UPPSC Prelims (GS I) Mock Test - 4 - UPPSC (UP) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - UPPSC Prelims (GS I) Mock Test - 4
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Which among the following is/are examples of non-point sources of pollution?
- Excess use of fertilizers
- Toxic chemicals from urban runoff
- Bacteria and nutrients from livestock
Select the correct answer using the codes given below.
Who among the following is not appointed by the State Governor?
Consider the following statement regarding the Bombay Plan?
- It was drafted by JRD Tata and GD Birla in 1944 .
- It emphasised mass education, scientific training & research.
- It was a widely accepted plan for India.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Under which of the following the Constituent Assembly of India was constituted?
With reference to Green Manuring, consider the following statements.
- Green manure is created by leaving uprooted or sown crop parts to wither on a field so that they serve as a mulch and soil amendment.
- Mostly leguminous plants are used as green manure.
- Green manures usually perform multiple functions that include soil improvement and soil protection.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
Which of the following are detritivores?
- Earthworms
- Jellyfish
- Millipedes
- Seahorses
- Woodlice
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
Consider the following statements with respect to Tanjore paintings :
- The paintings were created on paper or cloth.
- They used gemstones and cut glass.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
With reference to the "EL-NINO", which of the following statement/s is/are correct?
- El - Nino involves appearance of warm current of the coast of Peru in eastern pacific.
- This warm current increase the temperature of water on the Peruvian coast by 10°C there by increasing the amount of Plankton in the sea.
Select the correct answer using the code given below-
Which tiger reserve in Uttar Pradesh has been granted the Conservation Assure Tiger Standards (CATS) accreditation?
Who among the following has the constitutional authority to summon a joint session of Parliament?
The Central Vigilance Commission was set up by:
Which of the following is a type of farming?
I. Primitive Subsistence Farming
II. Commercial Farming
Which of the following statements with respect to the Interim Government formed after Second World War is Incorrect?
1. Its formation was proposed under the Cabinet Mission of 1946.
2. Muslim league never joined the Interim Government.
3. The Viceroy acted as the President of the Executive Council of the Interim Government.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
Statement I: The Oudh Kisan Sabha established in 1920 failed to bring under its wing any Kisan Sabhas.
Statement II: The Oudh Kisan Sabha asked the Kisans to refuse to till bedakhli land, not to offer hari and begar.
Consider the following statements:
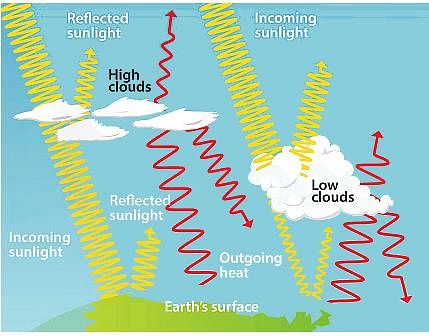
1. Noctilucent clouds are formed in the summer months in the Mesosphere.
2. The low thick clouds are poor in albedo and thus absorb the long wave radiation from earth thus heating the atmosphere.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Consider the following:
1. Takakia, a 390 million-year-old moss, has adapted to life in some of Earth’s harshest environments.
2. Takakia is the world's oldest moss could go extinct as a result of the climate crisis.
Which of the following statement/s is/are correct?
Consider the following statements:
1. The WHO Centre for Global Traditional Medicine is being set up in Himachal Pradesh.
2. The climate change and health hub is being set up in a partnership between India and the World Bank.
How many of the above statements is/are correct?
Which of the following statement is correct about the ripple effect in the context of ecology
Which initiative launched by the Uttar Pradesh government aims to provide free education to children of construction workers?
What legal action has been taken regarding the Shahi Idgah mosque in Mathura?
What annual financial assistance does the government provide for educational materials under the Right to Education Act?