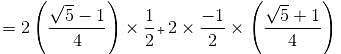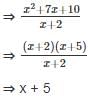KTET Paper 2: Science and Mathematics Test - 3 - KTET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - KTET Paper 2: Science and Mathematics Test - 3
A shopkeeper sold an article offering a discount of 5% and earned a profit of 23.5%. What would have been the percentage of profit earned if no discount was offered?
The area of a square is 16/π of the area of a circle. The ratio of the side of the square to the diameter of the circle is
What is the number of particles present in 10 g of calcium atoms?
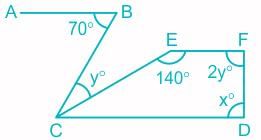
In the figure, if CD || EF || AB, then find the value of x-
In a triangle, angle A measures 60°. What is the measure of the adjacent angle to A, and what is it called?
A question and two statements are given. Decide which of the statement(s) is/are sufficient to answer the question.
Question:
Nitara has 20 colored pencils of four different colours. How many black pencils does she have?
Statements:
1. It has 5 red colored pencils.
2. She has 4 blue colored pencils.
3. The number of green pencils is twice that of blue pencils.
The value of 8 + (1/2 + 1/4) x 16 is:
Which of the following disease is caused by vitamin D deficiency?
Sum of mean and median of the numbers 5.02, 5.18, 5.12, 5.007 and 5.018 is
Which of the following statements is incorrect?
The speed of the boat in still water is 15 kmph. If the time taken by the boat to travel downstream is 1/5th the time taken to travel upstream, then find the speed of the stream.
Total internal reflection is possible when light travels from-
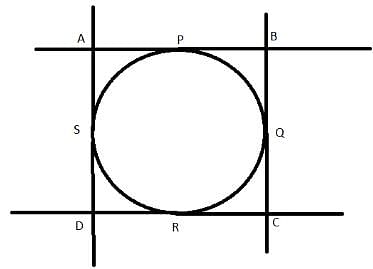
If four sides of a quadrilateral ABCD are tangential to a circle, then
An athlete of mass 60 kg can jump to a maximum height of 1.5 m in the playground. To what maximum height can the same athlete jump on the surface of the moon?
A number whose one-eighth part is increased by 5 is equal to the one-sixth part decreased by 5 is:
cos 12º + cos 84º + cos 132º + cos 156º =
A two digit number is such that the product of the two digits is 72 and their sum is 17. If the unit place is greater than ten's place ,Then number is ______.
From which of the following method, objectives is difficult to be achieved?
In science teaching, explanation method will be proved most useful when-
As per NCF 2005, one main goal of Mathematics education in schools is to
A teacher gives the following problem related to 'discount' to the students for solving:
"The Marked Prices (M.P.) of a shirt and sweater are Rs. 200 and Rs. 300 respectively, and the discounts on the marked prices of the shirt and sweater are 20% and 12% respectively. While preparing the bill, the shopkeeper interchanged the discounts on these items by mistake. On getting the bill, Hamida noticed the mistake and paid the actual amount to the shopkeeper. How much money did Hamida pay to the shopkeeper?"
What value does the teacher try to promote through this problem?
A teaching strategy followed by a physical science teacher who is most concerned about a visually challenged learner to teach neutralisation will be
In RCEM system, four objectives are classified in the form of:
Under which organisation's aided project did NCERT develop an instructional material titled "Science is Doing"?
Student draws neat and accurate figures. This specification relates to which of the following objectives?
Anjali asks the following tasks to be performed by students of Class VII while making an electromagnet (not in the correct sequence):
a. Place some pins near the end of a nail.
b. Switch on the current and observe what happens.
c. Wind a copper wire tightly around an iron nail.
d. Connect free ends of the wire to the terminals of a cell.
Which of the following is the correct sequence of tasks to be performed to achieve the desired result?
Coefficient of x in the expression (x2 + 7x + 10) ÷ (x + 2).
In a blueprint prepared for unit test in Mathematics, 2(1) is written at a place. What does it indicate?




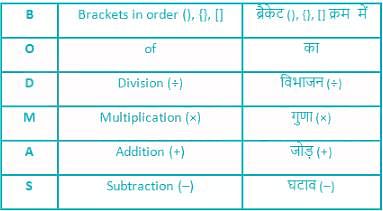
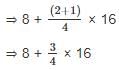
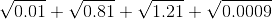 is
is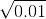 = 0.1
= 0.1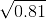 = 0.9
= 0.9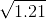 = 1.1
= 1.1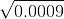 = 0.03
= 0.03