Software Development Exam > Software Development Tests > Test: General Science (Ecology & Environment) - Software Development MCQ
Test: General Science (Ecology & Environment) - Software Development MCQ
Test Description
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: General Science (Ecology & Environment)
Test: General Science (Ecology & Environment) for Software Development 2025 is part of Software Development preparation. The Test: General Science (Ecology & Environment) questions and answers have been prepared
according to the Software Development exam syllabus.The Test: General Science (Ecology & Environment) MCQs are made for Software Development 2025 Exam.
Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for Test: General Science (Ecology & Environment) below.
Solutions of Test: General Science (Ecology & Environment) questions in English are available as part of our course for Software Development & Test: General Science (Ecology & Environment) solutions in
Hindi for Software Development course.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Software Development Exam by signing up for free. Attempt Test: General Science (Ecology & Environment) | 10 questions in 12 minutes | Mock test for Software Development preparation | Free important questions MCQ to study for Software Development Exam | Download free PDF with solutions
Test: General Science (Ecology & Environment) - Question 1
Which is the first Biosphere reserve in India?
Detailed Solution for Test: General Science (Ecology & Environment) - Question 1
Test: General Science (Ecology & Environment) - Question 2
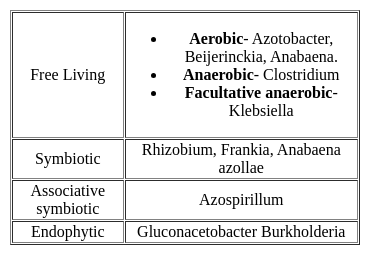
The manure also considered as bio-fertilizer is:
Detailed Solution for Test: General Science (Ecology & Environment) - Question 2
Test: General Science (Ecology & Environment) - Question 3
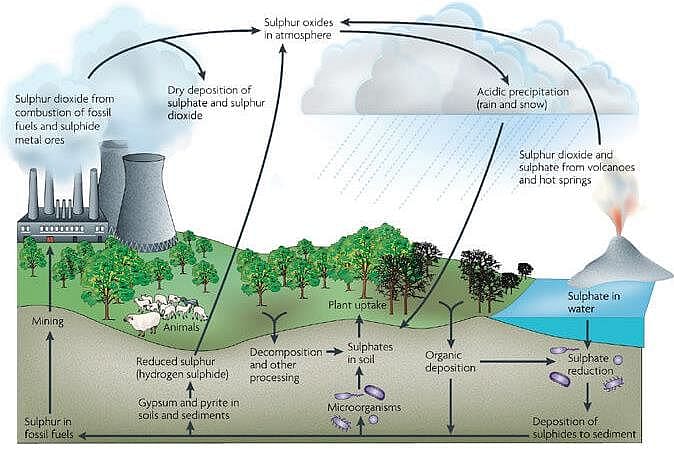
Which of the following biomes is also known as Sedimentary Cycle?
Detailed Solution for Test: General Science (Ecology & Environment) - Question 3
Test: General Science (Ecology & Environment) - Question 4
Which of the following crop is NOT a Kharif crop?
Detailed Solution for Test: General Science (Ecology & Environment) - Question 4
Test: General Science (Ecology & Environment) - Question 5
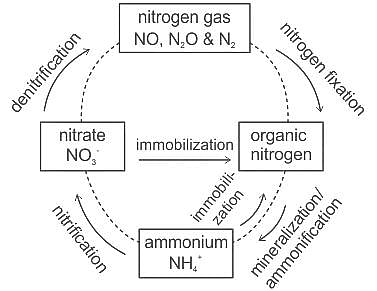
The process of converting ammonia into nitrates is called:
Detailed Solution for Test: General Science (Ecology & Environment) - Question 5
Detailed Solution for Test: General Science (Ecology & Environment) - Question 6
Test: General Science (Ecology & Environment) - Question 7
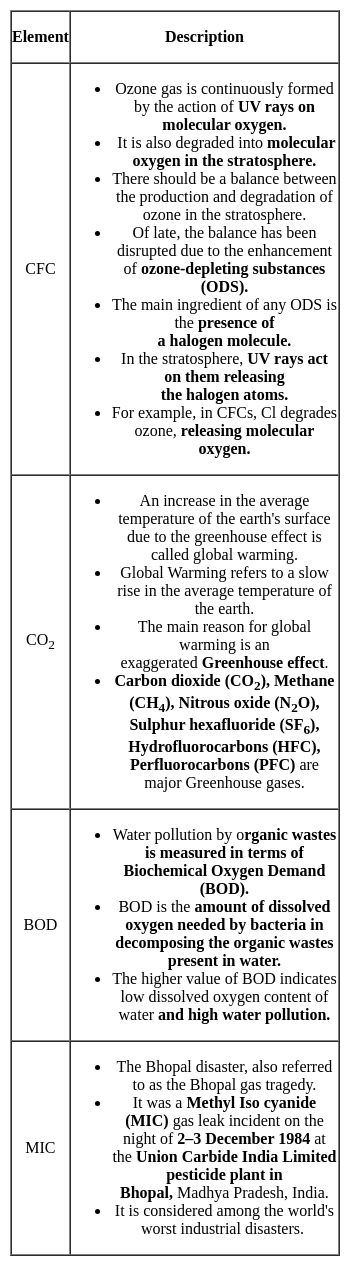
Which of the following is the largest source of water pollution in major rivers of India?
Detailed Solution for Test: General Science (Ecology & Environment) - Question 7
Test: General Science (Ecology & Environment) - Question 8
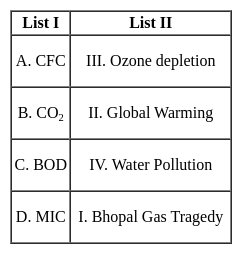
Match the items in List I with List II and select the correct answer using the codes given below:
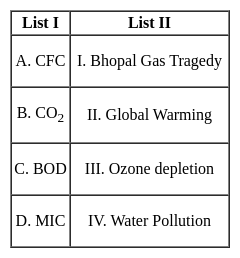
Detailed Solution for Test: General Science (Ecology & Environment) - Question 8
Test: General Science (Ecology & Environment) - Question 9
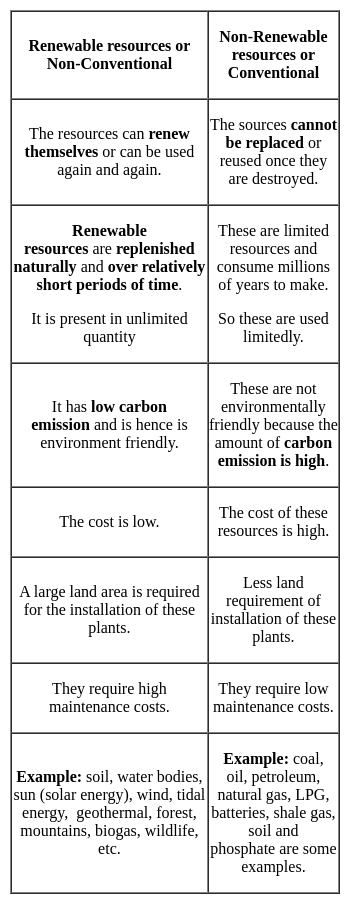
Biogas is which type of natural resources
Detailed Solution for Test: General Science (Ecology & Environment) - Question 9
Test: General Science (Ecology & Environment) - Question 10
The resources of water on the earth are:
Detailed Solution for Test: General Science (Ecology & Environment) - Question 10
Information about Test: General Science (Ecology & Environment) Page
In this test you can find the Exam questions for Test: General Science (Ecology & Environment) solved & explained in the simplest way possible.
Besides giving Questions and answers for Test: General Science (Ecology & Environment), EduRev gives you an ample number of Online tests for practice
Download as PDF