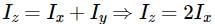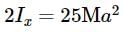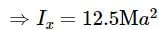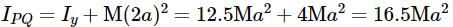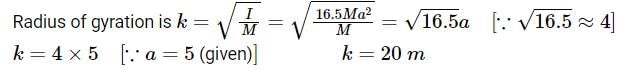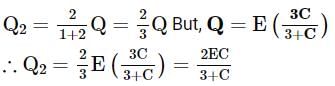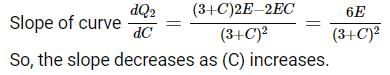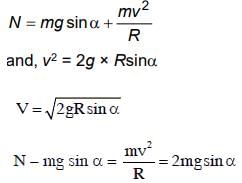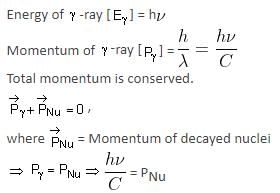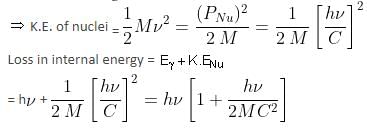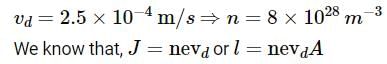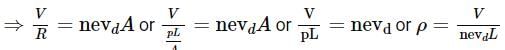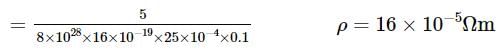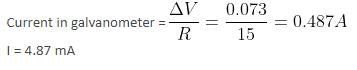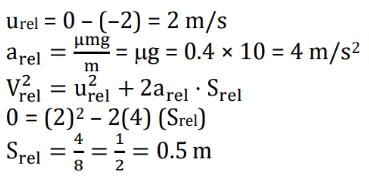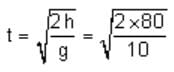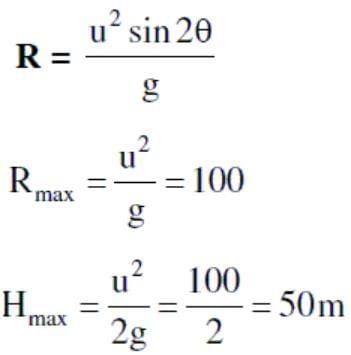KEAM Paper 1 Mock Test - 3 - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - KEAM Paper 1 Mock Test - 3
A box is floating in the river of speed 5m/s. The position of the block is shown in the figure at t = 0. A stone is thrown from point O at time t = 0 with a velocity 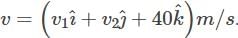 Find the value of v1, v2 such that the stone hits the box.
Find the value of v1, v2 such that the stone hits the box.

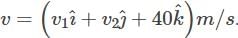 Find the value of v1, v2 such that the stone hits the box.
Find the value of v1, v2 such that the stone hits the box.
Two cannon ball A and B fall in water (density of balls is 0.6 x 103 Kg/m3 from the height 10m and 25m respectively. Find the ratio of the depth of ball A and B sink. Assume g=10m/s2
.
.
A light of intensity I0 is incident on a Polaroid which placed at 30º . Find the ratio of the intensity of light after and before polarization, if the light is polarized when Polaroid is at 60º.
A bullet of mass 5 g, travelling with a speed of 210 m/s, strikes a fixed wooden target. One half of its kinetic energy is converted into heat in the bullet, while the other half is converted into heat in the wood. The rise of temperature of the bullet if the specific heat of its material is 0.030 cal/(g-°C) (1 cal = 4.2 x 107 ergs) is close to
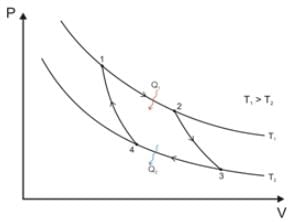
Carnot's heat engine works with an ideal monoatomic gas, and an adiabatic expansion ratio 5:3. Find the efficiency of Carnot's engine.
A wall has two layers A and B ach made of different materials. Both layers have the same thickness. The thermal conductivity of the material of A is twice that of B. Under thermal equilibrium, the temperature difference across the wall is 36∘C. The temperature difference across the layer A is:
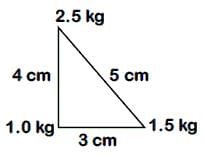
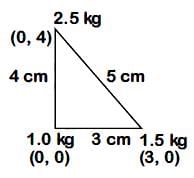
Three point particles of masses 1.0 kg, 1.5 kg and 2.5 kg are placed at three corners of a right angle triangle of sides 4.0 cm, 3.0 cm and 5.0 cm as shown in the figure. The centre of mass of system is at a point
two single turn circular loop of wire have radius 20 cm and 2 cm. The loops lies in the same plane and are concentric. Find the mutual inductance of the pair is:
A 25 x 10-3 m3 volume cylinder is filled with 1 mol of O2 gas at room temperature (300 K). The molecular diameter of O2 and its root mean square speed, are found to be 0.3 nm and 200 m/s, respectively. What is the average collision rate (per second) for an O2 molecule?
Two identical charged particles each having a mass 10 g and charge 2.0 x 10-7 C are placed on a horizontal table with a separation of L between them such that they stay in limited equilibrium. If the coefficient of friction between each particle and the table is 0.25, find the value of L. [Use g = 10 ms-2]
A body A of mass m is moving in a circular orbit of radius R about a planet. Another body B of mass m/2 collides with A with a velocity which is half 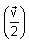 the instantaneous velocity
the instantaneous velocity 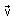 of A. The collision is completely inelastic. Then the combined body:
of A. The collision is completely inelastic. Then the combined body:
An electrical power line, having a total resistance of 2 Ω, delivers 10 kW at 220 V. The efficiency of the transmission line is approximately
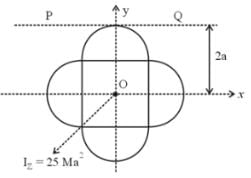
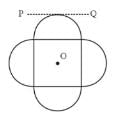
Asymmetric lamina of mass M = 10 kg, consists of a square shape with a semi-circular section over each of the edge of the square as in the figure. The side of the square is 2a=10 m. The moment of inertia of the lamina about an axis through its center of mass and perpendicular to the plane is 25Ma2. Find the radius of gyration about the tangent PQ in the plane of the lamina.
A copper block of mass 5.0 kg is heated to a temperature of 500°C and is placed on a large ice block. What is the maximum amount of ice that can melt?
[Specific heat of copper: 0.39 J g-1°C-1 and latent heat of fusion of water: 335 J g-1]
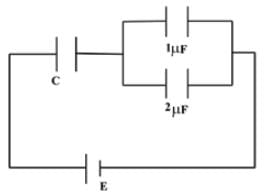
In the given circuit, charge Q2 on the 2μF capacitor changes as C is varied from 1μF to 3μF. Q2 as a function of C is given properly by:
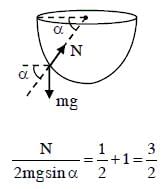
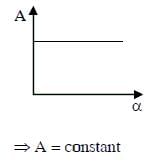
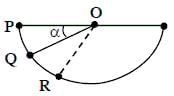
A ball is released from rest from point P of a smooth semi-spherical vessel as shown in figure. The ratio of the centripetal force and normal reaction on the ball at point Q is A while angular position of point Q is α with respect to point P. Which of the following graphs represents the correct relation between A and α when ball goes from Q to R?
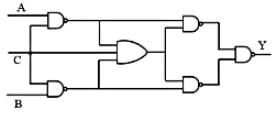
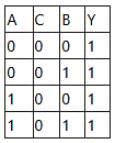
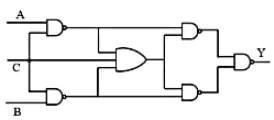
Which is the correct truth table for the circuit diagram as shown below? Assume that the 'C' is always 0.
A nucleus of mass M emits γ-ray photon of frequency 'v'. The loss of internal energy by the nucleus is:
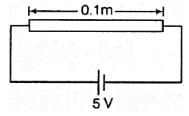
When 5V potential difference is applied across a wire length 0.1 m, the drift speed of electron is 2.5 x 10-4 ms-1 . If the electron density in the wire is 8 x 1028 m-3 , the resistivity of the material is close to
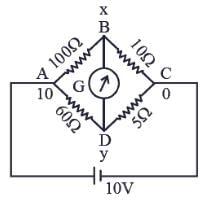
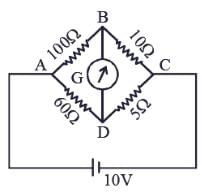
The four arms of a Wheatstone bridge have resistances as shown in the figure. A galvanometer of 15Ω resistance is connected across BD. Calculate the current through the galvanometer when a potential difference of 10V is maintained across AC.
Two gases A and B have equal pressure P, temperature T, and volume V. The two gases are mixed together and the resulting mixture has the same temperature T and volume V as before. The ratio of pressure exerted by the mixture to either of the two gases is:
In an adiabatic process, the density of a diatomic gas becomes 32 times its initial value. The final pressure of the gas is found to be n times the initial pressure. The value of n is
A cylinder of fixed capacity of 44.8 litres contains helium gas at standard temperature and pressure. The amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of gas in the cylinder by 20.0°C will be:
(Given: gas constant R = 8.3 JK-1 mol-1)
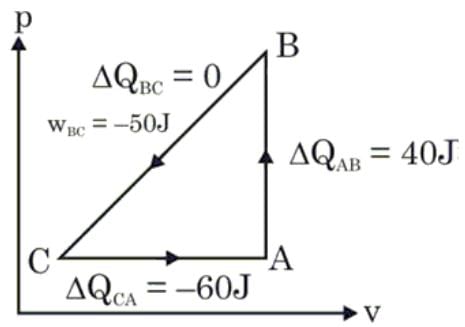
A sample of an ideal gas is taken through the cyclic process ABCA as shown in figure. It absorbs 40 J of heat during the part AB, no heat during BC and rejects 60 J of heat during CA. A work of 50 J is done on the gas during the part BC. The internal energy of the gas at A is 1560 J. The work done by the gas during the part CA is:
A Carnot engine has efficiency of 50%. If the temperature of sink is reduced by 40°C, its efficiency increases by 30%. The temperature of the source will be:
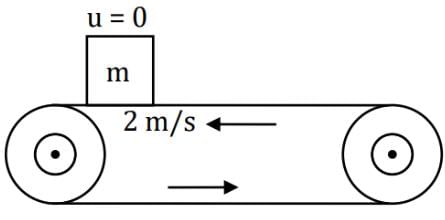
A bag is gently dropped on a conveyor belt moving at a speed of 2 m/s. The coefficient of friction between the conveyor belt and bag is 0.4. Initially, the bag slips on the belt before it stops due to friction. The distance travelled by the bag on the belt during slipping motion is:
[Take g = 10 ms-2]
Two balls A and B are placed at the top of 180 m tall tower. Ball A is released from the top at t = 0 s. Ball B is thrown vertically down with an initial velocity 'u' at t = 2 s. After a certain time, both balls meet 100 m above the ground. Find the value of 'u' in ms-1. [Use g = 10 ms-2]
A block of mass 10 kg starts sliding on a surface with an initial velocity of 9.8 ms-1. The coefficient of friction between the surface and block is 0.5. The distance covered by the block before coming to rest is [use g = 9.8 ms-2]
A person can throw a ball up to a maximum range of 100 m. How high above the ground can he throw the same ball?


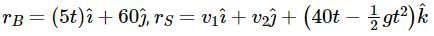
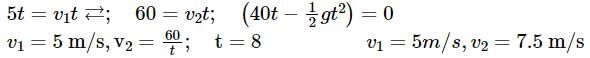
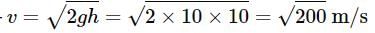
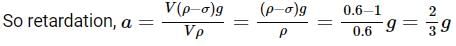

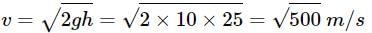
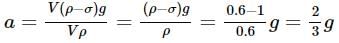

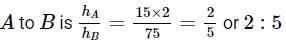

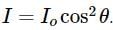 Since the light is polarized at angle 60º so the intensity of polarized light is
Since the light is polarized at angle 60º so the intensity of polarized light is 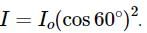
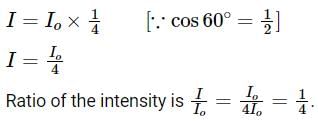
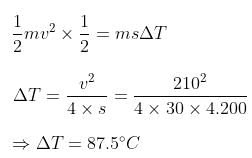
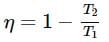
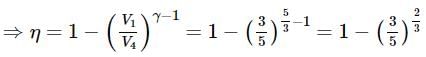
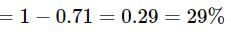
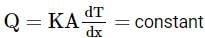
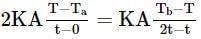
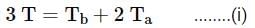
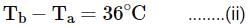
 .
.
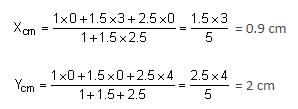
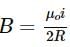 at its centre. Since the radius r = 2cm of the smaller loop is r<<R, so we may treat the flux through the small loop as being approximately
at its centre. Since the radius r = 2cm of the smaller loop is r<<R, so we may treat the flux through the small loop as being approximately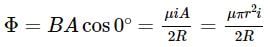
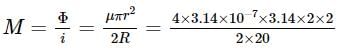
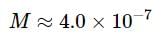

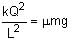

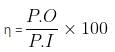
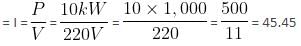
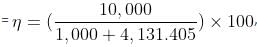 which is approximately equal to 96%.
which is approximately equal to 96%.