Software Development Exam > Software Development Tests > Test: General Awareness (Indian Constitution) - Software Development MCQ
Test: General Awareness (Indian Constitution) - Software Development MCQ
Test Description
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: General Awareness (Indian Constitution)
Test: General Awareness (Indian Constitution) for Software Development 2025 is part of Software Development preparation. The Test: General Awareness (Indian Constitution) questions and answers have been prepared
according to the Software Development exam syllabus.The Test: General Awareness (Indian Constitution) MCQs are made for Software Development 2025 Exam.
Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for Test: General Awareness (Indian Constitution) below.
Solutions of Test: General Awareness (Indian Constitution) questions in English are available as part of our course for Software Development & Test: General Awareness (Indian Constitution) solutions in
Hindi for Software Development course.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Software Development Exam by signing up for free. Attempt Test: General Awareness (Indian Constitution) | 10 questions in 10 minutes | Mock test for Software Development preparation | Free important questions MCQ to study for Software Development Exam | Download free PDF with solutions
Test: General Awareness (Indian Constitution) - Question 1
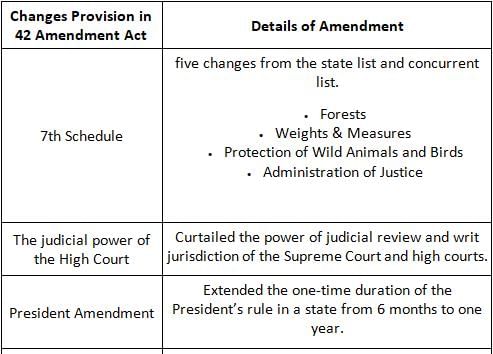
Which Amendment is called as "Mini Constitution"?
Detailed Solution for Test: General Awareness (Indian Constitution) - Question 1
Test: General Awareness (Indian Constitution) - Question 2
Which article of Indian constitution deals with constitutional amendments?
Detailed Solution for Test: General Awareness (Indian Constitution) - Question 2
Test: General Awareness (Indian Constitution) - Question 3
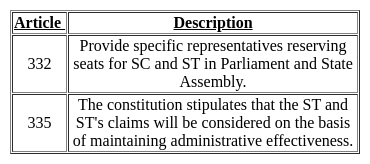
Who of the following have the power to determine the structure, jurisdiction and rights of the judiciary?
Detailed Solution for Test: General Awareness (Indian Constitution) - Question 3
Test: General Awareness (Indian Constitution) - Question 4
The Indian President is eligible for re-election for how many times?
Detailed Solution for Test: General Awareness (Indian Constitution) - Question 4
Test: General Awareness (Indian Constitution) - Question 5
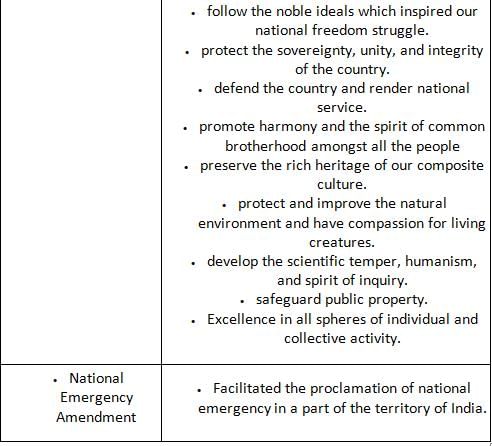
What was the objective of the Constitutionist to include the Directive Principal of State Policy?
Detailed Solution for Test: General Awareness (Indian Constitution) - Question 5
Test: General Awareness (Indian Constitution) - Question 6
The District and sessions judge works directly under the control of
Detailed Solution for Test: General Awareness (Indian Constitution) - Question 6
Test: General Awareness (Indian Constitution) - Question 7
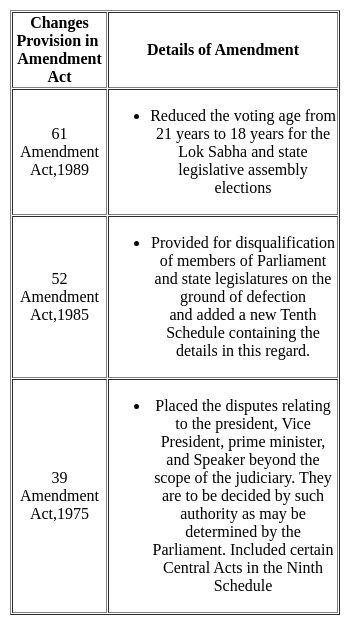
According to 73rd Amendment Act, if a Gram Panchayat is dissolved, its election are to be held within what period?
Detailed Solution for Test: General Awareness (Indian Constitution) - Question 7
Test: General Awareness (Indian Constitution) - Question 8
The Decentralization System was recommended by?
Detailed Solution for Test: General Awareness (Indian Constitution) - Question 8
Test: General Awareness (Indian Constitution) - Question 9
The Attorney General of India is appointed by
Detailed Solution for Test: General Awareness (Indian Constitution) - Question 9
Test: General Awareness (Indian Constitution) - Question 10
Who was appointed as the constitutional advisor/legal advisor to the Constituent Assembly?
Detailed Solution for Test: General Awareness (Indian Constitution) - Question 10
Information about Test: General Awareness (Indian Constitution) Page
In this test you can find the Exam questions for Test: General Awareness (Indian Constitution) solved & explained in the simplest way possible.
Besides giving Questions and answers for Test: General Awareness (Indian Constitution), EduRev gives you an ample number of Online tests for practice
Download as PDF