KTET Paper 1: Mathematics Test - 6 - KTET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - KTET Paper 1: Mathematics Test - 6
While planning a lesson on the concept of fraction addition, a teacher is using the activity of strip folding.
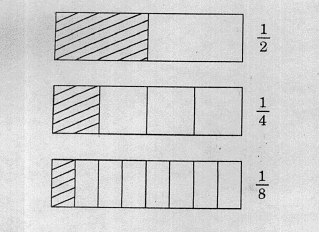
The above activity is a

The above activity is a
According to NCF-2005, the teaching of mathematics should enhance the child's resources:
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
The Academic Standard to be tested through the following test item. "Which is the largest 4-digit number formed with 5, 7, 2, 8"
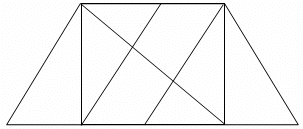
A Maths teacher provides a figure to his students and tells them to identify the number of triangles from the given figure. This is a type of ________ thinking.
A teacher uses the following riddle in a class while developing the concept of base 10 and place value "I am less than 8 tens and 4 ones." The objective of this activity is:
While teaching his class VIII students, Mr Jim presented a problem that was likely to initiate disagreement among the students. He did so to
Which of the following is/are involved in mathematical activities?
What are the socio-personal characteristics associated with mathematics learning that need to be assessed along with the assessment of achievement in mathematics concepts?
A child studying in Class IV exhibits difficulty in sorting, recognising patterns, orientating numbers and shapes, telling time, measuring etc. The child may be
The Sum of two natural/whole numbers does not change even if we change the position of numbers while adding.
This property of whole numbers is referred to as:
The length of a rectangle is 'l' and its width is half of its length. What will be the perimeter of the rectangle if the length is doubled keeping the width the same?
Possible indicator pertaining to visual memory barrier hampering with learner's Mathematical performance is:
Which of the following is not a characteristic of mathematics?
Most appropriate strategy that can be used to internalise the skill of addition of money is
According to NCF-2005, the teaching of mathematics should not enhance the child's resources:
A child of class VII defined the rectangle as follows:
"Rectangle is a quadrilateral whose opposite sides are parallel, and equal".
The definition reflects that the child-
Mathematics pedagogy provides a number of different ways to a teacher to teach his/her students effectively. This allows the teacher to understand the students' problem and provides remedy to it. Therefore, it can be said that Mathematics pedagogy hardly reverberates with
19 thousand + 19 hundred + 19 ones is equal to:
Arrange the following to build a correct sequence for teaching fractions
i. Recognizing fractions as rational numbers
ii. Representing fractions on a number line
iii. Introducing part-whole relations of objects
A teacher noticed that the learning style of every student is different. Some learn by understanding the concepts and formulas told in the class, some learn through interpersonal discussion among friends and some learn through practicing the sums on their own. Based on this, identify the correct type(s) of mathematics students.
Uma has not able to understand the concept of odd and even number. In order to improve her understanding, the teacher took 20 pebbles of different colors and asked her to pair them up and sort out the numbers from 1 to 20 from which pebbles get paired up. Uma _____.
Which of the following is an expectations of teaching mathematics at upper primary level?
Students are asked to establish a relation between vertically opposite angles. They draw various figures, measure the angles and observe that vertically opposite angles are equal. In this case, students according to Van Hiele thought are at
When teaching addition of fractions, a teacher came across the following error:
1/2 + 1/3 = 2/5
What remedial action can the teacher take in such a situation?
Which one of the following is not an effective technique for conducting a Mathematics curriculum in the classroom?
The number of milligrams in 6 grams is equal to the number of grams in how many kilograms?
In Class III a teacher asked the students to add 4562 and 728. A student responded to the question as follows:

The response reflects that the child lacks the:
A teacher wants to develop the spatial reasoning of the students. She discussed with her fellow teacher regarding the same. Four different teachers suggested 4 activities. Which of the following activities should be adopted by the teacher?
1) Solving Sudoku puzzles individually
2) Identifying tessellating figures in groups
3) Drawing bar graphs to represent data
4) Identifying patterns in a number-chart

















