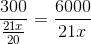KTET Paper 1: Mathematics Test - 5 - KTET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - KTET Paper 1: Mathematics Test - 5
Directions: Answer the following question by selecting the most appropriate option.
The number of books to be packed in wooden boxes is 10,290. If 98 books can be packed in one box and the cost of one box is Rs. 518, then the total cost of boxes needed for this purpose is
The number of books to be packed in wooden boxes is 10,290. If 98 books can be packed in one box and the cost of one box is Rs. 518, then the total cost of boxes needed for this purpose is
If an operator □ is defined as:
4□3=4+5+6
5□4=5+6+7+8
6□4=6+7+8+9
What will n□8 be equal to?
4□3=4+5+6
5□4=5+6+7+8
6□4=6+7+8+9
What will n□8 be equal to?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
- I am a 2-digit number.
- The digit in the tens place is an even prime number.
- The sum of the digit is 9.
The number is
Mathematics provides its various support and assistance in daily life problems. The application of mathematics provides
The most appropriate strategy that can be used to internalize the skill of addition of money is:
A child has learned the fundamentals skills of mathematics and applies the same whenever he goes to a stationary store. Which aspect of mathematics he is using in this case?
Which of the following is/are incorrect for any rational number x?
The Number of hours and minutes from 6:14 a.m. to 8:02 p.m. On the same day is _____.
Which of the following statements is true with respect to the objectives of mathematics at the primary level?
There are 660 students in a school. Two-thirds of them are boys. Three-fourths of the number of boys are players and one-fourth of the girls are players. What is the total number of players in the school?
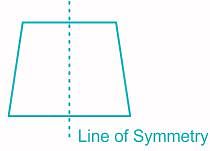
Isosceles trapezium have how many lines of symmetry?
There are 1320 people in a village. The city`s two-thirds population comprises males. Three-fourths of the males are farmers. One-fourth of the females are farmers. The total number of farmers in the village is
Proficiency in Mathematical language in classroom can be enhanced by presenting the problems in the following sequence:
What number should be subtracted from the product 1109 x 505 so as to get 505050 ?
Which of the following ICT tools can be effectively used for exploratory tasks in a geometry class?
To introduce the concept of fractions, a teacher can begin with:
In which class a child identifies basic 3D-shapes such as cuboid, cylinder, cone and sphere by their names?
Mr. Banvari Lal has just started his teacher career. He is a teacher of Maths. After delivering lecture to a few classes, he noticed that many of the students are not showing interest in learning Maths. Therefore, he started finding new ways to teach Maths and to create the interest of students in the subject. You are required to help the Mr. Lal by selecting the appropriate alternative that will be useful for teaching Maths.
What time is 4 hrs 59 minutes before 2:58 p.m.?
A car takes 2 hours less to cover a distance of 300 km when the speed is increased by 5%. Then, the usual speed is
In class the teacher asked the student to define a quadrilateral in different ways- using sides, using angles, using diagonals, etc. The teacher's objective is to _____.
Fill in the blanks
The least number by which 125 be multiplied to make it a perfect square is _____________.
While teaching the addition of fractions, it was observed by Mr. Singh that the following type of error is very common: 2/3 + 2/5 = 4/10.
Mr. Singh should take the following remedial action:
Look at the following table:
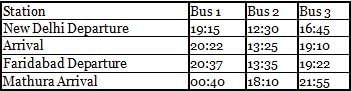
Which bus takes the least time to reach Mathura from New Delhi?
Achievement test are generally conducted to assess the acquired knowledge and skills of a candidate. The main objective of achievement test is:
Children at the primary stage are able to classify the given shapes based on their appearance. According to Van Hiele levels of geometry, they are at:
Which of the following are the broad and narrow objectives of mathematics education?
I. Customization
II. Use of heuristics.
III. Approximation and Presumption
IV. Representation