KTET Paper 1: Mathematics Test - 1 - KTET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - KTET Paper 1: Mathematics Test - 1
Directions: Answer the following question by selecting the most appropriate option.
The product of remainders of 19,009 ÷ 11 and 9,090 ÷ 11 is
The product of remainders of 19,009 ÷ 11 and 9,090 ÷ 11 is
The simple interest on ₹1000 for 1 year at the rate of 10% is:
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
A person travelled a distance of 50 km in 8 hours. He covered a part of the distance on foot at the rate of 4 km per hour and a part on a bicycle at the rate of 10 km per hour. How much distance (in km) did he travel on foot?
Use of Abacus in Class II does not help the students to
The solid as shown in the figure is made up of cubical blocks each of side 1 cm. The number of blocks is:
While playing his seven year old son, Raman took a piece of dough in his hands and shaped it into a ball. He then reshaped the same dough into a cylindrical shape. Raman was trying to:
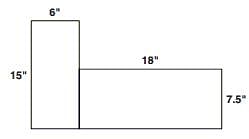
A mathematics teacher believes in teaching mathematics by giving an activity to the students so that the concepts become clear to all with ease. In order to teach area and perimeter, the teacher gives the following diagram. This activity comes under
Piaget believed that learning results from social institutions and a mathematics teacher believing in Piaget's theory shall use _____.
After explaining the operation of subtraction in Class Il, teacher drew the following diagram on the board and asked the students to fill in the circles:
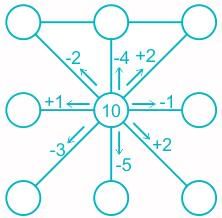
The purpose of the exercise is
The length of a rectangle is two times that of a square whose perimeter is 80 cm. If breadth of the rectangle is 20 cm, then the area (in cm2) of the rectangle exceeds the area of the square by
In a division sum, the divisor is 8 times the quotient and 6 times the remainder. If the remainder is 28, the dividend is –
Sequence the following tasks as they would be taken up while developing the understanding of shapes and space across primary classes:
I. Matches the properties of 2-D shapes by observing their sides and corners.
II. Describes intuitively the properties of 2-D shapes.
III. Sorts 2-D shapes.
IV. Describes the various 2-D shapes by counting their sides, corners and diagonals.
The mean of five consecutive numbers is 14. Calculate the average of the smallest and the largest numbers.
If the perimeter of a rectangle is 10 cm and the area is 4 cm2, then its length is
Rohan of Class II can do skip counting correctly. He is in which of the following developmental phases of numbers?
The NCF-2005 pronounced that succeeding in mathematics should be seen as the right of every child which can be achieved by:
Among the given statements, which one justifies that Culture and context has a role in constructing mathematical knowledge?
Study the graph given below carefully and find out the year in which the school gives the result of 95%.
"Recognition of patterns and their completion" is an essential part of Mathematics curriculum at primary stage as it _____.
The mean of 50 items was 24. Later on, it was discovered that two items were misread as 83 and 17 instead of 38 and 77. The correct mean is:
"If Kelly is taller than Ali and Ali is taller than Jo, who is the tallest?"
If a student draws a picture or needs an object to answer this question, then he is in
To introduce subtraction of two digits numbers in class 3, a teacher proceeded in the following steps
Step 1: Revision of two digit numbers with an understanding of the place-value system
Step 2: Use tally marks to show that a smaller number can be subtracted on numbers under each column of place value. In this case, the teacher is developing the lesson.
Look at the following pattern:
13 + 53 + 33 = 153
163 + 503 + 333 = 165033
1663 + 5003 + 3333 = 166500333
According to this pattern
16663 + 50003 + 33333 = ?
The important role of a Mathematics teacher in a class is
In a dice, the numbers on the opposite faces add up to 7. Which amongst the following will fold into a dice?
A child was given the following problem, 'After 3 pens were taken away from me, I had 4 pens left. How many pens did I have to begin with?' A student gave the answer as 1 as according to her, it was 4 - 3 = 1. This reflects that
The stages included in a diagnostic test include
Twenty-six and twenty-six hundredths is written as:
All round development of a child is reflected through _____.