Software Development Exam > Software Development Tests > Test: General Awareness (Indian History) - Software Development MCQ
Test: General Awareness (Indian History) - Software Development MCQ
Test Description
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: General Awareness (Indian History)
Test: General Awareness (Indian History) for Software Development 2025 is part of Software Development preparation. The Test: General Awareness (Indian History) questions and answers have been prepared
according to the Software Development exam syllabus.The Test: General Awareness (Indian History) MCQs are made for Software Development 2025 Exam.
Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for Test: General Awareness (Indian History) below.
Solutions of Test: General Awareness (Indian History) questions in English are available as part of our course for Software Development & Test: General Awareness (Indian History) solutions in
Hindi for Software Development course.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Software Development Exam by signing up for free. Attempt Test: General Awareness (Indian History) | 10 questions in 10 minutes | Mock test for Software Development preparation | Free important questions MCQ to study for Software Development Exam | Download free PDF with solutions
Test: General Awareness (Indian History) - Question 1
Gautam Buddha was elevated to the position of God by the time of
Detailed Solution for Test: General Awareness (Indian History) - Question 1
Test: General Awareness (Indian History) - Question 2
Who was the Physician of Magadh ruler Bimbisara?
Detailed Solution for Test: General Awareness (Indian History) - Question 2
Test: General Awareness (Indian History) - Question 3
What term is commonly used to refer to the "Old Stone Age" in prehistoric times?
Detailed Solution for Test: General Awareness (Indian History) - Question 3
Test: General Awareness (Indian History) - Question 4
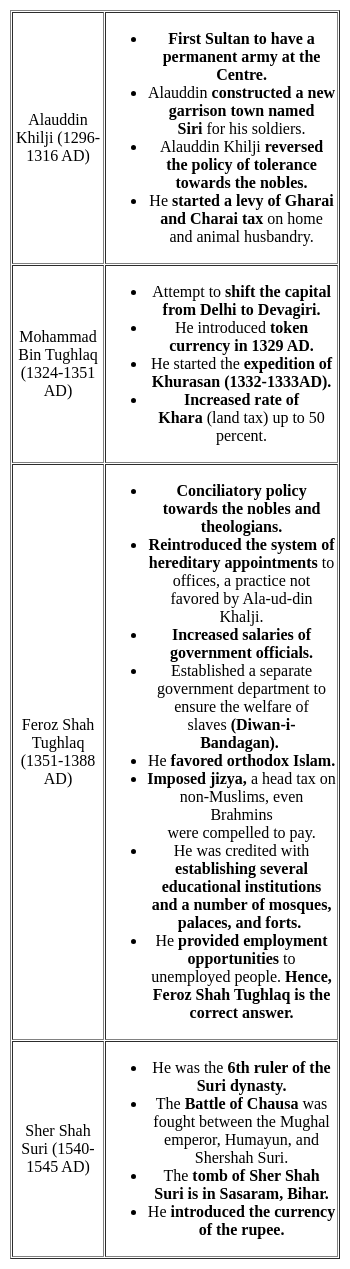
Which one of the following sultans provided employment to the unemployed?
Detailed Solution for Test: General Awareness (Indian History) - Question 4
Test: General Awareness (Indian History) - Question 5
Who was the founder of the Vijayanagara Empire?
Detailed Solution for Test: General Awareness (Indian History) - Question 5
Test: General Awareness (Indian History) - Question 6
Which of the following newspaper was founded by Raja Ram Mohan Roy?
Detailed Solution for Test: General Awareness (Indian History) - Question 6
Test: General Awareness (Indian History) - Question 7
Who described Jinnah as “the ambassador of Hindu-Muslim Unity”?
Detailed Solution for Test: General Awareness (Indian History) - Question 7
Detailed Solution for Test: General Awareness (Indian History) - Question 8
Test: General Awareness (Indian History) - Question 9
Which of the following was not the main feature of the Government of India Act, 1919 ?
Detailed Solution for Test: General Awareness (Indian History) - Question 9
Test: General Awareness (Indian History) - Question 10
Where was the Hindustan Socialist Republican Association established by revolutionaries like Chandrashekhar Azad and Sardar Bhagat Singh?
(a) Mumbai
(b) Nagpur
(c) Kolkata
(d) Delhi
Detailed Solution for Test: General Awareness (Indian History) - Question 10
Information about Test: General Awareness (Indian History) Page
In this test you can find the Exam questions for Test: General Awareness (Indian History) solved & explained in the simplest way possible.
Besides giving Questions and answers for Test: General Awareness (Indian History), EduRev gives you an ample number of Online tests for practice
Download as PDF