents that move the plates. This last theory is attractive because it gives some hope of explaining the enclosed seas, such as the Sea of Japan. These seas have a typical oceanic floor, except that the floor is overlaid by several kilometres of sediment. Their floors have probably been sinking for long periods. It seems possible that a sinking current of cooled mantle material on the upper side of the plate might be the cause of such deep basins. The enclosed seas are an important feature of the Earth’s surface, and seriously require explanation because, in addition to the enclosed seas that are developing at present behind island arcs, there are a number of older ones of possibly similar origin, such as the Gulf of Mexico, the Black Sea, and perhaps the North Sea.
According to the passage, the floor of the Black Sea can best be compared to a
The Bombay High Court stumped India’s most powerful sporting body, BCCI, by ordering it to move the cash cow IPL out of the drought-stricken Maharashtra. The court orders struck a chord among many, including die-hard cricket fans. The stark contrast between parched lands and dry throats of rural and semi-urban Maharashtra and the manufactured euphoria around water-guzzling cricket pitches did shake people’s conscience. The arguments in the court captured the latent and at times, simmering unease in the public mind over the degeneration of cricket from a sport to a money-spinner and worse.
Moreover, cricket, another colonial gift, had become the de facto national sport, crushing hockey and all other sports under its pitch rollers. On top of it, the mighty cricket board, perceived to be a hub of myriad commercial and political vested interests, became a law unto itself.
Q. What does the term ‘cash cow’ mean in the passage?
The Bombay High Court stumped India’s most powerful sporting body, BCCI, by ordering it to move the cash cow IPL out of the drought-stricken Maharashtra. The court orders struck a chord among many, including die-hard cricket fans. The stark contrast between parched lands and dry throats of rural and semi-urban Maharashtra and the manufactured euphoria around water-guzzling cricket pitches did shake people’s conscience. The arguments in the court captured the latent and at times, simmering unease in the public mind over the degeneration of cricket from a sport to a money-spinner and worse.
Moreover, cricket, another colonial gift, had become the de facto national sport, crushing hockey and all other sports under its pitch rollers. On top of it, the mighty cricket board, perceived to be a hub of myriad commercial and political vested interests, became a law unto itself.
Q. The Bombay High Court mainly ordered not to conduct the IPL matches in Maharashtra because of:
The Bombay High Court stumped India’s most powerful sporting body, BCCI, by ordering it to move the cash cow IPL out of the drought-stricken Maharashtra. The court orders struck a chord among many, including die-hard cricket fans. The stark contrast between parched lands and dry throats of rural and semi-urban Maharashtra and the manufactured euphoria around water-guzzling cricket pitches did shake people’s conscience. The arguments in the court captured the latent and at times, simmering unease in the public mind over the degeneration of cricket from a sport to a money-spinner and worse.
Moreover, cricket, another colonial gift, had become the de facto national sport, crushing hockey and all other sports under its pitch rollers. On top of it, the mighty cricket board, perceived to be a hub of myriad commercial and political vested interests, became a law unto itself.
Q. Why does the author mean by referring cricket as the ‘de facto national sport’ in the passage?
It has long been known that the rate of oxidative metabolism (the process that uses oxygen to convert food into energy) in any animal has a profound effect on its living patterns. The high metabolic rate of small animals, for example, gives them sustained power and activity per unit of weight, but at the cost of requiring constant consumption of food and water. Very large animals, with their relatively low metabolic rates, can survive well on a sporadic food supply, but can generate little metabolic energy per gram of body weight. If only oxidative metabolic rate is considered, therefore, one
might assume that smaller, more active, animals could prey on larger ones, at least if they attacked in groups. Perhaps they could if it were not for anaerobic glycolysis, the great equalizer. Anaerobic glycolysis is a process in which energy is produced, without oxygen, through the breakdown of muscle glycogen into lactic acid and adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the energy provider. The amount of energy that can be produced anaerobically is a function of the amount of glycogen present—in all vertebrates about 0.5 percent of their muscle’s weight. Thus, the anaerobic energy reserves of a vertebrate are proportional to the size of the animal. If, for example, some predators had attacked a 100-ton dinosaur, normally torpid, the dinosaur would have been able to generate almost instantaneously, via anaerobic glycolysis, the energy of 3,000 humans at maximum oxidative metabolic energy production. This explains how many large species have managed to compete with their more active neighbours: the compensation for a low oxidative metabolic rate is glycolysis.
Q. According to the author, glycogen is crucial to the process of anaerobic glycolysis because glycogen
It has long been known that the rate of oxidative metabolism (the process that uses oxygen to convert food into energy) in any animal has a profound effect on its living patterns. The high metabolic rate of small animals, for example, gives them sustained power and activity per unit of weight, but at the cost of requiring constant consumption of food and water. Very large animals, with their relatively low metabolic rates, can survive well on a sporadic food supply, but can generate little metabolic energy per gram of body weight. If only oxidative metabolic rate is considered, therefore, one might assume that smaller, more active, animals could prey on larger ones, at least if they attacked in groups. Perhaps they could if it were not for anaerobic glycolysis, the great equalizer. Anaerobic glycolysis is a process in which energy is produced, without oxygen, through the breakdown of muscle glycogen into lactic acid and adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the energy provider. The amount of energy that can be produced anaerobically is a function of the amount of glycogen present—in all vertebrates about 0.5 percent of their muscle’s weight. Thus, the anaerobic energy reserves of a vertebrate are proportional to the size of the animal. If, for example, some predators had attacked a 100-ton dinosaur, normally torpid, the dinosaur would have been able to generate almost instantaneously, via anaerobic glycolysis, the energy of 3,000 humans at maximum oxidative metabolic energy production. This explains how many large species have managed to compete with their more active neighbours: the compensation for a low oxidative metabolic rate is glycolysis.
Q. The passage suggests that the total anaerobic energy reserves of a vertebrate are proportional to the vertebrate’s size because
It has long been known that the rate of oxidative metabolism (the process that uses oxygen to convert food into energy) in any animal has a profound effect on its living patterns. The high metabolic rate of small animals, for example, gives them sustained power and activity per unit of weight, but at the cost of requiring constant consumption of food and water. Very large animals, with their relatively low metabolic rates, can survive well on a sporadic food supply, but can generate little metabolic energy per gram of body weight. If only oxidative metabolic rate is considered, therefore, one might assume that smaller, more active, animals could prey on larger ones, at least if they attacked in groups. Perhaps they could if it were not for anaerobic glycolysis, the great equalizer. Anaerobic glycolysis is a process in which energy is produced, without oxygen, through the breakdown of muscle glycogen into lactic acid and adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the energy provider. The amount of energy that can be produced anaerobically is a function of the amount of glycogen present—in all vertebrates about 0.5 percent of their muscle’s weight. Thus, the anaerobic energy reserves of a vertebrate are proportional to the size of the animal. If, for example, some predators had attacked a 100-ton dinosaur, normally torpid, the dinosaur would have been able to generate almost instantaneously, via anaerobic glycolysis, the energy of 3,000 humans at maximum oxidative metabolic energy production. This explains how many large species have managed to compete with their more active neighbours: the compensation for a low oxidative metabolic rate is glycolysis.
Q. The author suggests that, on the basis of energy production, a 100-ton dinosaur would have been markedly vulnerable to which of the following?
Repeated attacks by a single smaller, more active adversary
Sustained attack by numerous smaller, more active adversaries
An attack by an individual adversary of similar size
The H.C.F of two numbers, each having three digits, is 19 and their L.C.M. is 3553. The sum of the numbers will be:
The latest data to show that the overall power situation has gotten worse, with the ratio for peak load shortages now the highest in a decade. In absolute terms, the power deficit has hit record levels and seems almost certain to further deteriorate without real reforms on the ground. Even as aggregate technical and commercial losses in the power system remain much high at over a third of total generation, pan- India capacity addition is now well below target. A shortage of equipment and skills is blamed for the marked slow down in augmenting power capacity. But the dearth of resources can only be relative. In fact, the real bane of the sector is continuing revenue leakage in the state power utilities and unacceptably high aggregate technical and commercial losses, much of it plain theft of electricity. Given the preponderance of state utilities in power supply, the fact that they remain very much in red does affect investor comfort and return funds flow.
Q. Which of the following inference(s) is/are definitely true?
From ‘apparel to aerospace’, ‘steel to software’, the pace of technological innovation is quickening. No longer can companies afford to miss generation of technology and expect to remain competitive. Adding to the pressure, innovations are increasingly crossing industry boundaries; a new fibre developed by the textile industry has potential for building materials and medical equipment. Some companies are adept at using a diversity of technologies to create new products that transform markets. But many others are floundering because they rely on a technology strategy that no longer works in such a fast changing environment. The difference between success and failure is not how much a company spends on research and development
(R&D), but how it approaches it. There are two possible approaches. Either a company can invest in R&D that uses an older generation of technology, the ‘breakthrough’ approach-or its focus on combining existing technologies into hybrid technologies - the ‘technologies fusion’ approach. It blends incremental technical improvements from several previously separate fields of technology to create products that revolutionise markets. In a world where the old maxim ‘one technology one industry’ no longer applies, a singular breakthrough strategy is inadequate; companies need to include both the breakthrough and fusion approaches in their technology strategy. Relying on breakthroughs alone fails because it focuses the R&D efforts to narrowly, ignoring the possibilities of combining technologies. Yet many western companies still rely almost exclusively - on the breakthrough approach. The reasons are complex: a distrust of outside innovations and not-invented here engineering and arrogance and aversion to sharing research results.
Which of the following would correctly reflect the position regarding the two approaches to technology adoption?
From ‘apparel to aerospace’, ‘steel to software’, the pace of technological innovation is quickening. No longer can companies afford to miss generation of technology and expect to remain competitive. Adding to the pressure, innovations are increasingly crossing industry boundaries; a new fibre developed by the textile industry has potential for building materials and medical equipment. Some companies are adept at using a diversity of technologies to create new products that transform markets. But many others are floundering because they rely on a technology strategy that no longer works in such a fast changing environment. The difference between success and failure is not how much a company spends on research and development
(R&D), but how it approaches it. There are two possible approaches. Either a company can invest in R&D that uses an older generation of technology, the ‘breakthrough’ approach-or its focus on combining existing technologies into hybrid technologies - the ‘technologies fusion’ approach. It blends incremental technical improvements from several previously separate fields of technology to create products that revolutionise markets. In a world where the old maxim ‘one technology one industry’ no longer applies, a singular breakthrough strategy is inadequate; companies need to include both the breakthrough and fusion approaches in their technology strategy. Relying on breakthroughs alone fails because it focuses the R&D efforts to narrowly, ignoring the possibilities of combining technologies. Yet many western companies still rely almost exclusively - on the breakthrough approach. The reasons are complex: a distrust of outside innovations and not-invented here engineering and arrogance and aversion to sharing research results.
Which of the following features of technology has been highlighted most prominently by the author of the passage?
From ‘apparel to aerospace’, ‘steel to software’, the pace of technological innovation is quickening. No longer can companies afford to miss generation of technology and expect to remain competitive. Adding to the pressure, innovations are increasingly crossing industry boundaries; a new fibre developed by the textile industry has potential for building materials and medical equipment. Some companies are adept at using a diversity of technologies to create new products that transform markets. But many others are floundering because they rely on a technology strategy that no longer works in such a fast changing environment. The difference between success and failure is not how much a company spends on research and development
(R&D), but how it approaches it. There are two possible approaches. Either a company can invest in R&D that uses an older generation of technology, the ‘breakthrough’ approach-or its focus on combining existing technologies into hybrid technologies - the ‘technologies fusion’ approach. It blends incremental technical improvements from several previously separate fields of technology to create products that revolutionise markets. In a world where the old maxim ‘one technology one industry’ no longer applies, a singular breakthrough strategy is inadequate; companies need to include both the breakthrough and fusion approaches in their technology strategy. Relying on breakthroughs alone fails because it focuses the R&D efforts to narrowly, ignoring the possibilities of combining technologies. Yet many western companies still rely almost exclusively - on the breakthrough approach. The reasons are complex: a distrust of outside innovations and not-invented here engineering and arrogance and aversion to sharing research results.
What, according to the author, is adding to the pressure on the companies?
Excluding stoppages, the speed of a bus is 54 kmph and including stoppages, it is 45 kmph. For how many minutes does the bus stop per hour?
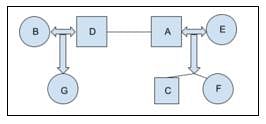
A, B, C, D, E, F and G are members of a family consisting of four adults and three children, two of whom, F and G are girls. A and D are brothers and A is a doctor. E is an engineer married to one of the brothers and has two children. B is married to D and G is their child. Who is C?
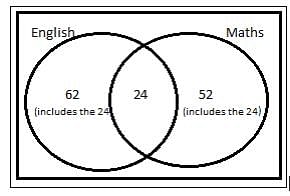
Out of 130 students appearing in an exam, 62 failed in Science, 52 failed in English, whereas 24 failed in both Science and English. The number of students who passed is
Directions: Study the following graph carefully to answer the questions given below it.
Production of Wheat (in Lakh tonnes) by three different countries America, Britain & Canada over the years is 51.66 , 43, 30.83 respectively.
What is the difference (in Lakh tonnes) between the average production per year of the country with highest average production and that of the country with the lowest average production?
Find the value of expression 98-99+100-101+102-103+ 998 - 999 + 1000
Passage-3
The Andromeda Galaxy, also known as Messier 31, NGC 224, is a spiral galaxy approximately 2.5 million light- years away from Earth. The Andromeda Galaxy is in the constellation Andromeda, and it is the nearest spiral galaxy to our own, the Milky Way. Both the Milky Way and the Andromeda Galaxy are members of the Local Group, which also includes the Griangulum Galaxy, among others. Until recently, it was believed that the Andromeda Galaxy had the greatest mass of the three Galaxies in the Local Group, but recent findings suggest that the Milky Way has the most dark matter out of the three, and this fact may suggest that in fact the Milky Way is the most massive. Scientists are still uncertain, and more research is needed to settle the matter. In terms of the actual number of stars, however, the Andromeda Galaxy contains approximately 1 trillion stars, which is much more than are contained in the Milky Way.
The Andromeda Galaxy is visible to the naked eye in a moderately dark sky, and it appears quite small without a telescope because only the central part is bright enough to be visible. However, the angular diameter of the Andromeda Galaxy is seven times that of the full moon, and so if all of the stars of the Andromeda Galaxy were easily visibly to the naked eye, the galaxy would be the dominant object in the sky.
Q. According to the passage, which of the following is TRUE?
Passage-3
The Andromeda Galaxy, also known as Messier 31, NGC 224, is a spiral galaxy approximately 2.5 million light- years away from Earth. The Andromeda Galaxy is in the constellation Andromeda, and it is the nearest spiral galaxy to our own, the Milky Way. Both the Milky Way and the Andromeda Galaxy are members of the Local Group, which also includes the Griangulum Galaxy, among others. Until recently, it was believed that the Andromeda Galaxy had the greatest mass of the three Galaxies in the Local Group, but recent findings suggest that the Milky Way has the most dark matter out of the three, and this fact may suggest that in fact the Milky Way is the most massive. Scientists are still uncertain, and more research is needed to settle the matter. In terms of the actual number of stars, however, the Andromeda Galaxy contains approximately 1 trillion stars, which is much more than are contained in the Milky Way.
The Andromeda Galaxy is visible to the naked eye in a moderately dark sky, and it appears quite small without a telescope because only the central part is bright enough to be visible. However, the angular diameter of the Andromeda Galaxy is seven times that of the full moon, and so if all of the stars of the Andromeda Galaxy were easily visibly to the naked eye, the galaxy would be the dominant object in the sky.
Q. In the passage, the author writes, "Scientists are still uncertain, and more research is needed to settle the matter," referring to the fact that scientists are uncertain about the relative masses of the Milky Way and the Andromeda Galaxy. If the author wanted to include more details about this, which of the following should also be included in the passage?
Passage 2
Do not study too long at once. So long as the mind works with ease, it may be allowed to continue working but if we find it moves slowly and extra trouble is needed to keep the attention fixed, it is far better to break off and take a walk or have some other recreation, that to go on plodding until one feels wholly exhausted. To continue to force the mind to work is likely to lead to injurious result and may end in a nervous breakdown from which recovery is slow and troublesome.
Q. The writer suggests that the main cause of nervous breakdown is
Passage 2
Do not study too long at once. So long as the mind works with ease, it may be allowed to continue working but if we find it moves slowly and extra trouble is needed to keep the attention fixed, it is far better to break off and take a walk or have some other recreation, that to go on plodding until one feels wholly exhausted. To continue to force the mind to work is likely to lead to injurious result and may end in a nervous breakdown from which recovery is slow and troublesome.
Q. A man feels that he is exhausted when
Passage 2
Do not study too long at once. So long as the mind works with ease, it may be allowed to continue working but if we find it moves slowly and extra trouble is needed to keep the attention fixed, it is far better to break off and take a walk or have some other recreation, that to go on plodding until one feels wholly exhausted. To continue to force the mind to work is likely to lead to injurious result and may end in a nervous breakdown from which recovery is slow and troublesome.
Q. The underlying tone of the passage is that
Passage 2
Do not study too long at once. So long as the mind works with ease, it may be allowed to continue working but if we find it moves slowly and extra trouble is needed to keep the attention fixed, it is far better to break off and take a walk or have some other recreation, that to go on plodding until one feels wholly exhausted. To continue to force the mind to work is likely to lead to injurious result and may end in a nervous breakdown from which recovery is slow and troublesome.
Q. While making the observation "Do not study too long", the author suggests that